The ancient Mayan civilization, one of the most intriguing and advanced societies in history, thrived in the heart of Central America.
Rich in culture and architectural wonders, the Mayan civilization spanned across what is now modern-day Mexico, Belize, Guatemala, Honduras, and El Salvador.
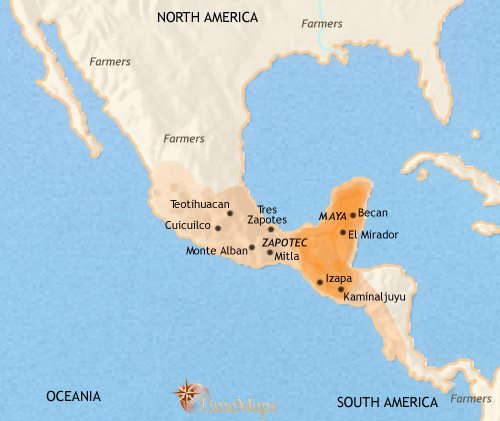
The Ancient Mayan Civilization was located in the regions known today as Mexico, Guatemala, Belize, Honduras, and El Salvador. These regions make up the Mesoamerican area where the Mayans thrived from 2000 BCE to 1500 CE. The heart of the civilization was in present-day Guatemala, with important cities like Tikal and El Mirador. The Mayans built impressive cities, developed a sophisticated writing system, and accomplished amazing architectural and astronomical feats, leaving behind a rich cultural legacy.
Contents
- The Geographic Location of the Ancient Mayan Civilization
- Location of the Ancient Mayan Civilization
- Key Takeaways
- Frequently Asked Questions
- 1. What is the geographical location of the Ancient Mayan Civilization?
- 2. How did the geographical location influence the Ancient Mayan Civilization?
- 3. Were there specific cities or sites where the Ancient Mayan Civilization thrived?
- 4. Did the Ancient Mayan Civilization have a capital city?
- 5. Is the Ancient Mayan Civilization still present today?
- The Maya Civilization Explained in 11 Minutes
The Geographic Location of the Ancient Mayan Civilization
The ancient Mayan civilization was located in what is now known as Mesoamerica, a region in Central America that spans modern-day Mexico, Belize, Guatemala, El Salvador, and Honduras. This fascinating civilization flourished for thousands of years, beginning around 2000 BCE and lasting until the arrival of the Spanish conquistadors in the 16th century CE. The Mayans were incredibly advanced in numerous areas, including agriculture, mathematics, astronomy, architecture, and art. They left behind a rich legacy of temples, pyramids, and intricate artwork that still captivates archaeologists and historians today.
The Mayan Heartland: Southern Mexico and Guatemala
The heartland of the ancient Mayan civilization was primarily located in the southern parts of Mexico and Guatemala. In modern-day Mexico, you can find significant Mayan ruins in the states of Yucatan, Quintana Roo, Campeche, and Chiapas. The ruins of Chichen Itza, Tulum, Uxmal, and Palenque are some of the most famous Mayan archaeological sites in these regions.
In Guatemala, the Mayan heartland extended through the northern lowlands and highlands. The city of Tikal, known for its towering pyramids and grand plazas, was one of the most influential Mayan cities and the political capital of the ancient Mayan civilization. Other important Mayan sites in Guatemala include El Mirador, Copan, and Quirigua.
The Mayan civilization thrived in these areas due to the fertile lands and access to resources such as waterways, forests, and limestone for construction. The geographic location provided the Mayans with a diverse ecosystem that supported their agricultural practices and allowed for the growth of complex urban centers.
The Mayan Influence in Belize and Honduras
While the heartland of the Mayan civilization was primarily in Mexico and Guatemala, their influence extended to neighboring regions, including Belize and Honduras.
In Belize, the southern region known as Toledo is home to several Mayan archaeological sites such as Lamanai, Xunantunich, and Altun Ha. These sites offer a glimpse into Mayan life and the rich cultural heritage of the civilization.
In Honduras, the Mayan influence is most prominently seen in the Copan Ruins, one of the most important archaeological sites in the Mayan world. The ruins of Copan reveal intricate carvings, hieroglyphic staircases, and impressive plazas, showcasing the artistic and intellectual achievements of the Mayan civilization.
The Mayans’ presence in Belize and Honduras demonstrates their ability to expand their cultural, political, and economic influence beyond their heartland, further highlighting the extent of their civilization.
Mayan Coastal Settlements and Trading Networks
In addition to their presence in the heartland and neighboring regions, the Mayans also established coastal settlements along the Caribbean Sea and the Gulf of Mexico. These coastal regions provided access to valuable trade networks and resources.
The city of Tulum, located on the eastern coast of the Yucatan Peninsula in Mexico, served as a major port and trading hub for the Mayans. Its strategic location allowed for maritime trade with other Mesoamerican cultures, including the Olmecs and the Aztecs.
The Mayans’ seafaring abilities and navigation skills enabled them to establish trade routes along the coasts, connecting various regions of Mesoamerica. Their trade networks traded goods such as jade, obsidian, cacao, feathers, textiles, and ceramics.
The Legacy of the Ancient Mayan Civilization
The ancient Mayan civilization holds tremendous significance in the history and culture of Mesoamerica. Their remarkable achievements in architecture, astronomy, mathematics, and art continue to amaze and inspire people around the world.
