The Industrial Revolution, which began in the late 18th century, was a period of significant economic and social transformation in which traditional manual labor industries were replaced by mechanized production. One of the key causes of this revolution was the development and implementation of new technologies, such as the steam engine and the spinning jenny, which greatly increased productivity and efficiency. These inventions led to the establishment of factories, where goods could be produced on a much larger scale, thus leading to the growth of industrialization.
Another major factor that contributed to the Industrial Revolution was the expansion of trade and imperialism. The discovery of new markets and the colonization of foreign territories provided access to valuable resources and raw materials that fueled industrial growth. This led to the establishment of global supply chains and the rise of capitalist systems. Additionally, the availability of cheap labor, resulting from population growth and urbanization, played a crucial role in driving industrialization.
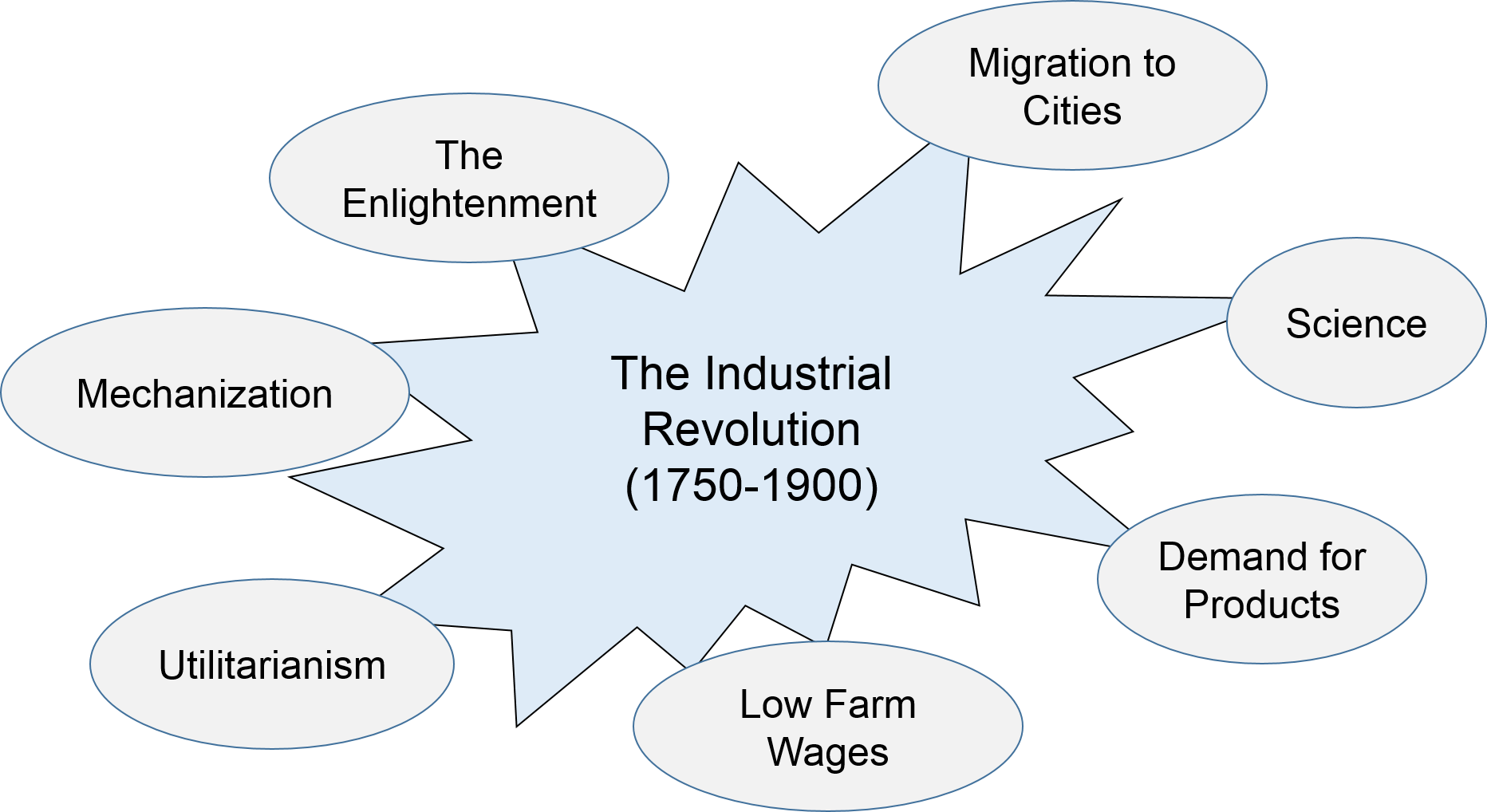
The causes of the Industrial Revolution were multifaceted. One key factor was the availability of natural resources like coal and iron, which fueled the growth of industries. Technological advancements and inventions, such as the steam engine and spinning jenny, also played a crucial role. Additionally, political and economic factors, like the Enclosure Movement and the rise of capitalism, contributed to the Industrial Revolution. The expansion of trade and colonization, as well as population growth, further stimulated industrialization.
