One cannot deny the significant impact of the Fourth Industrial Revolution on our lives. With advancements in technology and connectivity, this revolution has transformed the way we work, communicate, and live. It has opened up new opportunities for innovation and growth, but also poses challenges that require careful navigation. How do we adapt to this rapidly changing landscape and ensure that we harness the benefits while addressing the potential risks?
The Fourth Industrial Revolution is characterized by the integration of digital technologies, artificial intelligence, and automation into various industries. It builds upon the foundation of the previous three industrial revolutions but takes it to a new level with its unprecedented speed and scope. This revolution is not only reshaping industries and business models, but it is also impacting social structures and the way we interact with each other. As we embrace this transformation, it is crucial to foster a culture of continuous learning and adaptability, as well as to prioritize ethical considerations in order to ensure a sustainable and inclusive future.
The Fourth Industrial Revolution refers to the current and ongoing transformation of traditional industries due to advancements in technology. It is characterized by the fusion of technologies such as artificial intelligence, robotics, and the internet of things. This revolution is changing the way we live and work, with increased automation and connectivity. Industries are becoming more efficient and productive, leading to economic growth and new job opportunities. The Fourth Industrial Revolution is reshaping the global economy and society as a whole.

Contents
- The Impact of Automation in the Fourth Industrial Revolution
- The Fourth Industrial Revolution
- Key Takeaways
- Frequently Asked Questions
- 1. What are the key features of the Fourth Industrial Revolution?
- 2. How does the Fourth Industrial Revolution impact the workforce?
- 3. What are some examples of the Fourth Industrial Revolution in action?
- 4. What are the benefits of the Fourth Industrial Revolution?
- 5. What are the challenges of the Fourth Industrial Revolution?
- What is the Fourth Industrial Revolution? | CNBC Explains
The Impact of Automation in the Fourth Industrial Revolution
The Fourth Industrial Revolution, also known as Industry 4.0, is characterized by the merging of digital, physical, and biological technologies, resulting in a significant transformation of various industries. One of the key aspects of this revolution is the widespread use of automation in different sectors. Automation refers to the use of technology to perform tasks that were previously carried out by humans, leading to increased efficiency, productivity, and scalability. The impact of automation in the Fourth Industrial Revolution is profound and has the potential to reshape industries across the globe.
Enhanced Efficiency and Productivity
One of the primary benefits of automation in the Fourth Industrial Revolution is the enhanced efficiency and productivity it brings to industries. By replacing manual labor with machines and advanced technologies, automation enables faster and error-free processes. Machines can work continuously without the need for breaks, leading to increased productivity levels. Additionally, automation allows for the optimization of workflows and the elimination of mundane and repetitive tasks, freeing up human workers to focus on more complex and creative aspects of their work. Overall, automation plays a crucial role in streamlining operations and driving efficiency in various industries.
Automation also enables companies to achieve higher levels of productivity. With machines working round the clock, businesses can significantly increase their output capacity, meet growing demands, and reduce the time it takes to complete tasks. This increased productivity not only leads to higher profitability but also allows companies to stay competitive in a rapidly evolving market. By leveraging automation technologies such as robotics, artificial intelligence, and machine learning, businesses can optimize their production processes and achieve higher levels of output with minimal human intervention.
Furthermore, automation improves the accuracy and precision of tasks. Machines are programmed to perform tasks with high accuracy and minimal errors, eliminating the risk of human error in critical operations. This not only reduces the costs associated with rework and errors but also ensures consistent quality in the final products or services delivered. Automation can also gather and analyze vast amounts of data in real-time, enabling businesses to make data-driven decisions and further enhance their efficiency and productivity.
Impact on the Workforce
While automation brings numerous benefits, it also has implications for the workforce. The Fourth Industrial Revolution is expected to lead to a significant shift in the job market, with certain roles becoming obsolete and new ones emerging. As automation replaces repetitive and low-skilled tasks, workers in industries heavily impacted by automation may need to acquire new skills and adapt to changing job requirements. Companies will need to invest in reskilling and upskilling their workforce to ensure a smooth transition and mitigate the potential negative impacts of unemployment.
Automation has the potential to create new job opportunities as well. While some positions may be eliminated, the demand for skilled professionals in areas such as robotics, data analysis, and artificial intelligence is expected to rise. The workforce of the future will need to possess a combination of technical and soft skills to thrive in a highly automated environment. Businesses and educational institutions must collaborate to provide training programs that equip individuals with the necessary skills for the jobs of the future.
