The Industrial Revolution, one of the most significant periods in history, brought about immense changes in society and the economy. It revolutionized manufacturing, transportation, and communication, transforming the world into what we know today. But was this revolution ultimately a force for good or bad?
During the Industrial Revolution, technological advancements led to increased production and efficiency, improving the standard of living for some and creating new job opportunities. However, it also brought about harsh working conditions, exploitation of workers, and severe environmental consequences. Balancing the positive and negative impacts of this era is crucial in assessing whether the Industrial Revolution was a blessing or a curse.
The Industrial Revolution had both positive and negative impacts. On the positive side, it brought about significant advancements in technology, increased production efficiency, and improved living standards for many. However, it also led to harsh working conditions, child labor, environmental degradation, and widened the gap between the rich and the poor. It is important to recognize the benefits while also acknowledging the negative consequences of this transformative period in history.
Contents
- The Economic Impact of the Industrial Revolution
- The Social and Cultural Impact of the Industrial Revolution
- The Impact of the Industrial Revolution
- Key Takeaways – Was The Industrial Revolution Good Or Bad?
- Frequently Asked Questions
- 1. How did the Industrial Revolution affect the working class?
- 2. What were the environmental consequences of the Industrial Revolution?
- 3. Did the Industrial Revolution improve overall living conditions?
- 4. How did the Industrial Revolution impact technological advancements?
- 5. What were the long-term economic effects of the Industrial Revolution?
- The Industrial Revolution (18-19th Century)
The Economic Impact of the Industrial Revolution
The Industrial Revolution, which spanned the late 18th and early 19th centuries, marked a significant shift in the history of human civilization. It was a period characterized by the transition from an agrarian economy to one dominated by industrial manufacturing. The effects of the Industrial Revolution on society, economy, and the environment have been a subject of debate for many years. One unique aspect to consider when evaluating the impact of the Industrial Revolution is its economic consequences.
1. Economic Growth and Increased Production
An undeniable positive aspect of the Industrial Revolution was the significant economic growth and increased production it brought about. With the advent of new technologies, such as steam power and machinery, industries experienced a surge in productivity. Mass production became possible, leading to an abundance of goods and increased wealth. This economic growth expanded markets and trade, creating new employment opportunities for millions of people.
Additionally, the Industrial Revolution transformed agriculture through mechanization and advancements in farming techniques. This resulted in increased food production, which in turn catered to the growing population’s needs. The surplus food production allowed for urbanization and the concentration of labor in factories.
The economic growth brought about by the Industrial Revolution laid the foundation for the capitalist systems we see today. It created a wealthier society and contributed to the rise of the middle class, leading to higher living standards for many. Moreover, the increased production led to technological advancements and further innovation, setting the stage for future economic development.
a. Expansion of Industries
The Industrial Revolution saw a dramatic expansion of industries across various sectors. Textile manufacturing, iron and steel production, coal mining, and transportation underwent significant growth during this period. These industries became vital components of the economy and propelled economic progress. The development of factories and mass production methods led to the establishment of industrial hubs, generating employment opportunities that attracted workers from rural areas.
The expanded industries also created demand for raw materials, leading to increased mining and agriculture activities. This, in turn, stimulated further economic growth and specialization. The expansion of industries contributed to the growth of cities, leading to urbanization and the formation of vibrant urban centers. As a result, the Industrial Revolution set the stage for the growth of modern urban economies and the emergence of urban culture and lifestyle.
b. Technological Advancements
The Industrial Revolution brought about significant technological advancements, revolutionizing the way goods were produced. Innovations such as the steam engine, spinning jenny, and power loom transformed the production processes, increasing efficiency and output. This led to the development of new industries and the expansion of existing ones. The rise of the factory system allowed for better organization and specialization of labor, further boosting productivity.
Technological advancements also extended to transportation and communication. The invention of the steam-powered locomotive and steamship revolutionized transportation, making it faster, more reliable, and cost-effective. This facilitated the movement of goods and people over long distances, linking markets and creating broader economic networks. The telegraph, another significant invention of the time, revolutionized communication by enabling faster transmission of information.
These technological advancements not only transformed industries but also drove economic growth by enabling the efficient utilization of resources and increasing production capabilities. They laid the groundwork for future advancements and innovations, setting the stage for modern industrialization.
c. Wealth Creation and Trade
The Industrial Revolution brought about a significant increase in wealth creation and international trade. As industries expanded, more wealth was generated, leading to an increase in the overall affluence of society. The growth of factories and industrial centers created new business opportunities and jobs, enabling individuals to accumulate wealth.