Today, the ruins of ancient Mayan cities and structures stand as a testament to their ingenuity and cultural sophistication. They offer valuable insights into the complex social, political, and religious systems that governed Mayan society.
Studying the ancient Mayan civilization’s geographic location allows us to understand how their environment shaped their way of life. It helps us appreciate their remarkable accomplishments and the lasting impact they have had on the world.
Location of the Ancient Mayan Civilization
The ancient Mayan civilization was located in Mesoamerica, which is the region that encompasses parts of present-day Mexico, Belize, Guatemala, Honduras, and El Salvador. This expansive civilization flourished between 2000 BC and 1500 AD, leaving behind a rich cultural and architectural legacy.
The heartland of the Mayan civilization was the Yucatan Peninsula, which corresponds to modern-day southeastern Mexico and parts of Belize and Guatemala. Within this region, the Mayans built impressive city-states, such as Tikal, Palenque, and Chichen Itza, each with its own unique characteristics and monumental structures.
The Mayans were ingenious in adapting to diverse environments, from dense rainforests to arid highlands. They created an intricate network of roads and trade routes that connected their cities and allowed for the exchange of goods and ideas.
The ancient Mayan civilization remains a subject of fascination and curiosity, as its cultural and architectural achievements continue to captivate scholars and visitors alike.
Key Takeaways
- The Ancient Mayan civilization was located in Mesoamerica, primarily in present-day Mexico, Guatemala, Belize, Honduras, and El Salvador.
- The heartland of the Mayan civilization was the Yucatán Peninsula, where cities such as Chichen Itza and Tulum were located.
- The Mayans also inhabited the highlands of Guatemala and Belize, known for cities like Tikal and Caracol.
- Other important Mayan cities include Copan in Honduras and Joya de Cerén in El Salvador.
- The Ancient Mayan civilization thrived between 2000 BCE and 1500 CE, leaving behind countless architectural wonders and a rich cultural legacy.
Frequently Asked Questions
The Ancient Mayan Civilization was one of the most remarkable and advanced cultures in history. Let’s explore some of the frequently asked questions about the location of this fascinating civilization.
1. What is the geographical location of the Ancient Mayan Civilization?
The Ancient Mayan Civilization was located in Mesoamerica, primarily in what is now known as the southern part of Mexico and parts of Central America. Their civilization spread across the present-day countries of Mexico, Guatemala, Belize, Honduras, and El Salvador. The heart of the Mayan civilization was the Yucatan Peninsula in Mexico.
The diverse landscape of the region, including dense jungles, coastal areas, and highlands, provided the Maya with a wide range of resources and allowed them to develop a sophisticated society.
2. How did the geographical location influence the Ancient Mayan Civilization?
The geographical location of the Ancient Mayan Civilization played a significant role in shaping their culture, society, and way of life. The abundant natural resources, such as fertile soil for agriculture and access to the ocean for trade and transportation, contributed to the prosperity and development of the Mayan civilization.
The dense jungles and challenging terrain also provided the Mayans with natural defenses, allowing them to protect their cities and territory from external threats. Additionally, the natural features of the region, such as caves, cenotes, and mountains, held religious and spiritual significance for the Mayans and were integral to their beliefs and rituals.
3. Were there specific cities or sites where the Ancient Mayan Civilization thrived?
Yes, there were several significant cities and archaeological sites where the Ancient Mayan Civilization thrived. Some of the most prominent ones include:
– Tikal: Located in present-day Guatemala, Tikal was one of the largest and most powerful Mayan cities, known for its towering temples and palaces.
– Chichen Itza: Located in the Yucatan Peninsula of Mexico, Chichen Itza was a major Mayan city characterized by its iconic pyramid known as El Castillo, or the Temple of Kukulkan.
– Palenque: Located in the Mexican state of Chiapas, Palenque was known for its unique architecture and intricate stone carvings.
– Copan: Located in present-day Honduras, Copan was renowned for its remarkable sculptures and hieroglyphic stairway.
4. Did the Ancient Mayan Civilization have a capital city?
The Ancient Mayan Civilization did not have a centralized capital city. Instead, the Mayans built numerous city-states, each with its own ruling elite and government. These city-states were independent entities that often engaged in trade, alliances, and sometimes conflicts with one another.
However, some Mayan cities, such as Tikal and Calakmul, were powerful and influential and might be considered as major centers of political and economic activity during certain periods.
5. Is the Ancient Mayan Civilization still present today?
The Ancient Mayan Civilization, as a unified and flourishing civilization, disappeared around the 10th century AD. However, the Maya people and their cultural heritage continue to thrive in the modern world. Many Mayan communities still exist in the regions where their ancestors once flourished, and their traditions, language, and customs are preserved and celebrated.
Archaeological sites such as Chichen Itza, Tikal, and Palenque attract millions of visitors each year, showcasing the incredible architectural and cultural achievements of the Ancient Mayan Civilization.
The Maya Civilization Explained in 11 Minutes
In conclusion, the ancient Mayan civilization was located in Mesoamerica, a region that includes present-day Mexico, Guatemala, Belize, El Salvador, and Honduras.
The Mayans inhabited this area from around 2000 BC until the Spanish conquest in the 16th century AD. Their cities and settlements were spread across the diverse landscapes of the region, from dense jungles to highlands and coastal areas. The remnants of their remarkable civilization can still be seen in the ancient ruins and archaeological sites that exist today.