Interchangeable parts revolutionized the manufacturing industry during the Industrial Revolution. Before this innovation, products were often made by skilled craftsmen who would individually create each part. However, with the introduction of interchangeable parts, manufacturers could now mass-produce products using standardized components that could be easily replaced or exchanged. This breakthrough had a profound impact on efficiency, productivity, and the overall growth of industry.
The idea of interchangeable parts can be traced back to the late 18th century, with its widespread adoption occurring in the early 19th century. It was Eli Whitney, an American inventor, who is often credited with popularizing the concept. With interchangeable parts, machines and products became easier to assemble and repair, reducing downtime and increasing production rates. This not only transformed manufacturing processes but also paved the way for the development of complex machinery and the expansion of industries such as textiles, firearms, and transportation.
Interchangeable parts in the Industrial Revolution referred to the practice of creating standardized components that could be used in multiple products. This revolutionized manufacturing, allowing for faster production and easier repairs. Eli Whitney is often credited with popularizing interchangeable parts in the late 18th century, particularly in the production of firearms. This breakthrough led to increased efficiency, lower costs, and the mass production of goods, marking a significant milestone in industrialization.

Contents
- The Impact of Interchangeable Parts in the Industrial Revolution
- Conclusion
- Interchangeable Parts in the Industrial Revolution
- Key Takeaways: What Are Interchangeable Parts In The Industrial Revolution?
- Frequently Asked Questions
- 1. What are interchangeable parts?
- 2. How did interchangeable parts impact the Industrial Revolution?
- 3. Who is credited with the invention of interchangeable parts?
- 4. What were the benefits of using interchangeable parts in the Industrial Revolution?
- 5. How did interchangeable parts contribute to the development of modern manufacturing?
- The Invention of Interchangeable Parts 1798
The Impact of Interchangeable Parts in the Industrial Revolution
During the Industrial Revolution, the introduction of interchangeable parts revolutionized manufacturing processes and had a profound impact on various industries. Interchangeable parts are standardized components that are designed to be identical and can fit into any product of the same type. This innovation allowed for the efficient mass production of goods, leading to increased productivity, improved quality, and the development of new industries. In this article, we will explore the significance of interchangeable parts in the Industrial Revolution, their role in the transformation of manufacturing, and their lasting legacy in modern production processes.
The Birth of Interchangeable Parts
The concept of interchangeable parts emerged in the late 18th century, primarily attributed to the American inventor Eli Whitney. Whitney is best known for his invention of the cotton gin, but his contribution to the development of interchangeable parts cannot be understated. In 1798, Whitney presented a demonstration to the United States Congress, showcasing a musket he had produced using interchangeable parts. This demonstration marked the beginning of a new era in manufacturing, where the traditional practice of skilled craftsmen meticulously handcrafting every component gave way to a system of standardized parts.
Whitney’s idea of interchangeable parts stemmed from his observation of the inefficiencies in the production of firearms for the U.S. government. Prior to the introduction of interchangeable parts, gunsmiths individually handcrafted each component of a musket, resulting in inconsistencies and slow production rates. Whitney proposed the idea of manufacturing standardized parts that could be easily interchanged, eliminating the need for skilled craftsmen and streamlining the assembly process.
With the support of the U.S. government, Whitney embarked on the ambitious task of producing muskets using interchangeable parts. He built a factory in New Haven, Connecticut, and implemented various manufacturing processes to achieve this goal. Whitney’s success in producing muskets with interchangeable parts not only transformed the firearms industry but also set a precedent for other industries to adopt this efficient production method.
The Advantages of Interchangeable Parts
The introduction of interchangeable parts brought several advantages to the manufacturing process during the Industrial Revolution:
- Increased Efficiency: With standardized parts, manufacturers could produce goods at a faster rate, reducing the time and labor required for assembly.
- Improved Quality: Interchangeable parts allowed for greater precision and accuracy in manufacturing, resulting in products with consistent quality.
- Easier Repair and Maintenance: If a component broke or malfunctioned, it could be easily replaced with a new interchangeable part, simplifying the repair process.
- Cost-Effective Production: The mass production of interchangeable parts reduced production costs, making products more affordable and accessible to a wider consumer base.
Impact on Manufacturing Processes
The adoption of interchangeable parts revolutionized manufacturing processes in various ways:
1. Increased Specialization: With the standardization of parts, manufacturers could allocate specialized workers to specific tasks, leading to increased efficiency and productivity. Each worker could focus on producing a particular component, optimizing their skills and reducing production time.