Furthermore, the Industrial Revolution led to increased international trade. The expansion of industries and advancements in transportation allowed for the movement of goods on a global scale. Countries engaged in economic specialization, focusing on producing goods in which they had a comparative advantage. This specialization led to increased trade between nations and the establishment of global supply chains. As a result, economies became more interconnected and dependent on each other, fostering economic growth and prosperity.
The economic gains from increased wealth creation and international trade laid the foundation for the modern global economy. The Industrial Revolution propelled economic progress and set the stage for further advancements in technology, trade, and prosperity.
2. Social Impact and Labor Conditions
While the Industrial Revolution brought economic growth and prosperity, it also had profound social implications. The shift from an agrarian economy to an industrial one led to a fundamental transformation in the structure of society and the nature of work.
As industries boomed, urbanization increased, and rural communities faced significant changes. People flocked to cities in search of employment opportunities in the growing industries. This rapid urbanization led to overcrowded and unsanitary living conditions in urban slums. The lack of infrastructure and social services in these areas resulted in health issues, poor hygiene, and increased crime rates.
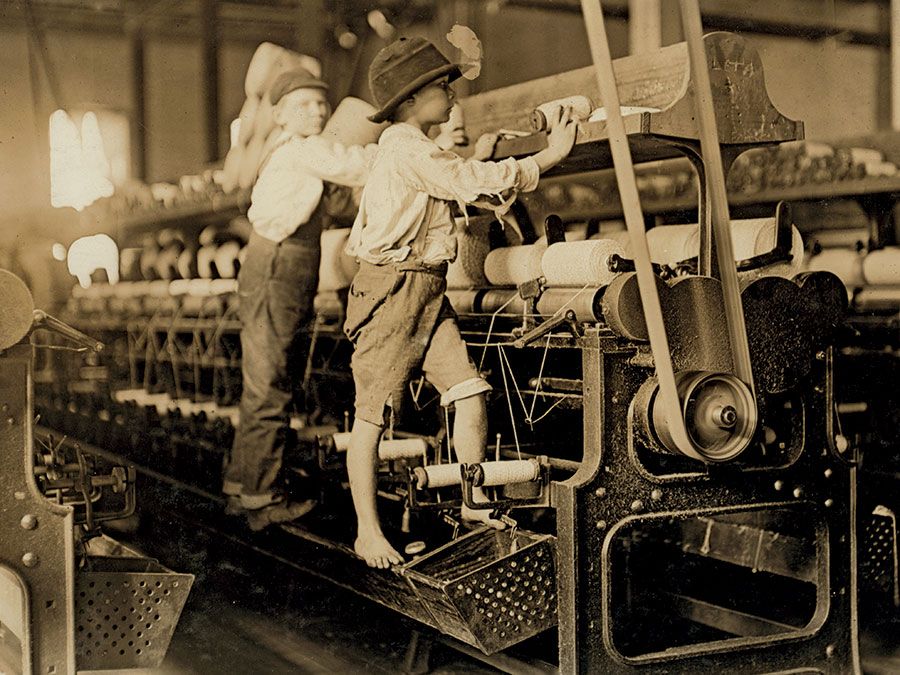
The working conditions in factories and mines during the Industrial Revolution were often harsh and unsafe. Workers, including women and children, were subjected to long hours, low wages, and dangerous working conditions. The lack of labor regulations and the desire for maximum profitability led to exploitative practices and limited workers’ rights.
However, it is important to note that the labor conditions and social issues of the time were not solely a result of industrialization but also reflected societal and economic realities. The Industrial Revolution exposed and exacerbated pre-existing inequalities and flaws in the socio-economic system.
a. Labor Movement and Workers’ Rights
The harsh working conditions during the Industrial Revolution fueled the emergence of the labor movement and the fight for workers’ rights. Workers began organizing and advocating for better working conditions, higher wages, and shorter workdays. Trade unions were formed to collectively bargain with employers and address the concerns of workers.
