The Byzantine Empire, one of the most influential and enduring civilizations in history, spanned across a vast geographical area. Located at the crossroads of Europe and Asia, the empire’s capital, Constantinople, served as a gateway between East and West. Its location along the Bosporus Strait made it a strategic center for trade and defense, allowing the Byzantines to exert significant political and cultural influence over the surrounding regions.
The Byzantine Empire, known for its rich history and cultural heritage, was situated in the eastern Mediterranean and the Balkans. With its roots in the Roman Empire, it emerged as a distinct entity in the 4th century AD and thrived until the 15th century. The empire extended from Italy in the west to present-day Syria in the east, encompassing territories that are part of modern-day Greece, Turkey, Bulgaria, and Egypt. Its diverse geographical location facilitated the blending of various civilizations and the preservation of classical knowledge, ensuring its enduring legacy in art, architecture, and politics.
The Byzantine Empire was located in the eastern part of Europe and western part of Asia. It spanned from the 4th century to the 15th century AD, with its capital initially in Constantinople (modern-day Istanbul, Turkey). The empire covered a vast area including the Balkans, Anatolia, Egypt, and parts of the Middle East. Its strategic location allowed it to control key trade routes connecting Europe, Asia, and Africa, making it a powerful and influential empire in the ancient world.
Contents
- The Influence and Expansion of the Byzantine Empire
- The Byzantine Empire’s Legacy and Significance in History
- Where Was the Byzantine Empire Located?
- Key Takeaways – Where Is The Byzantine Empire Located?
- Frequently Asked Questions
- 1. Where was the capital of the Byzantine Empire?
- 2. What other regions did the Byzantine Empire encompass?
- 3. What was the significance of the Byzantine Empire’s location?
- 4. How did the Byzantine Empire’s location influence its relationship with other powers?
- 5. What is the present-day significance of the Byzantine Empire’s location?
- The Byzantine Empire Explained in 13 Minutes
The Influence and Expansion of the Byzantine Empire
The Byzantine Empire, also known as the Eastern Roman Empire, was a highly influential civilization that lasted for over a thousand years. But where exactly was the Byzantine Empire located? Situated at the crossroads of Europe, Asia, and Africa, the empire’s strategic location played a significant role in its expansion, influence, and cultural exchange.
1. The Early Byzantine Empire and Its Location
The Byzantine Empire emerged as the successor to the Roman Empire in the 4th century AD, with its capital at Constantinople, present-day Istanbul in Turkey. Its strategic location on the Bosphorus Strait, which connects the Black Sea to the Mediterranean Sea, provided the empire with control over major trade routes and made it a key player in international commerce.
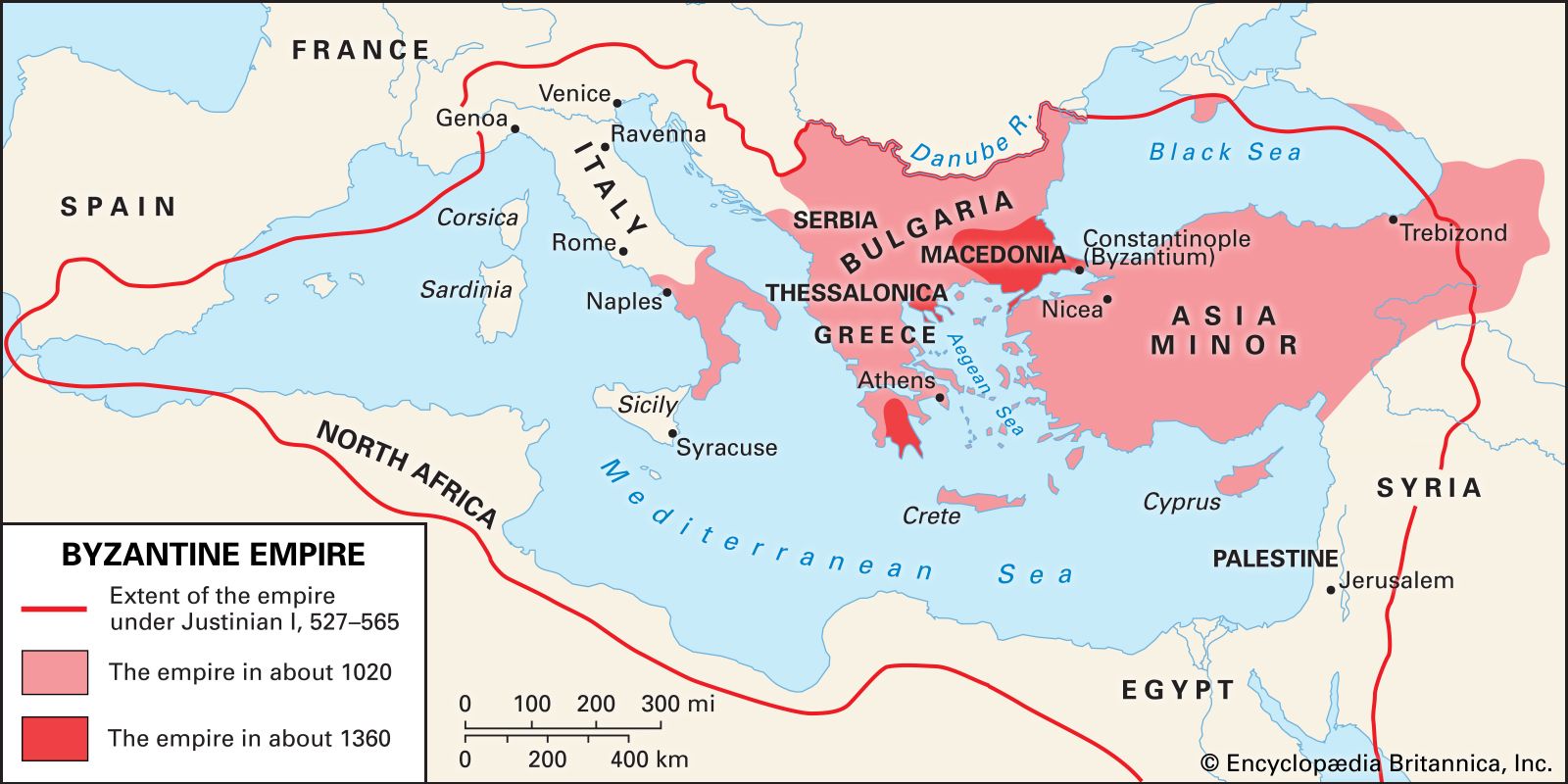
Bordered by the Danube River to the north, the Byzantine Empire extended across the Balkan Peninsula, including modern-day Greece, Bulgaria, Romania, and parts of Serbia and Macedonia. Furthermore, it encompassed Asia Minor (Anatolia), Syria, and Egypt, extending its reach into the Eastern Mediterranean and the Levant.