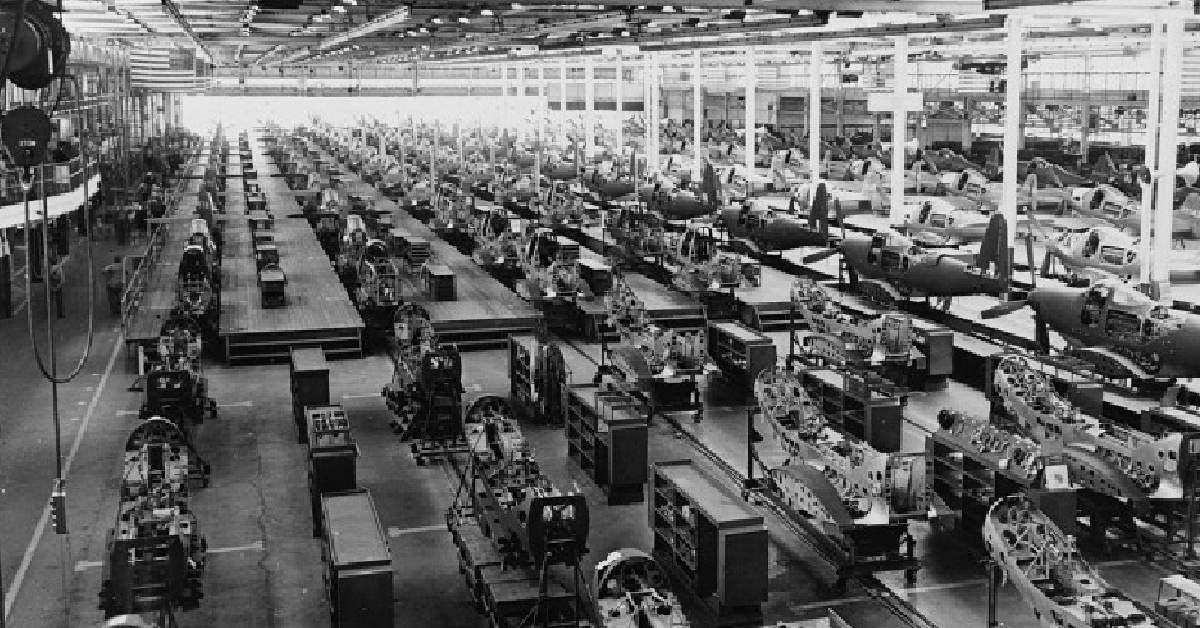
2. Assembly Line Production: The concept of interchangeable parts laid the foundation for the assembly line production system. Henry Ford, the pioneer of mass production, applied the principles of interchangeable parts to his automobile factory, creating a highly efficient assembly line where workers would specialize in specific tasks and seamlessly interchange standardized components.
3. Scalability: Interchangeable parts enabled manufacturers to scale up their production to meet the growing demands of the market. With standardized parts readily available, it became easier to increase production volumes without compromising quality or efficiency.
Expansion of Industries
The introduction of interchangeable parts paved the way for the expansion of various industries:
1. Textile Industry: The textile industry greatly benefited from the use of interchangeable parts, particularly in the production of spinning machines and looms. Standardized components allowed textile manufacturers to increase production capacity, leading to the growth of the industry.
2. Transportation Industry: The implementation of interchangeable parts in the manufacturing of automobiles, trains, and ships revolutionized the transportation industry. It allowed for the mass production of vehicles and the development of intricate systems that could be easily repaired and maintained.
3. Machinery and Equipment Manufacturing: Interchangeable parts played a significant role in the growth of machinery and equipment manufacturing industries. Manufacturers could produce machinery and equipment more efficiently, leading to advancements in agriculture, mining, and construction.
The Legacy of Interchangeable Parts
The influence of interchangeable parts in the Industrial Revolution extends far beyond that time period:
1. Modern Manufacturing Processes: The principles of interchangeable parts laid the foundation for modern manufacturing processes. Standardization, specialization, and assembly line production are still fundamental aspects of today’s mass production systems.
2. Technological Advancements: The development of interchangeable parts facilitated technological advancements in various industries. Advancements in precision engineering and automation have further improved the efficiency and quality of production processes.
3. Global Economy: The mass production of goods made possible by interchangeable parts transformed the global economy. It fueled economic growth, enabled mass consumption, and paved the way for the rise of consumer culture.
Continued Relevance
Interchangeable parts continue to be an essential element of manufacturing in various industries:
1. Automotive Industry: The automotive industry heavily relies on interchangeable parts for efficient production and maintenance. Manufacturers continue to produce standardized components that can be easily replaced, ensuring the longevity and accessibility of vehicle maintenance and repair.
2. Consumer Electronics: The production of consumer electronics, such as smartphones and laptops, relies on interchangeable parts. This enables manufacturers to quickly repair and replace components, enhancing the user experience and extending the lifespan of electronic devices.
3. Aerospace Industry: The aerospace industry relies on the use of interchangeable parts to ensure the safety and reliability of aircraft. Standardized components allow for simplified maintenance and replacement, crucial in the highly regulated and safety-conscious aviation sector.
Conclusion
The advent of interchangeable parts in the Industrial Revolution revolutionized manufacturing processes and had a profound impact on various industries. Eli Whitney’s introduction of standardized components paved the way for increased efficiency, improved quality, and the expansion of industries. The principles of interchangeable parts continue to shape modern manufacturing processes, driving technological advancements and contributing to the global economy. The legacy of interchangeable parts remains evident in the automotive, consumer electronics, and aerospace industries, where standardization and interchangeability are crucial elements of production and maintenance. Interchangeable parts are a testament to the enduring impact of innovation in manufacturing and stand as a testament to the transformative power of ideas.