Over time, these movements led to significant reforms in labor laws and improved working conditions. Legislations were enacted to regulate working hours, establish minimum wages, and provide safer working environments. This shift in labor dynamics laid the groundwork for the modern labor movement and the rights of workers we see today.
b. Social Changes and Living Standards
Despite the social challenges during the Industrial Revolution, it also brought about significant social changes and improvements in living standards. The expansion of industries and increased productivity led to an overall rise in living standards for many individuals. Consumers had access to a wider variety of goods at more affordable prices.
Moreover, the development of urban centers fostered the growth of cultural institutions, educational opportunities, and social reforms. The emergence of a middle class created social mobility and provided opportunities for upward economic mobility. The Industrial Revolution paved the way for social progress, challenging traditional hierarchies and contributing to the development of modern societies.
c. Gender and Class Divide
The Industrial Revolution also deepened existing gender and class divides. Women and children were often subjected to harsh working conditions and long hours in factories. The division of labor led to a further separation between the public sphere dominated by men and the private sphere associated with women’s roles. The industrial workforce was segregated, with men occupying higher-paying and more skilled positions.
However, the Industrial Revolution also provided avenues for challenging gender norms and advocating for women’s rights. Women played a crucial role in the labor force, contributing to the economic growth of society. This eventually paved the way for the women’s suffrage movement and the fight for gender equality in the following centuries.
3. Environmental Impact and Sustainability
The rapid industrialization during the Industrial Revolution had significant environmental consequences. The shift to steam power and coal as the primary source of energy led to increased pollution and deforestation.
Coal was burned on a large scale, releasing substantial amounts of greenhouse gases and pollutants into the atmosphere. This resulted in air pollution and a decline in air quality in urban areas. The emissions of sulfur dioxide from burning coal contributed to acid rain, causing damage to ecosystems and further degradation of the environment.
Moreover, industrial processes utilized large amounts of natural resources and raw materials, leading to depletion and overexploitation of natural resources. Forests were cleared to make way for industrial activities and to provide wood for fuel and construction.
However, it is important to note that the environmental impact of the Industrial Revolution was not fully understood at the time. The focus was primarily on economic growth and technological advancement, with little consideration for sustainability and environmental conservation.
a. Conservation Movements
The environmental consequences of the Industrial Revolution paved the way for the emergence of conservation movements and the recognition of the importance of protecting the natural environment. Later generations realized the need for sustainable practices and the preservation of natural resources.
Throughout history, environmental movements have advocated for the conservation of nature and the adoption of policies that promote sustainable development. The lessons learned from the environmental impact of the Industrial Revolution have shaped modern environmental regulations and practices.
b. Technological Advancements and Sustainable Solutions
While the Industrial Revolution had negative environmental impacts, it also spurred technological advancements that paved the way for sustainable solutions. As the world became more aware of the consequences of industrialization, efforts were made to develop cleaner technologies and renewable energy sources.
Today, renewable energy sources, such as solar and wind power, are increasingly being used as alternatives to coal and other fossil fuels. Additionally, innovations in manufacturing processes and waste management have improved resource efficiency and reduced the environmental footprint of industries.
The environmental challenges faced during the Industrial Revolution have highlighted the importance of sustainable development and the need to balance economic growth with environmental stewardship.
The Social and Cultural Impact of the Industrial Revolution
Another dimension to consider when evaluating the impact of the Industrial Revolution is its social and cultural consequences. This transformative period led to profound changes in society, reshaping social structures, modes of production, and cultural norms.
1. Social Transformation and Class Divide
The Industrial Revolution brought about a significant social transformation. Traditional social hierarchies were challenged as societies shifted from rural agrarian communities to industrial urban centers. The development of factories and the rise of industrial capitalism led to the emergence of a new middle class and the consolidation of a working class.
The class divide became more pronounced, with stark disparities between the wealthy industrialists and the working-class population. The capitalist system rewarded the owners of capital, leading to the accumulation of wealth and power in the hands of a few, while the working class faced economic inequality and exploitation.
However, it is also important to note that the Industrial Revolution brought about social mobility for some individuals. The emergence of industrial economies provided opportunities for upward economic mobility, allowing individuals to transcend their social classes.
a. Urbanization and Changing Lifestyles
The rapid urbanization during the Industrial Revolution led to significant changes in lifestyle and social dynamics. As people migrated to cities in search of employment opportunities, urban centers became overcrowded, resulting in cramped living conditions and the proliferation of slums.
