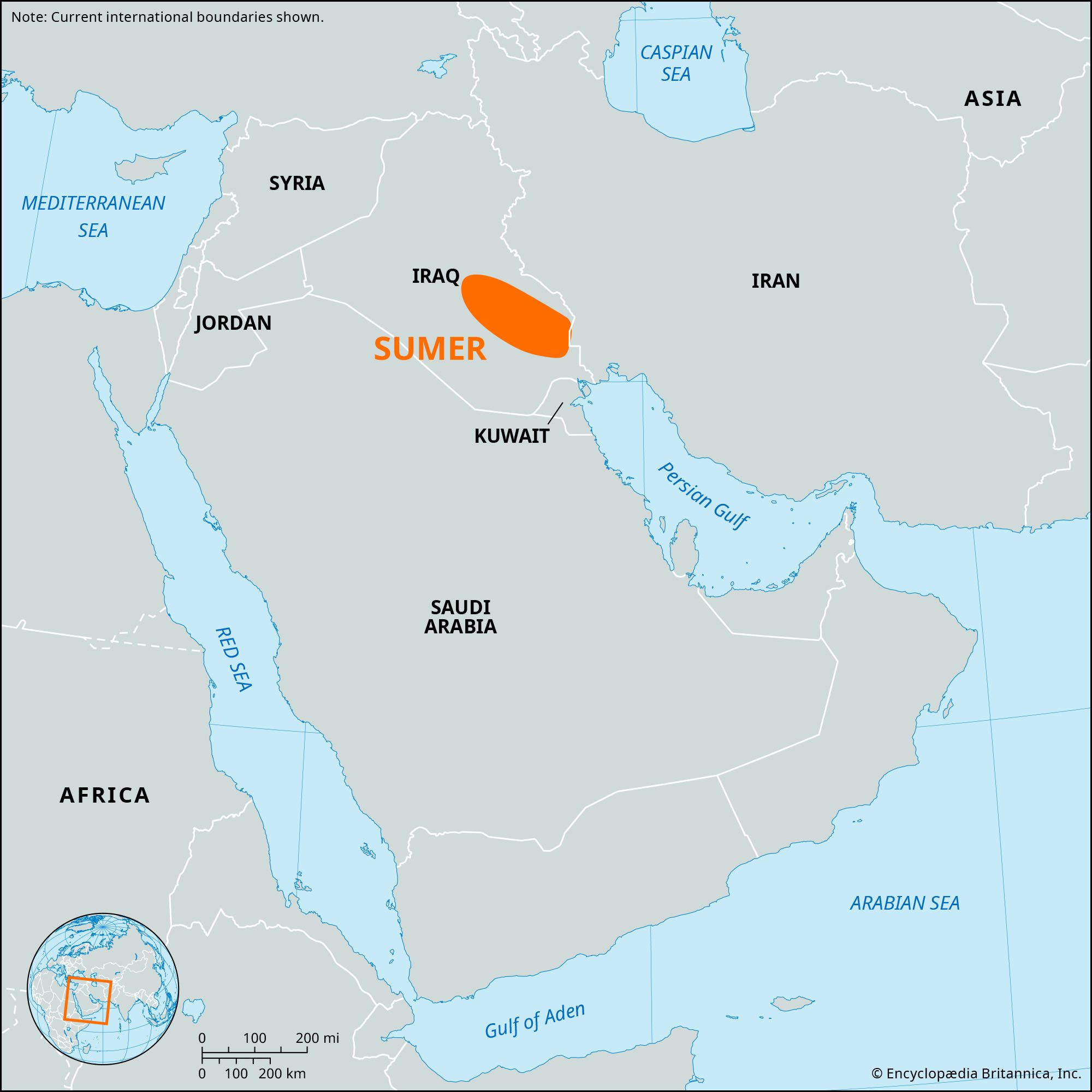
The ancient civilization of Sumer developed in Mesopotamia, a region known as the “Cradle of Civilization.” This term refers to the area between the Tigris and Euphrates Rivers, where Sumerians built one of the earliest complex societies in human history. Mesopotamia, meaning “between the rivers” in Greek, was located in present-day Iraq and parts of Syria and Turkey. It is fascinating to explore how this sophisticated civilization emerged in such a specific geographical location.