Contents
- The Impact of Technological Advancements on the Industrial Revolution
- Causes of the Industrial Revolution
- Key Takeaways
- Frequently Asked Questions
- 1. What economic factors contributed to the Industrial Revolution?
- 2. How did technological advancements contribute to the Industrial Revolution?
- 3. What role did social and political changes play in the Industrial Revolution?
- 4. What were the effects of the Industrial Revolution on society?
- 5. What were some of the environmental impacts of the Industrial Revolution?
- Why Did The Industrial Revolution Start?
The Impact of Technological Advancements on the Industrial Revolution
The Industrial Revolution, which took place from the 18th to the 19th century, was a period of significant economic and social transformation. One of the primary causes of this revolution was the rapid advancements in technology. The invention and improvement of various machines and techniques revolutionized the production process, leading to increased productivity and a shift from agrarian societies to industrialized nations. This article will explore the impact of technological advancements on the Industrial Revolution.
The Invention of the Steam Engine
The invention of the steam engine, pioneered by James Watt in the 1760s, was a pivotal moment in history. Prior to the steam engine, most power was derived from human labor or animal power. The steam engine, fueled by coal, provided a new and more efficient source of power. It greatly increased the productivity of industries, such as textile manufacturing and transportation.
The steam engine was used to power machinery in factories, replacing manual labor and accelerating production. It allowed factories to be located away from water sources, as steam engines could be used to pump water and power machinery. This innovation led to the growth of urban areas and the development of new industrial centers.
The widespread adoption of the steam engine revolutionized transportation as well. Steam-powered locomotives and steamships enabled the efficient movement of goods and people. They opened up new markets and facilitated the transportation of raw materials and finished products over long distances, contributing to the growth of global trade.
The Cotton Gin and Textile Industry
Another technological innovation that played a crucial role in the Industrial Revolution was the invention of the cotton gin by Eli Whitney in 1793. Prior to the cotton gin, separating cotton fibers from the seeds was a labor-intensive process. The cotton gin mechanized this process, making it faster and more efficient.
The cotton gin revolutionized the textile industry, which had a significant impact on the Industrial Revolution. With the ability to process cotton more efficiently, textile mills experienced a surge in production. This led to an increased demand for raw cotton, which, in turn, drove the expansion of plantation agriculture in the southern United States.
The growth of the textile industry also created a demand for new machinery and technologies. Innovations such as the spinning jenny, water frame, and power loom further improved the efficiency and productivity of textile manufacturing. These advancements not only increased production but also reduced costs, making textiles more affordable and accessible to a wider population.
The Invention of the Telegraph
The development of communication technology was another significant factor in the Industrial Revolution. The invention of the telegraph by Samuel Morse in the 1830s revolutionized long-distance communication. Prior to the telegraph, communication was limited to the speed of physical transportation or written correspondence.
The telegraph enabled near-instantaneous communication over vast distances. It facilitated the coordination of economic activities, allowed for the rapid spread of information, and improved the efficiency of business transactions. The telegraph played a crucial role in the expansion of railways, as it enabled the coordination of train schedules and ensured the safe operation of the rail network.
Furthermore, the telegraph had a transformative effect on the financial sector. It facilitated the transmission of stock prices, enabling the development of stock exchanges. The telegraph also revolutionized journalism, as news could be transmitted quickly, leading to the rise of the modern newspaper industry.
The technological advancements of the Industrial Revolution were the driving force behind the profound social and economic changes of the time. These innovations not only increased productivity and efficiency but also transformed society, creating new industries, changing the nature of work, and shaping the modern world. The Industrial Revolution set the stage for further advancements and laid the foundation for the modern industrialized societies we see today.

Causes of the Industrial Revolution
The Industrial Revolution was a period of significant economic and technological changes that occurred in the late 18th and early 19th centuries. It transformed societies from predominantly agrarian-based economies to industrialized nations. There were several key factors that contributed to the onset and progression of the Industrial Revolution:
- Economic factors: The accumulation of capital, a growing supply of natural resources, and a demand for goods and services fueled the need for industrialization.