It is crucial for policymakers, businesses, and society as a whole to address the impact of automation on the workforce. Strategies for job creation, retraining, and ensuring a just transition for workers must be implemented. This includes providing support for individuals affected by automation, fostering a culture of lifelong learning, and creating an environment that promotes entrepreneurship and innovation.
Digital Transformation and Connectivity
The Fourth Industrial Revolution is characterized by the pervasive use of digital technologies and the connectivity of various systems. Digital transformation refers to the integration of digital technologies into all aspects of a business, resulting in fundamental changes in how organizations operate and deliver value to customers. Automation plays a pivotal role in digital transformation efforts by enabling the seamless integration and optimization of processes, as well as the collection and analysis of vast amounts of data.
Automation technologies such as internet of things (IoT) devices, sensors, and artificial intelligence systems are key enablers of connectivity and data-driven decision-making. These technologies allow businesses to gather real-time data from various sources, enabling them to monitor and control operations remotely, optimize energy consumption, and enhance overall efficiency. The ability to collect and analyze data at scale provides organizations with valuable insights that can be used to improve processes, identify trends, and make informed business decisions.
Digital transformation facilitated by automation also leads to improved customer experiences. By leveraging automation technologies, businesses can personalize and tailor their products and services according to individual customer preferences. Automation enables the efficient delivery of customized products, faster response times, and personalized customer interactions, enhancing overall satisfaction and loyalty. Additionally, automation-driven connectivity allows for real-time communication between businesses and customers, leading to faster issue resolution and improved customer service.
Challenges and Considerations
While the digital transformation enabled by automation offers immense opportunities, it also poses challenges. Organizations must navigate issues related to data privacy and security, as the increased connectivity and reliance on data give rise to new risks. Protecting sensitive customer information and ensuring compliance with data protection regulations becomes paramount. Additionally, organizations must consider the ethical implications of automation, such as the impact on job security and the equitable distribution of resources.
Furthermore, digital transformation requires a cultural shift within organizations. Implementing automation technologies and embracing data-driven decision-making may require changes in organizational structure, work processes, and employee attitudes. Resistance to change and lack of digital skills can impede the successful adoption of automation and the realization of its benefits. Organizations must invest in change management strategies, provide adequate training and support, and foster a culture that embraces the opportunities presented by automation in the Fourth Industrial Revolution.
In conclusion, automation plays a central role in the Fourth Industrial Revolution, driving enhanced efficiency, productivity, and digital transformation. While it brings significant benefits, it also presents challenges that need to be addressed. The impact on the workforce requires careful consideration, with a focus on reskilling, upskilling, and ensuring a just transition. Digital transformation and connectivity enabled by automation have the potential to revolutionize industries and enhance customer experiences. However, organizations must be mindful of data privacy, security, and ethical considerations. By navigating these challenges and seizing the opportunities presented by automation, businesses can thrive in the Fourth Industrial Revolution.
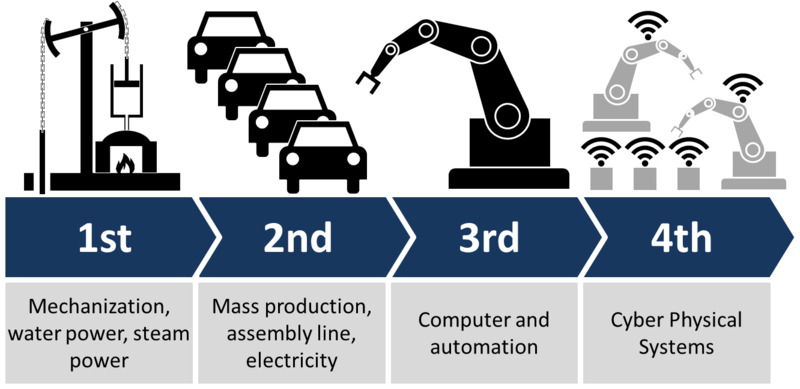
The Fourth Industrial Revolution
The Fourth Industrial Revolution is the current era of technological advancements characterized by the fusion of digital, physical, and biological systems. This revolution builds on the third industrial revolution of the 20th century, which introduced automation and computerization.
The key features of the Fourth Industrial Revolution include the widespread use of artificial intelligence, automation, robotics, the Internet of Things (IoT), big data, and cloud computing. It is reshaping industries and society as a whole by enabling efficient and intelligent automation, increasing productivity, and transforming how we live and work.
