The Industrial Revolution was a period of rapid industrialization and technological advancements that transformed society and revolutionized the way we live and work. During this time, a multitude of inventions were made that had profound impacts on various industries and everyday life.
Contents
- Paragraph 1: Exploring the Impact of Inventions
- Paragraph 2: Historical Background and Solutions
- The Impact of Steam Power on the Industrial Revolution
- Inventions of the Industrial Revolution
- Key Takeaways
- Frequently Asked Questions
- 1. What was the steam engine and how did it impact the industrial revolution?
- 2. What role did the spinning jenny play in the Industrial Revolution?
- 3. How did the steam-powered locomotive impact transportation during the Industrial Revolution?
- 4. What was the impact of the cotton gin on the cotton industry during the Industrial Revolution?
- 5. How did the Bessemer process revolutionize steel production?
- Industrial Revolution | Time Period \u0026 Inventions”,”navigationEndpoint”:{“clickTrackingParams”:”CIAEEJHeChgcIhMIkPS017zshAMVvkxMCB0gyQq-“,”loggingUrls”:[{“baseUrl”:”https://www.youtube.com/pagead/paralleladinteraction?ai=COf2aYxzvZYrFH52pn88PnryJ6A4AvqvmosURABACIABgyQaCARNwYXJ0bmVyLXlvdXR1YmUtc3JwqAMEqgQXT9DvZsYAzEMMRe0N74SAgAI_bicPviqQBwSoB-edsQKoB-idsQKoB4QI0gglCIBBEAEYXjICggI6CIBCgMCAgIAgSNmg0jVQFFj49LXXvOyEA7ALAboLOwgDEAUYDCALKAUwBUABSABYamAAaABwAYgBAJABAZgBAaIBCAoAqAIB2AICqAEBwAEB0AEB4AEBgAIBoBcB\u0026sigh=YPKQVHGRk-g\u0026cid=CAASFeRoKVeh7A_-upGLTGdNEgMKHi4wyw\u0026ad_mt=[AD_MT]\u0026acvw=[VIEWABILITY]\u0026gv=[GOOGLE_VIEWABILITY]\u0026nb=%5BNB%5D\u0026label=video_click_to_advertiser_site
Paragraph 1: Exploring the Impact of Inventions
One of the most significant inventions during the Industrial Revolution was the steam engine, developed by James Watt. This invention not only revolutionized transportation but also powered machinery, leading to the establishment of factories and mass production. Furthermore, the invention of the spinning jenny by James Hargreaves transformed the textile industry by allowing for the mass production of thread, thus spurring the growth of the textile industry and contributing to economic development.
Paragraph 2: Historical Background and Solutions
The Industrial Revolution, which began in the late 18th century in Britain, marked a shift from manual labor to machine-based manufacturing, resulting in increased production and efficiency. This era saw the development of numerous inventions that played crucial roles in shaping the modern world. For instance, the telegraph revolutionized communication, enabling messages to be transmitted across long distances in a matter of seconds. Additionally, the invention of the cotton gin by Eli Whitney revolutionized the cotton industry by dramatically reducing the time and effort required to process cotton, leading to increased cotton production and the expansion of slavery in the United States.
The Industrial Revolution brought forth a myriad of groundbreaking inventions that forever transformed society. Key inventions from this era include the steam engine, which powered factories and locomotives, and the spinning jenny, which revolutionized textile production. The telegraph revolutionized communication, while the Bessemer process drastically improved steel production. Other notable inventions include the sewing machine, the telephone, and the light bulb. These inventions laid the foundation for modern industrial societies and paved the way for technological advancements that continue to shape our world today.