- Technological advancements: Inventions and innovations such as the steam engine, textile machinery, and iron production methods significantly increased productivity and efficiency.
- Population growth: A rapidly expanding population created a large and available workforce, enabling factories to operate at a larger scale.
- Transportation and infrastructure improvements: The development of canal systems, railways, and road networks facilitated the transportation of raw materials and finished goods.
- Political and legal changes: Stable governments and supportive policies, such as patents and copyright laws, encouraged inventors and entrepreneurs to pursue industrial endeavors.
These combined factors created the perfect conditions for the Industrial Revolution to flourish, bringing about profound social, economic, and cultural changes that shaped the modern world.
Key Takeaways
- The Industrial Revolution was caused by a combination of factors including advancements in technology, population growth, and the rise of capitalism.
- Inventions such as the steam engine, spinning jenny, and power loom revolutionized the manufacturing industry and increased productivity.
- The growth of population led to an increased demand for goods and services, driving the need for more efficient production methods.
- The emergence of capitalism as an economic system provided the necessary framework for investment, innovation, and entrepreneurship.
- The Industrial Revolution had significant social and economic impacts, including urbanization, improved living standards, and increased economic inequality.
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are some commonly asked questions about the causes of the Industrial Revolution:
1. What economic factors contributed to the Industrial Revolution?
The Industrial Revolution was fueled by several key economic factors. One of the main factors was the availability of abundant natural resources, such as coal, iron, and water. These resources provided the necessary raw materials for industries to thrive. Additionally, the growth of international trade and colonization created new markets and increased demand for goods, driving industrial production. Lastly, the accumulation of capital through banking systems and investments provided the financial resources needed for industrial expansion.
Moreover, the agrarian revolution, which involved advancements in agricultural techniques and practices, freed up labor from the countryside. This surplus labor force migrated to urban areas, where they found employment in factories and industries.
2. How did technological advancements contribute to the Industrial Revolution?
Technological advancements played a crucial role in driving the Industrial Revolution. The development of new machinery, such as the spinning jenny and the steam engine, revolutionized production methods. These inventions allowed for faster and more efficient production, increasing output and reducing costs. Additionally, innovations in transportation, such as the advent of steam-powered locomotives and the construction of canals, facilitated the movement of goods and raw materials across long distances, connecting previously isolated regions and expanding markets.
Moreover, advancements in communication technologies, such as the telegraph, improved the flow of information and coordination between businesses, enabling faster decision-making and enhancing productivity.
Social and political changes were significant catalysts for the Industrial Revolution. As the feudal system waned and the power of the nobility weakened, there was a rise of a new middle class of entrepreneurs. These individuals had the financial means and social mobility to invest in industries and drive innovation. Additionally, the enclosure movement in agriculture led to the consolidation of land and increased productivity, forcing many small farmers to seek employment in urban industries.
Furthermore, political factors, such as stable governments and supportive policies, played a role in fostering industrial growth. Examples include the establishment of property rights, the protection of patents, and the promotion of trade through agreements and treaties.
4. What were the effects of the Industrial Revolution on society?
The Industrial Revolution brought about significant changes in society. On one hand, it led to urbanization as people migrated from rural areas to cities in search of employment opportunities. This resulted in crowded living conditions and the growth of slums.
On the other hand, the Industrial Revolution also led to improved living standards for many individuals. The increased production and efficiency brought down the costs of goods, making them more affordable. Additionally, advancements in medicine and public health improved sanitation and reduced mortality rates.
5. What were some of the environmental impacts of the Industrial Revolution?
The Industrial Revolution had significant environmental impacts. The extensive use of coal and other fossil fuels for energy led to air pollution, creating smog and contributing to respiratory ailments. The discharge of industrial waste into rivers and water bodies contaminated water sources, causing health problems and damaging aquatic ecosystems.
Additionally, deforestation occurred to meet the demand for timber and create space for industries. This loss of forests had adverse effects on biodiversity and contributed to soil erosion and climate change.
Why Did The Industrial Revolution Start?
To summarize, the Industrial Revolution was a major turning point in history that was caused by several key factors. One of the main causes was the agricultural revolution, which led to an increase in food production and population growth. This created a surplus of labor and fueled the demand for new technologies and industries.
Another important cause was the availability of natural resources, such as coal and iron ore. These resources were abundant in Britain and provided the necessary materials for industrialization. Additionally, advancements in transportation, such as the invention of the steam engine and the construction of canals and railroads, played a crucial role in promoting industrial growth.