Despite the challenging living conditions, cities also became hubs for cultural and intellectual activities. The concentration of people in urban areas fostered the exchange of ideas and the development of new cultural and artistic movements. The growth of industries and trade created a more interconnected and cosmopolitan society.
Urbanization also brought about advancements in infrastructure and public services. Cities began investing in public transportation systems, sanitation, and the construction of public spaces. These developments improved the quality of life for urban dwellers and further facilitated social interactions.
b. Social Reform Movements
The social issues and inequalities arising from the Industrial Revolution sparked various social reform movements. Activists and reformers sought to address the negative consequences of industrialization and advocate for social justice.
Reform movements emerged to address issues such as workers’ rights, child labor, women’s suffrage, and education reform. These movements laid the groundwork for significant social changes and the establishment of legal protections for workers and marginalized groups. The fight for social justice and equality continues to shape society to this day.
c. Intellectual and Artistic Movements
The Industrial Revolution brought about significant intellectual and artistic movements, challenging traditional modes of thinking and artistic expression. The exchange of ideas in urban centers fostered cultural and intellectual development.
The Romantic movement, for example, emerged as a response to the transformations brought about by industrialization. Romantic artists, writers, and thinkers criticized the effects of industrialization on nature, human relationships, and the individual. They emphasized the importance of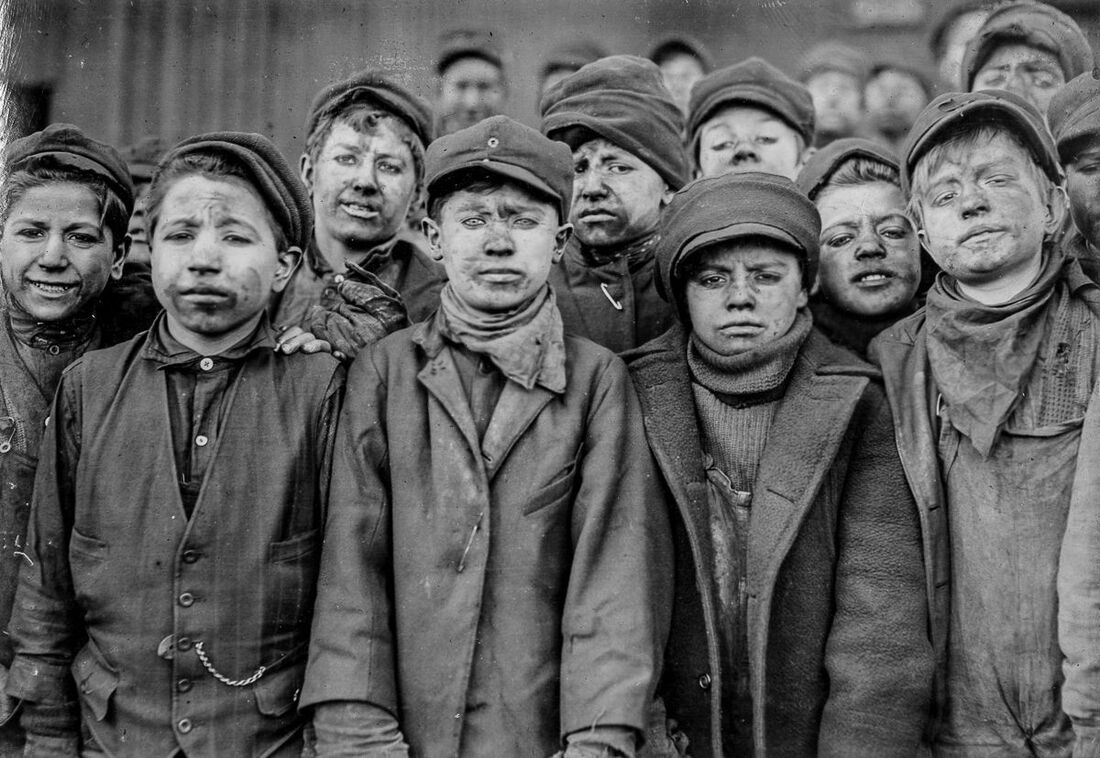
The Impact of the Industrial Revolution
The Industrial Revolution, which spanned from the late 18th to the early 19th century, had profound consequences for society, economy, and environment. It marked a shift from agrarian to industrial economies, initiating waves of technological advancements and urbanization.
