Who were the first ancient civilizations to emerge? It is a question that has fascinated historians and archaeologists for centuries. The origins of civilization are shrouded in mystery, with various contenders vying for the title of the first civilization. From the early city-states of Mesopotamia to the mighty pharaohs of Egypt, the first ancient civilizations shaped the course of human history.
One of the earliest ancient civilizations to emerge was Sumer, located in Mesopotamia (modern-day Iraq) around 4000 BCE. Sumerians developed a highly advanced system of writing known as cuneiform and built impressive cities with large, temple-like structures called ziggurats. Another significant civilization that emerged around the same time was ancient Egypt, known for its iconic pyramids and elaborate burial rituals. These early civilizations laid the foundation for the complex societies that would follow, paving the way for key developments in agriculture, governance, and culture.
Around 3000 BCE, the first ancient civilizations began to emerge in different parts of the world. In Mesopotamia, the Sumerians built the earliest known civilization, complete with a system of writing, a complex social structure, and thriving agriculture. In Egypt, the Nile River provided the foundation for the development of a powerful civilization that built magnificent pyramids and left behind awe-inspiring artifacts. In the Indus Valley, the Harappan civilization emerged, showcasing advanced urban planning and sophisticated water management systems. These civilizations laid the groundwork for the development of the ancient world as we know it.
Contents
- Ancient Mesopotamia: The Cradle of Civilization
- The Olmec Civilization: Pre-Columbian Mesoamerica
- In Conclusion
- The First Ancient Civilizations
- Key Takeaways
- Frequently Asked Questions
- 1. Which ancient civilization emerged first?
- 2. What about the Indus Valley Civilization?
- 3. Were there other ancient civilizations that emerged around the same time?
- 4. What were the contributions of these ancient civilizations?
- 5. Is there evidence of interaction between these civilizations?
- Origins of the First Civilization
Ancient Mesopotamia: The Cradle of Civilization
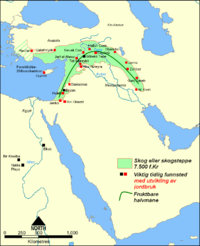
The emergence of ancient civilizations is a topic of great fascination for historians and archaeologists. Among the first known civilizations to emerge in human history is ancient Mesopotamia, often referred to as the cradle of civilization. Located in the region of modern-day Iraq, Mesopotamia was the birthplace of many significant developments that shaped human civilization. This article explores the origins, achievements, and legacy of ancient Mesopotamia, shedding light on its status as one of the first ancient civilizations to emerge.
The Origins of Mesopotamian Civilization
The ancient civilization of Mesopotamia emerged around 4000 BCE in the fertile lands located between the Tigris and Euphrates rivers. The geographical location of Mesopotamia provided an abundant water supply and fertile soil, facilitating agricultural development. The earliest known city-states in Mesopotamia, such as Uruk and Ur, flourished as centers of trade and political organization.
One of the key factors in the development of the Mesopotamian civilization was the invention of writing. The people of Mesopotamia developed a writing system known as cuneiform, using wedge-shaped marks on clay tablets to record information. This development allowed for the recording of laws, literature, and administrative documents, contributing to the growth of a complex society.
The city-states of Mesopotamia were governed by influential rulers known as kings. These kings held significant power and acted as religious leaders, ensuring the well-being of their city-state and its inhabitants. Religion played a crucial role in Mesopotamian society, with temples serving as important centers of worship and economic activity. The construction of monumental structures, such as ziggurats, highlights the importance of religion in ancient Mesopotamia.
Agriculture was the backbone of the Mesopotamian economy. The fertile soil allowed for the cultivation of crops such as barley, wheat, and dates. The irrigation systems, such as canals and dikes, played a vital role in the success of agriculture and the growth of surplus food. This surplus food enabled other advancements, such as the development of specialized crafts, trade networks, and the establishment of social hierarchies.
Achievements and Innovations of Mesopotamia
Ancient Mesopotamia witnessed numerous achievements and innovations that had a lasting impact on human civilization. One of the most significant contributions was the invention of the wheel, which revolutionized transportation and facilitated trade. The development of the wheel also led to the creation of chariots and improved agricultural tools.