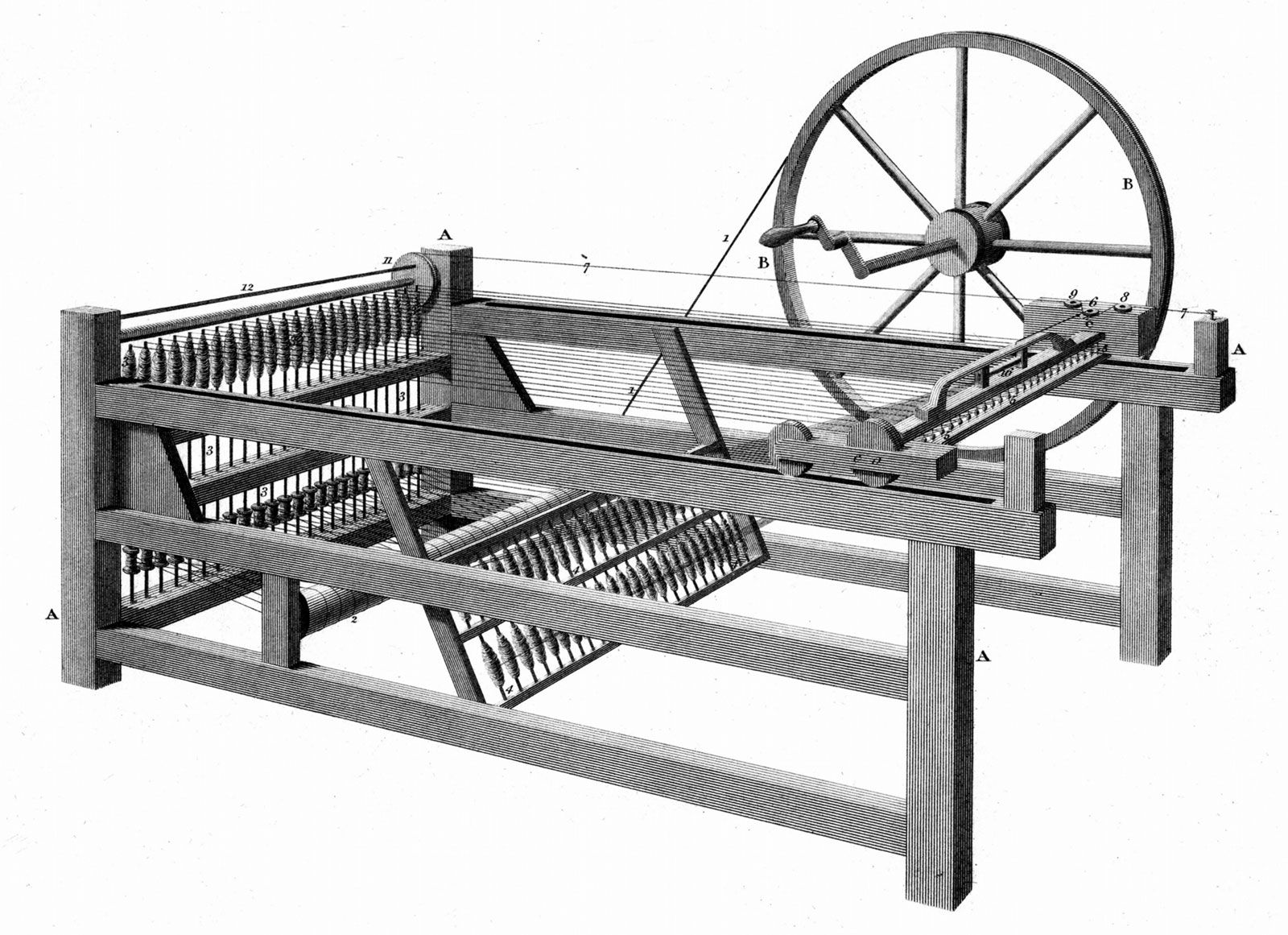
The Impact of Steam Power on the Industrial Revolution
The Industrial Revolution, which took place from the 18th to the 19th century, was a period of significant technological advancements and economic growth. Steam power played a crucial role in driving this revolution, revolutionizing industries and transforming the way people lived and worked. The invention and widespread adoption of steam power opened up new possibilities and set the stage for further innovation. This article explores the inventions made during the Industrial Revolution, with a particular focus on the impact of steam power.
The Steam Engine: Revolutionizing Transportation and Manufacturing
One of the most significant inventions of the Industrial Revolution was the steam engine. Patented by James Watt in 1769, the steam engine revolutionized transportation and manufacturing. Prior to the steam engine, most transportation relied on animal power or wind, limiting the speed and efficiency of travel. With the introduction of steam-powered locomotives and steamships, goods and people could be transported much faster and over longer distances.
The steam engine also had a profound impact on manufacturing. Before its invention, production was primarily done in small workshops using manual labor. The steam engine allowed for the development of large-scale factories where machinery could be powered by steam. This led to a significant increase in production efficiency and output. Steam-powered machinery such as textile looms transformed the textile industry, increasing production rates and reducing costs.
Additionally, the steam engine enabled the development of new industries, such as mining and iron production. Steam engines were used to pump water out of mines, allowing for deeper and more extensive mining operations. The ability to produce iron on a large scale was essential for the construction of machinery, railways, and bridges. The steam engine played a central role in the expansion and modernization of industries during the Industrial Revolution.
The Spinning Jenny and Textile Innovation
In addition to the steam engine, several other inventions had a significant impact on the textile industry. One notable invention was the spinning jenny, developed by James Hargreaves in 1764. The spinning jenny was a multi-spindle spinning frame that allowed a single worker to spin multiple threads at once. This innovation greatly increased productivity in textile manufacturing and played a crucial role in the growth of the cotton industry.