The Industrial Revolution brought both positive and negative outcomes. On one hand, it led to significant economic growth, increased productivity, and improved living standards for some. It created job opportunities and enhanced access to goods and services. The development of factories also propelled scientific and technological advancements, paving the way for modern innovation and progress.
However, the Industrial Revolution also had adverse effects. Rapid industrialization exploited workers, leading to harsh working conditions, long hours, and child labor. The pollution caused by factories and the destruction of natural resources had detrimental impacts on the environment. Social inequality increased as wealth concentrated in the hands of a few, while many endured poverty and exploitation.
In conclusion, the Industrial Revolution brought significant changes and advancements to society. Its positive impacts include economic growth and technological progress, while its negative consequences include exploitation, pollution, and inequality. Evaluating whether it was ultimately good or bad depends on the perspective taken, as it had both advantages and disadvantages for different segments of society.
Key Takeaways – Was The Industrial Revolution Good Or Bad?
- The Industrial Revolution had both positive and negative impacts on society.
- Advancements in technology and industry led to economic growth and increased productivity.
- However, it also led to harsh working conditions and exploitation of workers.
- The Industrial Revolution sparked social and political reforms to address these issues.
- Overall, the Industrial Revolution had a complex impact on society, with both positive and negative consequences.
Frequently Asked Questions
The Industrial Revolution was a pivotal period in history that transformed societies and economies. It brought about significant changes in manufacturing, technology, and the overall way of life. However, it is important to consider the impact of this revolution on different aspects of society. Here are some frequently asked questions about the Industrial Revolution and its implications.
1. How did the Industrial Revolution affect the working class?
The Industrial Revolution had both positive and negative effects on the working class. On one hand, it provided employment opportunities and increased wages for many workers. This led to improved living conditions and a rise in the standard of living for some. However, it also brought long working hours, dangerous working conditions, and child labor for many workers. The exploitation of workers during this period highlighted some of the darker aspects of industrialization.
2. What were the environmental consequences of the Industrial Revolution?
The Industrial Revolution had significant environmental consequences. The rapid industrialization led to increased pollution and degradation of natural resources. Factories emitted harmful pollutants, such as smoke and chemicals, which polluted the air and water. Deforestation also occurred on a large scale to meet the growing demand for resources. These environmental impacts had long-lasting effects on ecosystems and continue to be a concern even today.
3. Did the Industrial Revolution improve overall living conditions?
The Industrial Revolution brought about improvements in overall living conditions, but these were not distributed evenly. While some individuals and communities experienced economic growth and improved standards of living, others faced dismal living conditions and poverty. The divide between the rich and the poor widened, leading to social inequalities and disparities. Thus, while the Industrial Revolution did lead to progress for some, it also exacerbated existing societal issues.
4. How did the Industrial Revolution impact technological advancements?
The Industrial Revolution was a period of significant technological advancements. It marked the transition from manual labor to machine-based production, leading to the invention of various machines and technologies. These innovations revolutionized industries such as manufacturing, transportation, and communication. The developments in technology during this time laid the foundation for further advancements in the modern era and shaped the world we live in today.
5. What were the long-term economic effects of the Industrial Revolution?
The Industrial Revolution had profound and long-lasting economic effects. It resulted in economic growth, increased productivity, and the expansion of industries. The revolution stimulated trade, created new job opportunities, and boosted the overall economy. However, it also led to the concentration of wealth and power in the hands of a few individuals, contributing to socioeconomic disparities. The economic effects of the Industrial Revolution continue to influence global economies to this day.
The Industrial Revolution (18-19th Century)
In conclusion, the Industrial Revolution had both positive and negative impacts. On one hand, it brought about significant advancements in technology, increased production and improved the standard of living for many people. It led to the creation of new industries, job opportunities, and a boost in economic growth. The Industrial Revolution also paved the way for modernization and innovation, driving progress in various fields such as transportation, communication, and medicine.
However, the Industrial Revolution also had its drawbacks. The working conditions during this time were often harsh and dangerous, with long hours, low wages, and poor living conditions for many workers. It contributed to inequality, as a small group of wealthy industrialists profited immensely while the majority of the population faced hardships and exploitation. Additionally, the rapid industrialization resulted in environmental degradation and pollution, leading to negative consequences for our planet. In evaluating the overall impact of the Industrial Revolution, it is important to consider and address both the positive advancements and the negative consequences that emerged as a result.