In the Fourth Industrial Revolution, technologies are interconnected, smart, and capable of constantly learning and adapting. This revolution is revolutionizing industries such as manufacturing, healthcare, transportation, agriculture, and finance. It is also leading to the emergence of new job roles and skills, requiring individuals and organizations to adapt and upskill to stay relevant.
The Fourth Industrial Revolution presents both opportunities and challenges. It has the potential to empower individuals, improve quality of life, and drive sustainable development. However, it also raises concerns about privacy, cybersecurity, inequality, job displacement, and ethical implications.
Key Takeaways
- The Fourth Industrial Revolution refers to the ongoing combination of technologies and innovations that are blurring the lines between the physical, digital, and biological worlds.
- It is characterized by the integration of digital technologies, artificial intelligence, and automation across various industries.
- The Fourth Industrial Revolution is expected to have a significant impact on the economy, job market, and society as a whole.
- It presents opportunities for increased productivity, efficiency, and innovation, but also raises concerns about job displacement and inequality.
- To navigate the challenges and reap the benefits of the Fourth Industrial Revolution, individuals and organizations need to adapt, upskill, and embrace lifelong learning.
Frequently Asked Questions
The Fourth Industrial Revolution refers to the current era of technological advancements that are transforming various industries and societies. It involves the integration of digital technologies into every aspect of our lives, including the way we work, communicate, and interact with machines.
1. What are the key features of the Fourth Industrial Revolution?
The Fourth Industrial Revolution is characterized by several key features:
a. Digitalization: It involves the use of digital technologies, such as artificial intelligence, big data, and the Internet of Things (IoT).
b. Automation: It includes the automation of various tasks and processes through robotics and advanced algorithms.
c. Connectivity: It emphasizes the interconnectedness of devices, systems, and people through advanced networks and communication technologies.
d. Disruption: It disrupts traditional industries and business models, creating new opportunities and challenges.
e. Human-Machine Interaction: It explores the interaction between humans and machines, blurring the lines between physical and digital realms.
2. How does the Fourth Industrial Revolution impact the workforce?
The Fourth Industrial Revolution has a profound impact on the workforce:
a. Job Automation: It leads to the automation of repetitive and mundane tasks, resulting in job displacement in certain industries.
b. Skills Redefinition: It necessitates the development of new skills and the redefinition of traditional job roles to cater to the changing demands of the digital economy.
c. Entrepreneurship Opportunities: It creates new opportunities for entrepreneurship and innovation, enabling individuals to start their own businesses and leverage emerging technologies.
d. Multidisciplinary Collaboration: It encourages collaboration between different disciplines and industries to address complex challenges and foster innovation.
3. What are some examples of the Fourth Industrial Revolution in action?
Here are a few examples of the Fourth Industrial Revolution:
a. Artificial Intelligence: The development of AI-powered assistants, autonomous vehicles, and intelligent systems that can learn and adapt.
b. Internet of Things (IoT): The network of interconnected devices that collect and exchange data, enabling smart homes, cities, and industries.
c. 3D Printing: The ability to create three-dimensional objects from digital designs, revolutionizing manufacturing and prototyping.
d. Blockchain Technology: The decentralized and transparent system that allows secure and efficient transactions, impacting finance, supply chain, and healthcare.
4. What are the benefits of the Fourth Industrial Revolution?
The Fourth Industrial Revolution offers several benefits:
a. Increased Efficiency: It streamlines processes and enhances productivity through automation and digitalization.
b. Improved Quality of Life: It brings innovative solutions to healthcare, transportation, and urban development, improving the quality of life for individuals and communities.
c. Accessible Information: It provides easy access to information and knowledge, empowering individuals with learning opportunities and promoting digital inclusion.
d. Sustainable Development: It enables more sustainable practices and solutions, addressing environmental challenges and promoting resource efficiency.
5. What are the challenges of the Fourth Industrial Revolution?
The Fourth Industrial Revolution also presents some challenges:
a. Job Displacement: The automation of tasks can lead to unemployment and job loss, particularly in industries heavily relying on manual labor.
b. Skill Gaps: The rapid technological changes require individuals and organizations to continuously upskill and reskill to remain relevant.
c. Ethical Concerns: The rise of AI and autonomous systems raises ethical considerations regarding privacy, security, and the responsible use of technology.