Another notable invention in the textile industry was the power loom, developed by Edmund Cartwright in the late 1780s. The power loom automated the process of weaving, reducing the need for skilled hand weavers and increasing production rates. With the power loom, fabrics could be produced faster and in larger quantities, meeting the growing demand for textiles during the Industrial Revolution.
Furthermore, the cotton gin, invented by Eli Whitney in 1793, revolutionized the cotton industry by mechanizing the process of separating cotton fibers from the seeds. This invention greatly increased the efficiency of cotton processing, making it more profitable and driving the expansion of cotton production.
Transportation Innovations: Canals and Railways
Alongside the development of steam power, significant advancements were made in transportation during the Industrial Revolution. Canals and railways were critical innovations that transformed the movement of goods and people.
Canals played a vital role in connecting different regions, enabling the transportation of goods over long distances. The construction of canals, such as the Bridgewater Canal in England, facilitated the movement of raw materials, finished goods, and coal between industrial areas. Canals provided a cost-effective and efficient mode of transportation, reducing reliance on packed dirt roads or navigable rivers.
The development of rail transport was another significant breakthrough. The first steam-powered locomotive was built by George Stephenson in 1814. Railways greatly improved transportation efficiency, as they were faster, more reliable, and could handle heavier loads compared to canals and horse-drawn wagons. Railways facilitated the growth of industries by providing a reliable means of transporting raw materials and finished goods across the country.
The construction of railways also led to the development of related industries, such as iron and steel production. The demand for rails and locomotives drove advancements in metallurgy and engineering, providing a catalyst for further innovation and industrial growth.
Mechanization and Agricultural Innovations
The Industrial Revolution also saw significant advancements in agriculture through the introduction of mechanization and innovative farming techniques.
The seed drill, invented by Jethro Tull in 1701, revolutionized farming by automating the sowing of seeds. This innovation increased crop yields and reduced the amount of labor required for planting. Combined with improvements in crop rotation techniques, the seed drill played a crucial role in increasing agricultural productivity, supporting the growing population.
Another important agricultural invention was the reaper, developed by Cyrus McCormick in the early 19th century. The reaper mechanized the harvesting of crops, reducing the labor-intensive process and increasing efficiency. This invention allowed farmers to harvest larger quantities of crops in less time, contributing to increased agricultural output.
The invention of the threshing machine by Andrew Meikle in 1784 further improved agricultural productivity. The threshing machine automated the process of separating grain from the chaff, reducing the time and effort required for manual threshing. This innovation enabled farmers to process larger quantities of grain and improved the overall efficiency of harvesting and grain storage.
Other Innovations: Telegraph and Steam-Powered Printing Press
Beyond the steam engine and advancements in transportation and agriculture, the Industrial Revolution also saw the emergence of other significant inventions.
The telegraph, invented by Samuel Morse in the 1830s, revolutionized long-distance communication. The telegraph enabled messages to be transmitted quickly over vast distances using Morse code, making communication more reliable and efficient. This innovation had a profound impact on various industries, including finance, news, and transportation.
Another noteworthy invention was the steam-powered printing press, patented by Friedrich Koenig in 1814. This invention allowed for faster and more efficient printing, reducing the cost and time required for producing printed materials. The steam-powered printing press facilitated the mass production of books, newspapers, and other printed materials, making information more accessible and contributing to the spread of knowledge during the Industrial Revolution.
These various inventions and innovations made during the Industrial Revolution transformed industries, revolutionized transportation and manufacturing, and drove significant economic growth. The impact of steam power, along with other technological advancements, shaped the world we live in today, setting the stage for further advancements in the years to come.
Inventions of the Industrial Revolution
The Industrial Revolution, which took place from the 18th to 19th centuries, was a period of significant technological advancements and innovations. During this time, various inventions were made that revolutionized the manufacturing and transportation industries, ultimately transforming the social and economic landscape of many nations.
- The Steam Engine: One of the most significant inventions of the Industrial Revolution, the steam engine powered machines and locomotives, replacing traditional sources of energy like humans, animals, and water.
- The Spinning Jenny: This invention revolutionized the textile industry by enabling the mass production of yarn, reducing manual labor and increasing efficiency.
- The Cotton Gin: Invented by Eli Whitney, the cotton gin mechanized the process of separating cotton fibers from seeds, leading to a boom in cotton production and the expansion of the slave trade in the American South.
- The Telegraph: Developed by Samuel Morse, the telegraph revolutionized long-distance communication by transmitting coded messages over long distances using electrical signals.
- The Steamboat: Invented by Robert Fulton, the steamboat revolutionized water transportation, making it faster and more efficient, and opening up new opportunities for trade and travel.
These inventions, among many others, played a crucial role in the Industrial Revolution by improving productivity, transforming industries, and paving the way for further advancements. They laid the foundation for modern industrialization and continue to impact our lives today.