The Mesopotamians made remarkable strides in the field of mathematics, introducing the concept of a numerical system based on the number 60. This system influenced the way we measure time (60 minutes in an hour, 360 degrees in a circle) and is still used in modern-day geometry. They also developed an advanced system of mathematics that included algebra, geometry, and arithmetic.
The Mesopotamians were skilled astronomers, observing and studying celestial bodies. They created one of the earliest known star catalogs, which consisted of detailed descriptions of various constellations. They also developed a calendar based on the lunar cycle, which is believed to be one of the earliest calendars ever created.
The Indus Valley Civilization: Urban Planning and Trade
The Indus Valley Civilization, also known as the Harappan Civilization, emerged around 3300 BCE in what is present-day Pakistan and northwest India. It is considered one of the earliest urban civilizations in the world. The Indus Valley Civilization is renowned for its advanced urban planning, sophisticated drainage systems, and trade networks.
The cities of the Indus Valley Civilization were meticulously planned, with grids of streets and well-organized houses made of baked bricks. The most famous city of this civilization is Mohenjo-Daro, which had an intricate system of streets, public buildings, and private residences. The advanced urban planning of the Harappan cities showcases their sophisticated understanding of architecture and city design.
The Indus Valley Civilization had a well-developed system of trade. Archaeological excavations have uncovered evidence of long-distance trade with regions as far as Mesopotamia and Egypt. The presence of seals and standardized weights indicates a system of economic control and regulation. The existence of dockyards suggests that the Harappans engaged in maritime trade as well.
The Indus Valley Civilization had an intricate drainage system that included well-built and covered drains, indicating their advanced knowledge of sanitation and urban planning. These efficient drainage systems contributed to the overall cleanliness and hygiene of the cities, highlighting the civilization’s commitment to public health.
Art and Culture of the Indus Valley Civilization
The art and culture of the Indus Valley Civilization are characterized by their intricate pottery, jewelry, and figurines. The Harappans were skilled craftsmen who produced a wide range of artifacts using materials such as terracotta and bronze. The presence of seals with engraved symbols suggests the existence of a writing system, although it has not been deciphered.
Religion likely played a significant role in the lives of the Indus Valley people, as evidenced by the presence of numerous, well-planned ritual baths or “Great Baths.” These large communal structures were likely used for ritual purification and may have been associated with religious practices.
The decline of the Indus Valley Civilization remains a subject of debate among historians and archaeologists. Potential reasons for its decline include environmental changes, such as the drying up of the Saraswati River, and the possible influx of Indo-Aryan peoples from the north.
Ancient Egypt: The Gift of the Nile
Ancient Egypt, located in northeastern Africa, emerged around 3100 BCE and is one of the oldest civilizations in the world. The civilization was shaped by the Nile River, which provided fertile land and water for agriculture, transportation, and trade.
The ancient Egyptians developed a complex society with a central government ruled by pharaohs, who were considered divine. The construction of monumental structures, such as the pyramids of Giza and the temples of Luxor and Karnak, reflects the architectural prowess and religious beliefs of the Egyptians.
One of the significant achievements of ancient Egypt was the development of a system of writing known as hieroglyphics. Hieroglyphics were pictorial symbols that represented sounds, objects, or ideas. This form of writing was primarily used for religious and monumental inscriptions and has provided valuable insights into ancient Egyptian life and culture.
The Egyptians held an elaborate belief system centered around the concept of the afterlife. They believed in a complex pantheon of gods and goddesses and the idea of judgment after death. This belief system influenced their burial practices, with the construction of elaborate tombs and the practice of mummification.
Advancements in Science and Technology in Ancient Egypt
Ancient Egypt made significant advancements in various fields, demonstrating their scientific and technological prowess. They were skilled in the field of medicine, using herbs and natural remedies to treat various ailments. The Edwin Smith Papyrus, dating back to the 16th century BCE, is one of the earliest known medical texts and provides detailed information on surgical procedures.
