The Industrial Revolution, a transformative period in history, brought about significant changes in various aspects of society. It marked a shift from agrarian and handcraft-based economies to mechanized industries. So, when exactly did this pivotal period occur?
The Industrial Revolution took place between the late 18th century and the early 19th century. It began in Britain around the 1760s and gradually spread to other parts of Europe and North America. This era of rapid industrialization and technological advancements had a profound impact on the world, revolutionizing production methods, transportation, and living conditions.
The Industrial Revolution took place from the late 18th century to the early 19th century. It began in Britain and then spread to other parts of the world. This transformative period marked the transition from hand production methods to machine manufacturing, leading to significant advancements in technology, industries, and transportation. The Industrial Revolution had a profound impact on society and economy, shaping the modern world as we know it.
Contents
- The Birth of the Industrial Revolution
- When Did The Industrial Revolution Take Place?
- Key Takeaways
- Frequently Asked Questions
- 1. What was the timeline of the Industrial Revolution?
- 2. What were the key technological innovations during the Industrial Revolution?
- 3. How did the Industrial Revolution impact society?
- 4. What were the major consequences of the Industrial Revolution?
- 5. How does the Industrial Revolution still influence us today?
- Why Did The Industrial Revolution Start?
The Birth of the Industrial Revolution
The Industrial Revolution, a period of significant technological advancements and socioeconomic changes, revolutionized the world as we know it. It marked the transition from traditional manual labor-based economies to machine-based manufacturing processes. A multitude of factors led to the rise of the Industrial Revolution, each playing a crucial role in shaping the timeline of this transformative era.
Early Industrialization: The Origins
The origins of the Industrial Revolution can be traced back to the mid-18th century in Great Britain. One of the key factors that fueled this early industrialization was the availability of natural resources, particularly coal and iron ore. The discovery and extraction of these resources provided the necessary fuel and raw materials for the development of new technologies and machinery. Additionally, Britain’s colonial empire had access to vast overseas markets, which created a demand for goods and further encouraged industrial growth.
Inventions and innovations played a pivotal role in the early stages of the Industrial Revolution. The development of the steam engine by James Watt in the late 18th century revolutionized transportation and power generation, enabling factories to be built away from traditional water sources. The spinning jenny, power loom, and cotton gin revolutionized textile manufacturing, leading to increased production and efficiency. These advancements in machinery and technology set the stage for the rapid industrialization that would follow.
The Industrial Revolution also witnessed significant changes in the agricultural sector. Technological advancements in agriculture, such as the introduction of the seed drill and mechanized harvesting equipment, increased agricultural productivity. This surplus in agricultural production resulted in a population boom, providing a larger workforce for the emerging factories and industries.
The Industrial Revolution Spreads
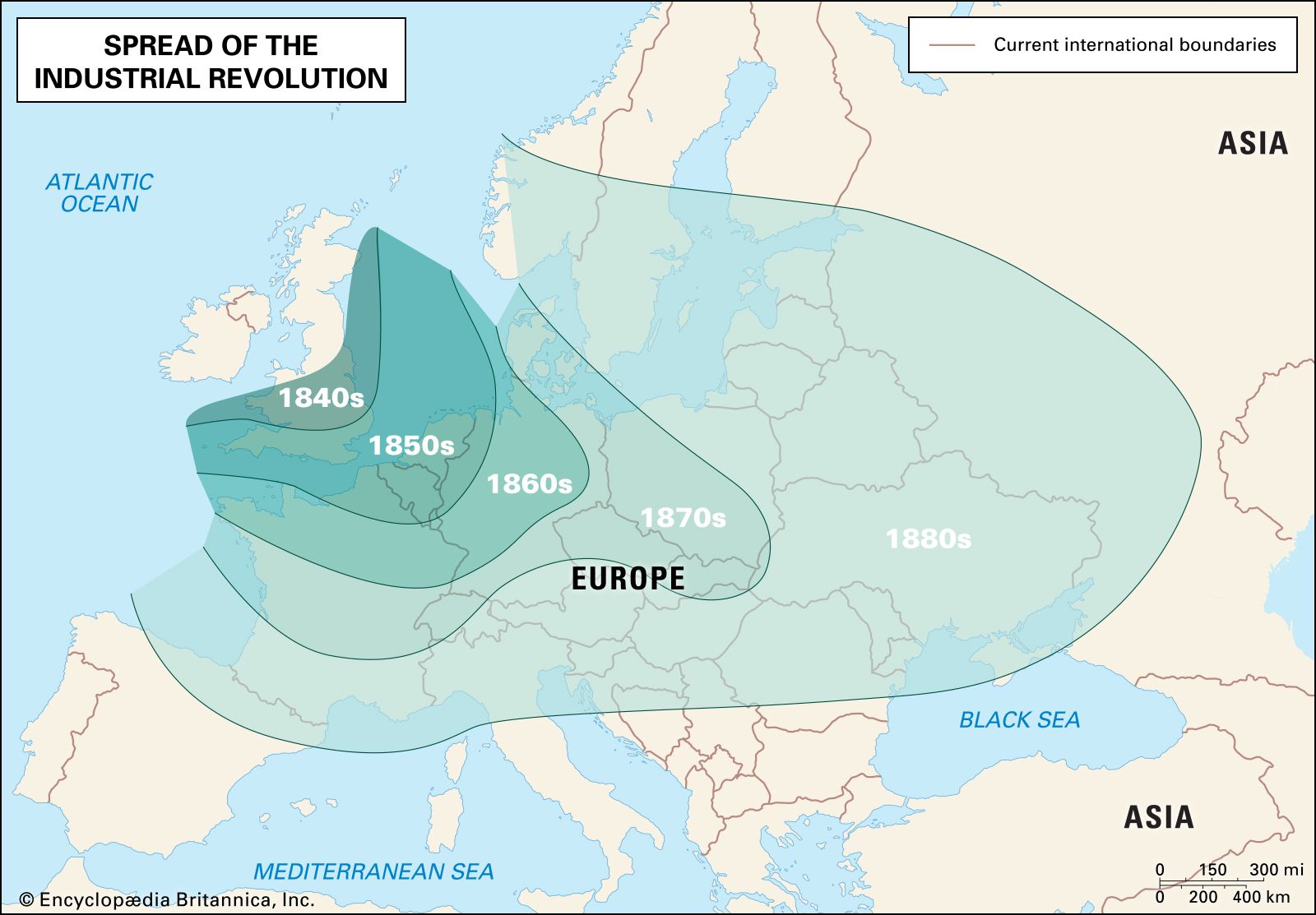