The development of the ancient civilization of Sumer was intricately linked to the fertile land between the Tigris and Euphrates Rivers. Known as the “Fertile Crescent,” this region provided the Sumerians with a reliable source of water, fertile soil for agriculture, and a strategic location for trade and communication. The Sumerians were able to harness the power of these rivers by constructing complex irrigation systems, which allowed them to cultivate crops and build prosperous cities. This innovative approach to agriculture and the utilization of the rivers’ resources contributed to the rise and success of the Sumerian civilization.
The ancient civilization of Sumer developed in Mesopotamia, which is modern-day Iraq. Sumer was located between the Tigris and Euphrates rivers, known as the Fertile Crescent. This region provided an ideal environment for agriculture and trade, leading to the emergence of a sophisticated civilization around 4500 BCE. Sumerians established city-states such as Ur, Uruk, and Nippur, and made significant contributions to writing, law, mathematics, and architecture.
Contents
- The Origin of the Ancient Civilization of Sumer
- The Development of the Ancient Civilization of Sumer
- Key Takeaways – Where Did The Ancient Civilization Of Sumer Develop?
- Frequently Asked Questions
- 1. What is the significance of Sumer in ancient history?
- 2. How did the geography of Mesopotamia influence the development of Sumer?
- 3. What were the major cities of Sumer?
- 4. Did the Sumerians have a written language?
- 5. What led to the decline of the Sumerian civilization?
- Ancient Sumerian Civilization | Culture, History \u0026 Location”,”navigationEndpoint”:{“clickTrackingParams”:”CNoEEJHeChgcIhMIyL7XtvvohAMVj2FMCB25yg9A”,”loggingUrls”:[{“baseUrl”:”https://www.youtube.com/pagead/paralleladinteraction?ai=C_9lwT0XtZaeKFr_E2OMP9d-luA8A7uy26fARABAEIABgyQaCARNwYXJ0bmVyLXlvdXR1YmUtc3JwqAMEqgQXT9DdyTHJLJNWIP93EosML4bx_7ia6AeQBwSoB-edsQKoB-idsQKoB4QI0gglCIBBEAEYXjICggI6CIBCgMCAgIAgSNmg0jVQFFiA4Ni2–iEA7ALAboLOwgDEAUYDCALKAUwBUABSABYamAAaABwAYgBAJABAZgBAaIBCAoAqAIB2AICqAEBwAEB0AEB4AEBgAIBoBcB\u0026sigh=uv1joBdkz8s\u0026cid=CAASFeRoENZfSuUkNHAg8SWo30LHZ8itUw\u0026ad_mt=[AD_MT]\u0026acvw=[VIEWABILITY]\u0026gv=[GOOGLE_VIEWABILITY]\u0026nb=%5BNB%5D\u0026label=video_click_to_advertiser_site
The Origin of the Ancient Civilization of Sumer
The ancient civilization of Sumer, one of the earliest known civilizations in the world, developed in Mesopotamia, which is the region located in modern-day southern Iraq. This remarkable civilization flourished in the fertile lands between the Tigris and Euphrates rivers, often referred to as the “Cradle of Civilization.” The origin of the Sumerian civilization dates back to approximately 4500 BCE, making it one of the most ancient and influential societies in history.
The Geography of Sumer
The geographical location of Sumer played a crucial role in its development. Situated in the lower part of Mesopotamia, it had a fertile landscape, conducive to agriculture. The presence of the Tigris and Euphrates rivers allowed the Sumerians to harness water for irrigation, enabling them to cultivate crops and establish a thriving agricultural economy. The rivers also facilitated trade and transportation, connecting Sumer to neighboring regions.
The landscape of Sumer had distinct features, including vast marshlands, alluvial plains, and a sun-baked desert. The marshlands provided a habitat for various flora and fauna, while the alluvial plains offered rich soil for farming. However, the harsh desert environment limited the expansion of settlements in certain areas, causing populations to concentrate in the more habitable regions along the rivers.