This expansive territory allowed the Byzantine Empire to maintain a diverse population and foster cultural diversity. It served as a bridge between the Western and Eastern worlds, facilitating the exchange of ideas, trade, and technological advancements.
1.1. Cultural Influences of the Byzantine Empire
The Byzantine Empire was renowned for its rich cultural heritage, blending elements from various civilizations. Its location at the crossroads of Europe, Asia, and Africa facilitated the fusion of Roman, Greek, Persian, and Arab influences.
One of the key cultural influences of the Byzantine Empire was its art and architecture. Byzantine architecture was characterized by the use of domes, arches, and intricate mosaics. Examples of this can be seen in the iconic Hagia Sophia in Istanbul, which was initially a Byzantine cathedral and later converted into a mosque.
The Byzantine Empire also played a vital role in the preservation and transmission of ancient Greek and Roman texts. Byzantine scholars translated and studied these texts, preserving the knowledge of classical civilizations during the Middle Ages, which laid the foundation for the Renaissance in Western Europe.
2. The Later Byzantine Empire and Its Expansions
As the Byzantine Empire solidified its power in the centuries following its establishment, it extended its influence and territorial dominion. Under Emperor Justinian I, the empire witnessed a period of significant expansion. Justinian’s campaigns aimed to reclaim territories that were once part of the Roman Empire.
Justinian’s reconquest efforts resulted in the temporary reclamation of North Africa, Italy, and parts of Spain. The Byzantine Empire’s eastern territories remained relatively stable, with the empire maintaining control of Anatolia, Syria, Palestine, and Egypt.
Over time, however, the empire faced numerous challenges from external threats, including invasions by various barbarian tribes and the rise of Islamic powers in the Middle East. These pressures led to the gradual decline and fragmentation of the Byzantine Empire, eventually leading to its collapse in 1453 when Constantinople was captured by the Ottoman Turks.
2.1. Legacy and Lasting Influence of the Byzantine Empire
The Byzantine Empire’s lasting influence can be seen in various aspects of art, culture, religion, and governance. Byzantine art continued to thrive in the form of religious icons, mosaics, and frescoes, which heavily influenced later artistic movements, particularly in Eastern Europe and Russia. It also influenced the development of medieval and Renaissance art in Western Europe.
The Byzantine Empire also played a crucial role in the spread of Christianity. Byzantine Christianity, characterized by its distinct theological and liturgical traditions, helped shape the development of Eastern Orthodox Christianity.
Furthermore, the Byzantine administrative system, influenced by Roman precedents, served as a blueprint for future medieval and early modern governments. Its legacy can be observed in the governance structures of many nations, particularly in the Eastern Mediterranean region.
The Byzantine Empire’s Legacy and Significance in History
The Byzantine Empire’s location provided it with a strategic advantage, allowing it to connect and influence the regions of Europe, Asia, and Africa. Its cultural exchanges, intellectual achievements, and remarkable art and architecture have left an indelible mark on the world. Despite its ultimate demise, the Byzantine Empire’s legacy continues to shape various aspects of our modern society.