The Industrial Revolution spread beyond the shores of Great Britain and reached other parts of Europe and the United States in the 19th century. The availability of natural resources, technological advancements, and the exchange of ideas among nations facilitated this spread.
In the United States, the Industrial Revolution took place in the early to mid-19th century, primarily driven by the expansion of the textile industry and the development of transportation infrastructure. The invention of the cotton gin by Eli Whitney revolutionized cotton production and propelled the growth of the textile industry. The construction of canals, railroads, and the expansion of steam-powered ships enabled the transportation of goods and raw materials over long distances, stimulating industrial growth.
In Europe, countries such as Germany and France experienced industrialization in the late 19th century. Germany’s industrial revolution was influenced by its rich coal and iron ore reserves, as well as the establishment of universal education and research institutions. France, on the other hand, underwent industrialization primarily in the areas of textiles, metallurgy, and chemical industries.
The Industrial Revolution also reached other parts of the world, including Japan. In the late 19th century, the Japanese government actively promoted industrialization, leading to the establishment of modern factories and the adoption of Western technologies. This period of industrialization propelled Japan’s transformation into a global economic power.
The Impact of the Industrial Revolution
The Industrial Revolution had a profound impact on numerous aspects of society, including the economy, social structure, and living conditions. As industrialization advanced, there was a shift from a predominantly agrarian society to an urbanized society centered around factories and industrial production.
The economic impact of the Industrial Revolution was substantial. Industrialized nations experienced rapid economic growth, as the efficiency and scale of production increased. The division of labor and the specialization of tasks led to increased productivity. This surge in production and the expansion of markets resulted in higher profits and economic prosperity.
Socially, the Industrial Revolution brought significant changes. The rise of factories and industrial work created a new class structure, with wealthy industrialists and a growing working class. The working conditions in factories were often harsh, with long hours, low wages, and poor living conditions. Workers began to advocate for their rights, leading to the emergence of trade unions and the labor movement.
The Industrial Revolution also had a profound impact on the environment. The increased use of coal as a source of energy led to pollution and environmental degradation. The growth of cities and industrial areas resulted in overcrowding and unhealthy living conditions. However, the negative environmental and social impacts eventually led to reforms and the development of regulations aimed at improving labor conditions and protecting the environment.
The Legacy of the Industrial Revolution
The Industrial Revolution forever transformed the world, ushering in an era of unprecedented technological advancements and societal changes. It paved the way for modern manufacturing processes and set the stage for further waves of industrialization and innovation in the centuries to come.
Today, we continue to live in the legacy of the Industrial Revolution, benefiting from the technological breakthroughs and advancements that emerged during this transformative period. From the development of the steam engine to the proliferation of mass production techniques, the Industrial Revolution laid the foundation for the modern world and shaped the way we live, work, and interact with one another.