The Egyptians also excelled in the fields of mathematics and engineering. They had a decimal system of numbers and advanced knowledge of geometry, which was crucial in the construction of monumental structures. They developed sophisticated techniques in quarrying and building, using pulleys, ramps, and levers to move and lift heavy stones.
Astronomy was an important aspect of ancient Egyptian culture. The Egyptians closely observed the movement of celestial bodies and developed calendars based on astronomical observations. They also aligned their monumental structures with celestial bodies, such as the pyramids’ alignment with the North Star.
The Olmec Civilization: Pre-Columbian Mesoamerica
The Olmec civilization emerged in Mesoamerica, an area that encompasses parts of modern-day Mexico and Central America, around 1400 BCE. The Olmecs are considered the “mother culture” of Mesoamerica, influencing later civilizations such as the Maya and Aztecs.
The Olmecs were renowned for their monumental stone sculptures, featuring colossal heads and intricate carvings. The stone heads, weighing several tons, are believed to depict rulers or important individuals and demonstrate the extraordinary craftsmanship of the Olmec civilization.
Agriculture was crucial to the Olmec civilization, and they developed advanced farming techniques. They built drainage systems and canals to control water flow and create fertile agricultural fields. Corn, beans, and squash were staple crops in their diet.
The Olmecs had a complex social and political structure, with a ruling elite holding power over the population. Religion played a significant role in the Olmec society, as evidenced by the presence of religious structures and artifacts. The Olmecs worshiped deities associated with natural forces and fertility.
The Legacy of the Olmec Civilization
The Olmec civilization had a profound influence on the development of Mesoamerican cultures that followed. Their art, religious beliefs, and agricultural practices laid the foundation for subsequent civilizations in the region. The Olmecs introduced the ritual ballgame, which became an integral part of the Mesoamerican cultures.
The decline of the Olmec civilization remains a mystery, with possible causes including environmental changes, internal conflict, or the rise of new regional powers. Despite their decline and disappearance, the legacy of the Olmec civilization endures, leaving a lasting impact on the cultures that succeeded them.
In Conclusion
The emergence of ancient civilizations marked significant milestones in human history and laid the foundations for the development of complex societies. Ancient Mesopotamia, the Indus Valley Civilization, ancient Egypt, and the Olmec civilization were among the first ancient civilizations to emerge, each contributing unique advancements and shaping their respective regions. From the invention of writing and wheel to urban planning and monumental architecture, these early civilizations left a lasting legacy that continues to awe and inspire.
The First Ancient Civilizations
Several ancient civilizations emerged throughout history, laying the foundations for modern society. These early civilizations were characterized by their advancements in agriculture, technology, governance, and culture.
The Sumerians were one of the first ancient civilizations to emerge around 4000 BCE in Mesopotamia (present-day Iraq and Kuwait). They developed a system of writing called cuneiform and established city-states with sophisticated irrigation systems.
In ancient Egypt, the Pharaohs ruled along the Nile River, creating a powerful and prosperous civilization starting around 3100 BCE. They built magnificent pyramids as tombs for their rulers and developed a system of hieroglyphic writing.
In the Indus Valley, the Harappan civilization flourished from around 2600 BCE to 1900 BCE. This advanced civilization had well-planned cities with sewage systems and remarkable craftsmanship.
- The Chinese civilization emerged along the Yellow River around 1600 BCE. They developed the earliest forms of written language and contributed to advancements in art, philosophy, and science.
- The Mesoamerican civilization originated in present-day Mexico and Central America around 2000 BCE. The Olmecs, Maya, and Aztecs developed complex societies with impressive architecture and mathematical knowledge.
Key Takeaways
- The first ancient civilizations to emerge were Mesopotamia and Ancient Egypt.
- Mesopotamia, located in modern-day Iraq, was the cradle of civilization and gave rise to the Sumerian, Akkadian, Babylonian, and Assyrian civilizations.
- Ancient Egypt, located along the Nile River, was known for its advanced agriculture, monumental architecture, and a sophisticated writing system called hieroglyphics.