Where Was the Byzantine Empire Located?
The Byzantine Empire, also known as the Eastern Roman Empire, was located in the eastern Mediterranean region, predominantly centered around the city of Constantinople (present-day Istanbul, Turkey). It emerged as the continuation of the Roman Empire in the 4th century AD and lasted until the 15th century AD.
The empire’s territory spanned across portions of southeastern Europe, western Asia, and northern Africa. It bordered the Black Sea to the north, the Mediterranean Sea to the south, and various kingdoms and empires to the west and east.
The Byzantine Empire served as a bridge between the civilizations of the ancient world and the medieval period, preserving and transmitting classical knowledge, arts, and culture. It exerted significant influence over the development of Christianity and played a crucial role in the political and cultural landscapes of its time.
The empire’s strategic location allowed it to control key trade routes between Europe and Asia, making Constantinople a hub of economic activity and a coveted prize for many regional powers throughout history.
Key Takeaways – Where Is The Byzantine Empire Located?
- The Byzantine Empire was located in modern-day Turkey and Greece.
- The capital of the Byzantine Empire was Constantinople, now known as Istanbul.
- The Byzantine Empire lasted from 330 AD to 1453 AD.
- The Byzantine Empire was a continuation of the Roman Empire in the East.
- The Byzantine Empire was an important center of trade, culture, and Christianity.
Frequently Asked Questions
The Byzantine Empire was a vast and influential state that existed for over a thousand years. Located at the crossroads of Europe and Asia, it had a strategic position that allowed it to thrive and exert its power in various regions. Here are some frequently asked questions about the location of the Byzantine Empire.
1. Where was the capital of the Byzantine Empire?
The capital of the Byzantine Empire was Constantinople, which is now known as Istanbul in modern-day Turkey. Located on the shores of the Bosporus Strait, Constantinople was strategically placed between Europe and Asia, making it a major hub of trade, culture, and political power.
With its strong fortifications and advantageous position, Constantinople played a crucial role in the defense and expansion of the Byzantine Empire. Its location also allowed it to control key trade routes, connecting the Mediterranean Sea to the Black Sea and beyond.
2. What other regions did the Byzantine Empire encompass?
While the capital was located in Constantinople, the Byzantine Empire extended its influence over vast territories. These included regions such as Greece, Egypt, Asia Minor (modern-day Turkey), the Balkans, and portions of the Middle East.
By controlling these regions, the Byzantine Empire was able to exert its dominance over important trade routes, natural resources, and strategic locations. Its geographical spread played a vital role in shaping its political, cultural, and economic impact throughout history.
3. What was the significance of the Byzantine Empire’s location?
The location of the Byzantine Empire had profound implications for its development and influence. Situated at the intersection of Europe and Asia, it became a melting pot of different cultures, languages, and traditions. This cultural diversity contributed to the Byzantine Empire’s unique identity, blending aspects of Roman, Greek, and Eastern influences.
Furthermore, the strategic position of the Byzantine Empire allowed it to control crucial trade routes, allowing for the prosperous exchange of goods, ideas, and technologies. It also served as a buffer zone between the Eastern and Western worlds, playing a significant role in the transmission of knowledge and trade between these regions.
4. How did the Byzantine Empire’s location influence its relationship with other powers?
The location of the Byzantine Empire placed it at the crossroads of major powers throughout history. It bordered various kingdoms, empires, and nomadic tribes, which influenced its relationships and geopolitical dynamics.
For example, the Byzantine Empire had diplomatic and military exchanges with the Persian Empire, the Arab Caliphates, the Crusader States, and various Eastern European kingdoms. Its location facilitated interactions, conflicts, and alliances with these powers, shaping its history and geopolitical position.
5. What is the present-day significance of the Byzantine Empire’s location?
The geographical region once occupied by the Byzantine Empire continues to hold great historical, cultural, and geopolitical importance today. Constantinople, now Istanbul, remains a vibrant and cosmopolitan city that bridges Europe and Asia.
The Byzantine Empire’s legacy can be seen in the rich architectural, artistic, and religious heritage of the region. Additionally, the historical interactions and exchanges that took place in this area continue to shape political and cultural dynamics between Europe, Asia, and the Middle East.
The Byzantine Empire Explained in 13 Minutes
In summary, the Byzantine Empire was located in the southeastern part of Europe and the western part of Asia. Its capital city, Constantinople, was strategically located on the Bosporus Strait, connecting the Mediterranean Sea to the Black Sea. This advantageous position allowed the empire to control major trade routes and serve as a bridge between Europe and Asia.
The Byzantine Empire also encompassed regions that are now part of modern-day Turkey, Greece, Italy, Egypt, Syria, and Israel. Its location proved to be vital for its survival and influence, making it a significant and enduring empire in history.