Key Takeaways
- The Industrial Revolution saw the emergence of numerous groundbreaking inventions.
- The steam engine revolutionized transportation and powered factories.
- The spinning jenny and power loom revolutionized the textile industry.
- The telegraph and telephone revolutionized communication.
- The light bulb and electric motor transformed daily life and industry.
Frequently Asked Questions
The Industrial Revolution was a period of rapid industrialization, innovation, and technological advancements that occurred in the 18th and 19th centuries. Many significant inventions were made during this time. Here are answers to some frequently asked questions about the inventions of the Industrial Revolution.
1. What was the steam engine and how did it impact the industrial revolution?
The steam engine was one of the most important inventions of the Industrial Revolution. It was first developed by James Watt in the late 18th century. The steam engine revolutionized various industries, especially transportation and manufacturing. It provided an efficient and reliable source of power, replacing manual labor and animal power. The steam engine enabled the development of steamships, railways, and factories, significantly speeding up production and transportation processes.
With the steam engine, goods could be produced and transported on a much larger scale, leading to the mass production and global distribution of goods. It also fueled the rise of the Industrial Revolution and transformed society, leading to urbanization and the growth of industrial cities.
2. What role did the spinning jenny play in the Industrial Revolution?
The spinning jenny was an invention that revolutionized the textile industry during the Industrial Revolution. It was invented by James Hargreaves in the mid-18th century. The spinning jenny allowed a single worker to operate multiple spinning machines, increasing productivity and output. This invention significantly sped up the process of spinning cotton and other fibers, leading to a higher demand for cotton and the growth of the cotton industry.
The spinning jenny played a crucial role in the mechanization of the textile industry, paving the way for further advancements in textile machinery. It led to the development of larger-scale spinning machines, such as the spinning mule and the water frame, further transforming the textile industry and driving the industrialization process.
3. How did the steam-powered locomotive impact transportation during the Industrial Revolution?
The steam-powered locomotive, commonly known as the steam train, had a profound impact on transportation during the Industrial Revolution. The invention of the steam train is credited to George Stephenson in the early 19th century. With the steam train, goods and passengers could be transported over long distances at a much faster speed than ever before.
This revolutionized the transportation industry, making it possible to connect cities and regions more efficiently. The steam train facilitated the expansion of rail networks, enabling the transportation of goods on a larger scale. It also played a crucial role in the growth of urban centers, as it made commuting between cities and the countryside easier, leading to increased migration to industrialized areas.
4. What was the impact of the cotton gin on the cotton industry during the Industrial Revolution?
The cotton gin was a machine that greatly impacted the cotton industry during the Industrial Revolution. It was invented by Eli Whitney in the late 18th century. The cotton gin mechanized the process of removing seeds from cotton fibers, making cotton production faster and more efficient. This invention revolutionized the cotton industry by increasing productivity and reducing the labor-intensive process of separating seeds from cotton manually.
The cotton gin led to a significant increase in cotton production, which fueled the growth of the textile industry. It transformed cotton into a highly profitable crop and played a crucial role in the economic development of regions that depended on cotton production, such as the southern United States. However, it also perpetuated the demand for slave labor in the cotton industry, reinforcing the institution of slavery during this period.
5. How did the Bessemer process revolutionize steel production?
The Bessemer process was a breakthrough innovation in steel production during the Industrial Revolution. It was developed by Henry Bessemer in the mid-19th century. Before the Bessemer process, steel production was costly and time-consuming, requiring skilled labor and extensive manual work. The Bessemer process introduced a new method of producing steel by blowing air through molten iron to remove impurities.
This process greatly increased the production of steel and made it more affordable. It enabled the mass production of steel, which had a wide range of applications in various industries, including construction, railways, and machinery manufacturing. The Bessemer process revolutionized the steel industry and played a crucial role in the development of modern infrastructure and industrialization during the Industrial Revolution.
To sum it up, the Industrial Revolution brought about a multitude of groundbreaking inventions that transformed society and forever changed the way we live. Key inventions during this time included the steam engine, which revolutionized transportation and power generation, and the spinning jenny, which revolutionized the textile industry. These inventions, along with many others like the telegraph, the telephone, and the light bulb, propelled the world into a new era of progress and innovation.
By harnessing the power of steam, inventors and entrepreneurs were able to increase productivity, enhance efficiency, and create new opportunities for economic growth. The Industrial Revolution laid the foundation for the modern industrialized world we live in today, shaping the way we work, communicate, and travel. Although this period brought about immense transformation, it also sparked social and environmental challenges that are still felt to this day. Nonetheless, the inventions made during the Industrial Revolution continue to shape our lives, highlighting the incredible impact that innovation can have on society.