- The Indus Valley civilization, situated in modern-day Pakistan and northwestern India, was one of the earliest urban civilizations and had advanced city planning and sanitation systems.
- The Shang Dynasty in China, which emerged around 1600 BCE, was one of the first recorded ancient civilizations in East Asia, known for its bronze metallurgy and oracle bone script.
Wondering about the earliest ancient civilizations? Here are some commonly asked questions to help you learn more about the first ancient civilizations that emerged.
1. Which ancient civilization emerged first?
The Sumerian civilization, located in Mesopotamia (modern-day Iraq), is considered as one of the first ancient civilizations to emerge. Around 4000 BCE, the Sumerians developed a complex society characterized by advanced agriculture, sophisticated trade networks, and the invention of writing. Their contributions laid the foundation for future civilizations in the region.
Additionally, the ancient Egyptian civilization, dating back to around 3100 BCE, is also among the earliest ancient civilizations. With their impressive architectural achievements, such as the construction of the pyramids, and the development of hieroglyphic writing, the ancient Egyptians left a significant cultural and historical legacy.
2. What about the Indus Valley Civilization?
The Indus Valley Civilization, also known as the Harappan civilization, emerged around 2500 BCE in the region of present-day Pakistan and northwest India. While it is contemporaneous with the Sumerian and Egyptian civilizations, the Indus Valley Civilization developed independently and had its unique characteristics.
The civilization flourished along the banks of the Indus River, with major cities like Mohenjo-Daro and Harappa. They had advanced urban planning, with well-structured grids and drainage systems. The Indus Valley people engaged in trade, created intricate pottery, and had a script that has not yet been fully deciphered.
3. Were there other ancient civilizations that emerged around the same time?
Around the same time as the Sumerians, Egyptians, and the Indus Valley Civilization, there were other notable ancient civilizations that appeared on the historical stage. The Norte Chico civilization in modern-day Peru developed around 3500 BCE and is considered one of the first civilizations in the Americas.
The ancient Chinese civilization began around 2100 BCE, with the establishment of the Xia Dynasty. It laid the groundwork for the subsequent Chinese dynasties, marking the beginning of a rich and complex cultural, technological, and political history in East Asia.
4. What were the contributions of these ancient civilizations?
The Sumerians made significant contributions to human civilization, including the invention of the wheel, the development of the first known writing system (cuneiform), and the establishment of the first city-states. They also pioneered complex religious beliefs and practices.
The ancient Egyptians left a profound impact on architecture, art, and religion. Their monumental structures, such as the pyramids and temples, still captivate people today. The Egyptians also made progress in medicine, mathematics, and astronomy.
The Indus Valley Civilization excelled in urban planning, with advanced systems for water supply and sanitation. They also had a sophisticated trade network and produced unique artifacts in crafts like pottery and jewelry.
The Norte Chico civilization laid the foundation for later civilizations in the Americas and had impressive agricultural terraces and monumental architecture. The ancient Chinese civilization contributed to various fields, including writing, agriculture, philosophy, and governance.
5. Is there evidence of interaction between these civilizations?
While direct evidence of interaction between these early civilizations is limited, there are indications of possible trade and cultural exchanges. For instance, ancient Mesopotamian artifacts have been found in the Indus Valley, hinting at some form of connection. Additionally, similarities in architectural styles between the Sumerians and Egyptians suggest possible influence or shared inspiration.
Further research and archaeological discoveries continue to shed light on the connections and exchanges that may have occurred between these ancient civilizations.
Origins of the First Civilization
In conclusion, the first ancient civilizations to emerge were the Sumerians in Mesopotamia and the Egyptians along the Nile River. These civilizations developed around 3000 BCE and laid the foundation for future civilizations.
The Sumerians, located in modern-day Iraq, were known for their advancements in agriculture, politics, and writing. They built city-states, invented the wheel, and created the first known system of writing called cuneiform. On the other hand, the Egyptians built massive pyramids and created a unique system of writing called hieroglyphics. They were also known for their complex religious beliefs and powerful pharaohs.