The Byzantine Empire, known for its rich history and cultural achievements, was also a powerhouse when it came to wealth. One fascinating aspect of the empire’s riches is its gold reserves. Did you know that the Byzantine Empire amassed such a vast amount of gold that it became the envy of the world? This immense wealth played a significant role in shaping the empire’s power and influence during its existence.
The Byzantine Empire’s wealth can be attributed to various factors. Firstly, its strategic location at the crossroads of Europe and Asia made it a hub of trade, enabling the empire to accumulate tremendous wealth through commerce and taxation. Additionally, the empire controlled lucrative trade routes, such as the Silk Road, further boosting its economic prosperity. Furthermore, the Byzantines had developed a sophisticated bureaucracy and efficient taxation system, allowing them to generate substantial revenue. As a result, the Byzantine Empire was not only culturally and militarily influential but also incredibly affluent, making it one of the wealthiest empires in history.
The Byzantine Empire was incredibly wealthy and prosperous. It had a robust economy backed by constant trade routes that connected Europe, Asia, and Africa. Its wealth was derived from various sources, including agriculture, trade, and taxation. The empire controlled valuable trade routes, such as the Silk Road, and benefited from its strategic location between Europe and Asia. Additionally, it had a significant revenue stream from taxes imposed on its vast territory. The empire’s wealth can be observed through its magnificent architectural wonders, impressive art and mosaics, and luxurious lifestyle of its nobility.
Contents
- Economy of the Byzantine Empire: A Tale of Wealth and Prosperity
- The Wealth of the Byzantine Empire
- Key Takeaways
- Frequently Asked Questions
- 1. How did the Byzantine Empire accumulate its wealth?
- 2. What were some of the key economic activities of the Byzantine Empire?
- 3. How did the Byzantine Empire’s wealth compare to other medieval empires?
- 4. How did the wealth of the Byzantine Empire impact its society?
- 5. What were some challenges to the wealth of the Byzantine Empire?
- The rise and fall of the Byzantine Empire – Leonora Neville
Economy of the Byzantine Empire: A Tale of Wealth and Prosperity
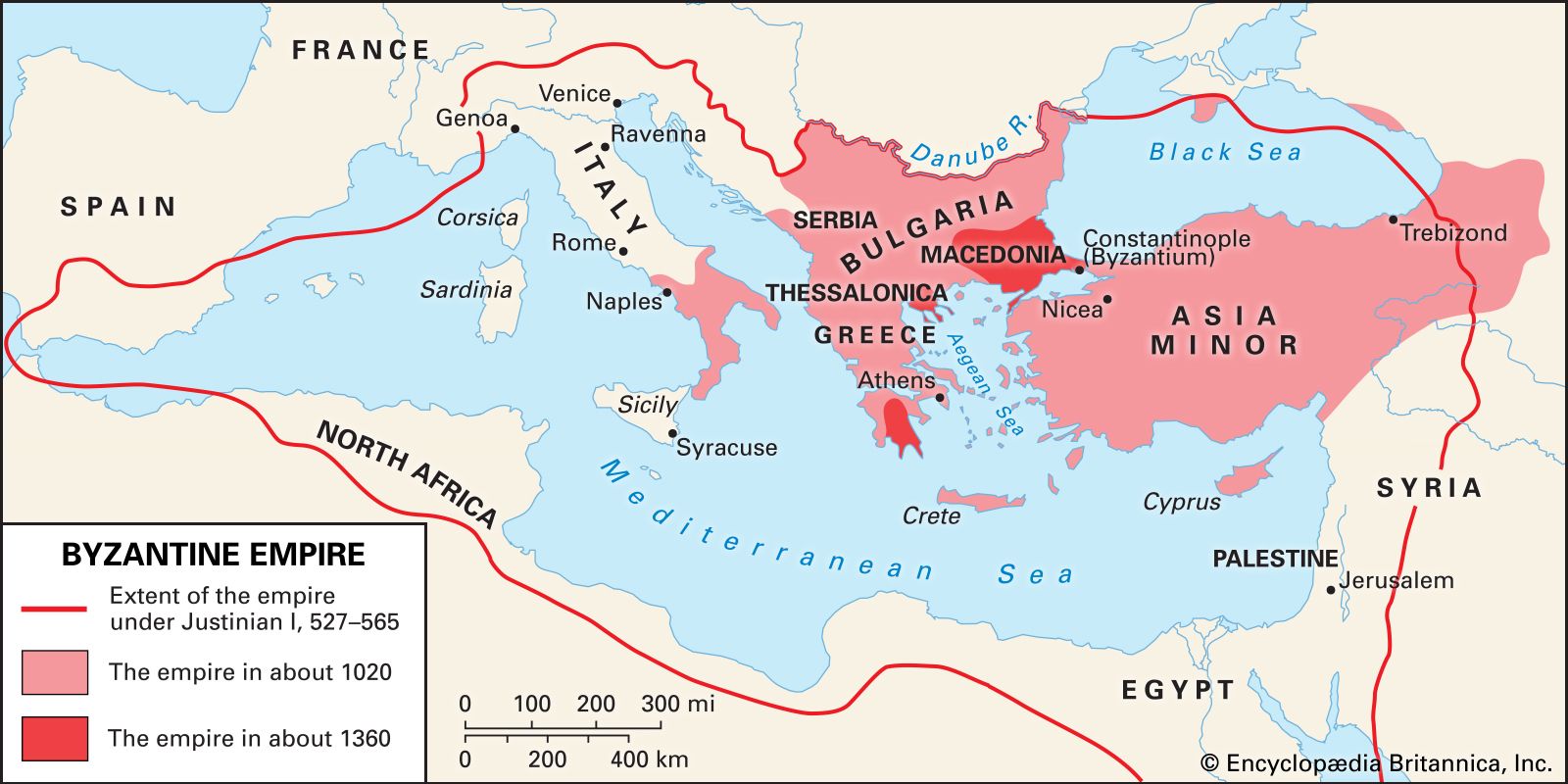