When Did The Industrial Revolution Take Place?
The Industrial Revolution, a period of rapid industrialization and technological advancement, took place during the late 18th to mid-19th centuries. It started in Great Britain and subsequently spread to other parts of Europe, the United States, and eventually the rest of the world. This significant period in history had a profound impact on various aspects of society, including manufacturing, transportation, agriculture, and social structure.
The Industrial Revolution was characterized by the transition from manual labor to machine-based manufacturing. It brought about the introduction of inventions like the steam engine, which revolutionized transportation and powered factories. This era also saw the development of factories, urbanization, and the growth of working-class communities. Furthermore, it led to the emergence of new industries, such as textiles, iron, and coal mining.
The Industrial Revolution transformed methods of production, increased productivity, and facilitated new trade networks. It brought significant economic growth and led to improvements in living standards for some, but also resulted in harsh working conditions and economic disparities.
The Industrial Revolution marked a pivotal moment in history, shaping the modern world we live in today.
Key Takeaways
- The Industrial Revolution took place from the 18th to the 19th century.
- It began in Great Britain and spread to other parts of Europe and America.
- The revolution brought significant changes in agriculture, manufacturing, mining, and transportation.
- Technological advancements, such as the steam engine and textile machinery, played a crucial role in the revolution.
- The Industrial Revolution had both positive and negative impacts on society and the economy.
Frequently Asked Questions
The Industrial Revolution was a time of significant technological advancements and societal changes. It marked the transition from an agrarian-based economy to one dominated by industry and manufacturing. Here are some frequently asked questions about the timing of this transformative period.
1. What was the timeline of the Industrial Revolution?
The Industrial Revolution spanned from the mid-18th century to the mid-19th century. It is generally understood to have begun in Great Britain, specifically in the 1760s, and gradually spread to other parts of Europe and the United States.
This period can be divided into three main phases: the First Industrial Revolution (1760-1840), the Second Industrial Revolution (1840-1870), and the Third Industrial Revolution (1870-early 20th century). Each phase had its distinctive technological advancements and socio-economic impacts.
2. What were the key technological innovations during the Industrial Revolution?
The Industrial Revolution introduced numerous transformative innovations. Some notable examples include:
– The steam engine, pioneered by James Watt, revolutionized transportation and powered factories.
– The spinning jenny and power loom revolutionized textile production, increasing efficiency and output.
– The telegraph and the telephone revolutionized communication, connecting people across long distances.
– The development of the railway system transformed transportation and trade, enabling goods to be transported quickly and consistently.
These innovations and many others played a crucial role in shaping the Industrial Revolution and laying the foundation for modern industrialized societies.
3. How did the Industrial Revolution impact society?
The Industrial Revolution had far-reaching effects on society, fundamentally transforming the economic, social, and cultural landscape:
– The rapid industrialization led to urbanization, with people migrating from rural areas to cities in search of employment opportunities.
– The division of labor became more specialized, leading to the rise of factories and mass production.
– There were significant changes in social classes, with a growing working class and the emergence of an industrial bourgeoisie.
– The Industrial Revolution also sparked advancements in education, transportation, and healthcare.
4. What were the major consequences of the Industrial Revolution?
The Industrial Revolution had both positive and negative consequences:
– On the positive side, it led to economic growth, technological progress, and improved living standards for some segments of society.
– However, it also resulted in harsh working conditions, exploitation of workers, and environmental degradation.
– The Industrial Revolution also had far-reaching geopolitical effects, contributing to the rise of colonialism and imperialism.
Overall, the Industrial Revolution had a profound and lasting impact on the world.
5. How does the Industrial Revolution still influence us today?
The Industrial Revolution laid the foundation for modern society and continues to shape our lives in various ways:
– It established the importance of technological innovation and industrialization as drivers of economic growth.
– The division of labor and mass production techniques pioneered during this period still form the basis of modern manufacturing processes.
– The legacy of the Industrial Revolution can also be seen in the ongoing debates surrounding workers’ rights, income inequality, and environmental sustainability.
In short, the Industrial Revolution continues to shape and influence various aspects of our society and economy.
Why Did The Industrial Revolution Start?
The Industrial Revolution took place from the 18th to the 19th century, starting in Britain and then spreading to other parts of Europe and North America. It was a time of significant economic, social, and technological transformation.
During this period, there was a shift from manual labor to machine-based manufacturing, leading to the development of factories and the mechanization of industries. This revolution had profound effects on agriculture, transportation, communication, and overall living standards. It marked a turning point in history, shaping the modern world as we know it today.