The strategic location of Sumer, with its access to waterways and proximity to neighboring civilizations, allowed for cultural exchange, trade, and the development of a complex society. The natural resources and agricultural surplus of Sumer attracted migrants from surrounding areas, leading to the formation of a diverse population with distinct cultural and linguistic identities.
The Rise of City-States in Sumer
One of the significant aspects of the ancient civilization of Sumer was the emergence of city-states. These were independent city-based political entities that featured a central city and the surrounding agricultural hinterland. The city-states of Sumer were autonomous, each with its own government, laws, and local deity.
City-states such as Ur, Uruk, Lagash, and Nippur thrived in Sumer, serving as administrative, religious, and economic centers. The transition from small agricultural villages to sophisticated urban centers brought about transformative changes in Sumerian society. The city-states represented the pinnacle of Sumerian political organization and were characterized by monumental architecture, complex social hierarchies, and extensive trade networks.
These city-states were often ruled by dynastic kings, who were believed to have a divine mandate to govern. The kings acted as intermediaries between the gods and the people, ensuring the prosperity and welfare of their city-state. The temple complexes, known as ziggurats, were the religious and cultural focal points of the city-states, serving as sacred spaces for worship and administration.
Sumerian Innovation and Achievements
The ancient civilization of Sumer was marked by numerous innovations and remarkable achievements across various fields. Sumerians were among the first to develop writing, known as cuneiform, which revolutionized human communication and record-keeping. They created a system of mathematics based on the number 60, which led to the development of the concept of minutes and hours, as well as the twelve-month calendar.
The Sumerians also excelled in architecture, constructing monumental buildings such as ziggurats and palaces. These structures showcased their advanced engineering skills and served as symbols of power and religious devotion. Furthermore, Sumerians made significant advancements in the fields of astronomy, medicine, agriculture, and irrigation, providing a solid foundation for future civilizations in the region.
Their cultural and artistic achievements are evident in the intricate craftsmanship of their jewelry, pottery, and sculptures. Sumerian art often depicted scenes from daily life, religious rituals, and mythical narratives, providing valuable insights into their beliefs and societal structure.
Decline and Legacy of Sumer
Despite its rich achievements, the ancient civilization of Sumer eventually declined due to a combination of factors such as environmental changes, political conflicts, and invasion by neighboring empires. The once-flourishing city-states gradually lost their autonomy and were absorbed into larger empires, including the Akkadian, Babylonian, and Assyrian empires.
However, the legacy of Sumer endured, as its innovations and cultural contributions influenced subsequent civilizations throughout the ancient Near East. The cuneiform writing system, for example, spread beyond Sumer and became the dominant form of writing in the region for centuries. The mathematical system based on 60 also persisted and influenced various ancient cultures.
The ancient civilization of Sumer left an indelible mark on human history, establishing the foundations of urban life, governance, and innovation. Its legacy serves as a testament to the enduring impact of early human societies and their remarkable achievements.
The Development of the Ancient Civilization of Sumer
The ancient civilization of Sumer developed in the southern region of Mesopotamia, which is present-day Iraq. This ancient civilization emerged around 4500 BCE and thrived for nearly 2,000 years. Sumerian cities were centered around the fertile land between the Tigris and Euphrates rivers, often referred to as the “cradle of civilization.”
The cities in Sumer, such as Uruk, Ur, and Lagash, were characterized by their advanced urban planning, sophisticated irrigation systems, and monumental architecture. The Sumerians were skilled in agriculture, and their agricultural practices allowed them to produce surplus food, leading to the rise of urban settlements.
The Sumerians also made significant contributions to human civilization, including the development of the earliest known form of writing called cuneiform, a system of symbols impressed onto clay tablets. They created the world’s first legal codes, established complex bureaucracies, and practiced early forms of religious worship.
The decline of the Sumerian civilization began around 2000 BCE due to conflicts with neighboring civilizations and environmental changes. However, the legacy of Sumerian culture continued to influence subsequent civilizations in the region.