Interchangeable Parts in the Industrial Revolution
In the Industrial Revolution, the development of interchangeable parts revolutionized manufacturing processes, leading to increased efficiency and standardization. Interchangeable parts are components of a product that are designed to be identical and replaceable, allowing for easy assembly and repair.
Prior to the Industrial Revolution, products were often handmade or custom-made, resulting in time-consuming and costly production processes. With the introduction of interchangeable parts, manufacturers could now produce goods more quickly and at a lower cost. This development was particularly significant in industries such as textiles, firearms, and machinery.
The use of interchangeable parts also led to the rise of mass production, as it allowed for the assembly of products using standardized components. This enabled manufacturers to scale up production and meet the growing demand during the Industrial Revolution.
Furthermore, interchangeable parts facilitated easier repair and maintenance of products. If a component broke or malfunctioned, it could be easily replaced with a new one, eliminating the need to repair the entire product.
In conclusion, interchangeable parts played a crucial role in the Industrial Revolution by improving manufacturing processes, enabling mass production, and facilitating repair and maintenance. This innovation continues to shape modern manufacturing practices and has become a standard in various industries.
Key Takeaways: What Are Interchangeable Parts In The Industrial Revolution?
- Interchangeable parts were identical components that could be used in multiple products.
- They revolutionized manufacturing by allowing for faster production and easier assembly.
- Eli Whitney is often credited with popularizing interchangeable parts in the late 18th century.
- Interchangeable parts increased efficiency, reduced costs, and made repairs and replacements easier.
- The use of interchangeable parts played a crucial role in the development of mass production during the Industrial Revolution.
Frequently Asked Questions
In the Industrial Revolution, interchangeable parts played a significant role in revolutionizing manufacturing processes. They allowed for the mass production of goods and the assembly line production system. Here are some frequently asked questions about interchangeable parts in the Industrial Revolution:
1. What are interchangeable parts?
Interchangeable parts are components that are designed to be exactly identical to one another, allowing them to be easily fitted into any product without the need for customization or adjustment. They are made using standardized specifications, ensuring that each part fits interchangeably with other parts of the same type.
Before the advent of interchangeable parts, products were mostly handmade, and each component had to be individually crafted and customized to fit into a specific product. This made production slow and expensive. Interchangeable parts brought about a revolutionary change by enabling the efficient mass production of goods.
2. How did interchangeable parts impact the Industrial Revolution?
Interchangeable parts revolutionized manufacturing in the Industrial Revolution by introducing the concept of standardization. This meant that parts could be produced in large quantities and stored as inventory, ready to be quickly assembled into finished products. It significantly reduced the time, effort, and cost involved in producing goods.
The introduction of interchangeable parts also facilitated the development of the assembly line production system. This system allowed for the efficient division of labor, where each worker would focus on a specific task, such as assembling a particular component. As a result, production became faster, more consistent, and less reliant on skilled craftsmen.
3. Who is credited with the invention of interchangeable parts?
Eli Whitney is often credited with popularizing the concept of interchangeable parts. In the late 18th century, Whitney introduced the idea of manufacturing firearms with standardized, interchangeable components. He successfully showcased this concept to the United States government in the form of muskets, which greatly impressed officials and led to widespread adoption of interchangeable parts in various industries.
However, it is important to note that the concept of interchangeable parts had been explored by others before Whitney. For example, French engineer Honoré Le Blanc developed a method for manufacturing interchangeable gun parts in the 18th century, and the concept can be traced back even further to ancient civilizations.
4. What were the benefits of using interchangeable parts in the Industrial Revolution?
The use of interchangeable parts brought several benefits during the Industrial Revolution:
1. Increased Efficiency: With standardized parts, manufacturing processes became more efficient, as workers could quickly assemble products without the need for customization or adjustments.
2. Mass Production: Interchangeable parts allowed for the mass production of goods, making products more affordable and accessible to a larger population.
3. Ease of Repair: The use of interchangeable parts made it easier to repair and replace components, reducing downtime and improving the longevity of products.
4. Scalability: The concept of interchangeable parts made it possible to scale up production and meet increasing demand without compromising quality or efficiency.
5. How did interchangeable parts contribute to the development of modern manufacturing?
The concept of interchangeable parts introduced in the Industrial Revolution laid the foundation for modern manufacturing practices. It paved the way for automation, standardization, and the concept of mass production. Today, interchangeable parts and assembly line production systems are still widely used across various industries, allowing for efficient, cost-effective, and scalable production.
The Invention of Interchangeable Parts 1798
In conclusion, interchangeable parts were a revolutionary concept during the Industrial Revolution. They allowed for mass production, improved efficiency, and reduced costs in manufacturing. This innovation transformed the way products were made, leading to significant advancements in various industries.
By producing standardized parts that could be easily replaced, manufacturers eliminated the need for custom-made pieces and reduced the time required for repairs. This not only increased productivity but also spurred innovation, as designers and engineers could focus on improving specific components rather than creating entirely new objects.