Key Takeaways – Where Did The Ancient Civilization Of Sumer Develop?
- The ancient civilization of Sumer developed in Mesopotamia.
- Mesopotamia is located in present-day Iraq.
- Sumer was one of the earliest urban civilizations in human history.
- The Sumerians built city-states with advanced infrastructure and centralized governments.
- The cities of Uruk, Ur, and Nippur were important centers of Sumerian civilization.
Frequently Asked Questions
The ancient civilization of Sumer developed in the region known as Mesopotamia, which is modern-day Iraq. This region is often referred to as the “cradle of civilization” because it is one of the earliest known sites of complex human societies.
1. What is the significance of Sumer in ancient history?
The ancient civilization of Sumer holds immense significance in ancient history. It is considered one of the earliest urban civilizations in the world, flourishing around 4500 BCE. The Sumerians made significant contributions to various fields, including architecture, governance, literature, mathematics, and science. They developed the first known writing system, known as cuneiform, and created impressive structures such as ziggurats.
Sumerian culture had a profound impact on subsequent civilizations in the region and beyond. Their system of city-states, with each city having its own government and ruler, influenced the political structures of later empires. Additionally, many of the Sumerian myths, religious beliefs, and epic tales, such as the famous Epic of Gilgamesh, continue to resonate in modern-day culture.
2. How did the geography of Mesopotamia influence the development of Sumer?
The geography of Mesopotamia played a crucial role in the development of Sumer. Mesopotamia, meaning “land between rivers,” is situated in the fertile crescent between the Tigris and Euphrates rivers. The extensive network of waterways provided the Sumerians with a reliable source of water for agriculture.
The Sumerians developed advanced irrigation techniques to harness the water from the rivers and cultivate the land. This allowed them to produce surplus food, which led to population growth and the establishment of permanent settlements. The favorable agricultural conditions, combined with the strategic location for trade, contributed to the socioeconomic development of Sumer.
3. What were the major cities of Sumer?
The major cities of Sumer were Ur, Uruk, Larsa, Nippur, Lagash, and Eridu. These cities were centers of political, economic, and cultural activity during the Sumerian civilization. Each city had its own ruler and government, and they often engaged in trade and warfare with each other.
Ur, one of the most prominent cities, was known for its impressive ziggurat and its role as a center of trade. Uruk, considered one of the oldest cities in the world, had a significant influence on Sumerian culture and was home to famous literary works like the Epic of Gilgamesh.
4. Did the Sumerians have a written language?
Yes, the Sumerians developed one of the earliest known writing systems called cuneiform. Cuneiform involved inscribing wedge-shaped marks on clay tablets using a stylus. Initially used for record-keeping purposes, cuneiform evolved into a comprehensive writing system that encompassed various aspects of Sumerian life.
The Sumerians used cuneiform to record administrative documents, legal codes, religious texts, and literary works. It enabled the transmission of knowledge and facilitated communication across the vast Sumerian city-states. The decipherment of cuneiform tablets by modern scholars has provided valuable insights into the history, culture, and achievements of the Sumerians.
5. What led to the decline of the Sumerian civilization?
The decline of the Sumerian civilization can be attributed to various factors. One significant factor was external invasions by neighboring empires, such as the Akkadians and the Babylonians. These invasions disrupted the political stability of Sumer and led to the downfall of many city-states.
Additionally, environmental factors, such as droughts and floods, affected agricultural productivity and caused economic hardships. The decline in agricultural output and the ensuing social unrest further weakened the Sumerian civilization. Over time, power shifted to other empires in the region, marking the end of the Sumerian dominance in Mesopotamia.
In conclusion, the ancient civilization of Sumer developed in Mesopotamia, which is located in modern-day Iraq.
The Sumerians thrived in this region around 4000 BCE and were known for their advancements in agriculture, writing, and city-building. Their cities, such as Ur and Uruk, were centers of trade and culture, and they established a complex system of government and religious beliefs. The Sumerians laid the foundation for future civilizations in the region and their contributions continue to influence our world today.