The Byzantine Empire, also known as the Eastern Roman Empire, was one of the most prosperous and influential civilizations in history. Spanning over a thousand years, from the 4th century AD to the 15th century AD, the Byzantines managed to build a vast and wealthy empire that encompassed the Eastern Mediterranean, parts of Europe, and even extended its influence into the Middle East. The wealth of the Byzantine Empire was derived from various sources, including trade, agriculture, taxation, and control over strategic resources such as gold mines. Let us delve into the details of how rich the Byzantine Empire truly was and the factors that contributed to its wealth and prosperity.
Trade and Commerce: A Gateway to Prosperity
One of the key factors that contributed to the wealth of the Byzantine Empire was its strategic location as a gateway between Europe and Asia. Situated at the crossroads of major trade routes, the empire served as a hub for the exchange of goods and ideas. The Byzantines controlled vital trade routes such as the Silk Road, connecting Europe with the Far East, which allowed them to capitalize on the lucrative spice and silk trades. They also had a monopoly on the trade of luxury goods, such as precious metals, gems, and silk, which further boosted their wealth.
The strength of the Byzantine navy also played a crucial role in facilitating trade and protecting merchant vessels from piracy. The Empire established a powerful fleet known as the Byzantine Navy, which ensured the safe passage of goods and fostered maritime trade. This maritime dominance allowed the Byzantines to control trade in the Mediterranean, giving them a significant advantage in terms of wealth accumulation.
Furthermore, the Byzantines developed a sophisticated financial system that facilitated international trade. They introduced a stable currency, the gold solidus, which became the standard medium of exchange in the medieval Mediterranean. The solidus was widely accepted and recognized for its purity, ensuring the confidence of traders and facilitating commerce across borders.
Agrarian Economy: The Foundation of Byzantine Wealth
Despite their strong focus on trade, agriculture served as the backbone of the Byzantine economy. The empire had vast fertile lands, allowing for the cultivation of a wide variety of crops. Byzantine farmers utilized advanced irrigation techniques and crop rotation methods to maximize agricultural output. The rich soil and favorable climate of the Byzantine Empire contributed to high crop yields, ensuring a steady supply of food and raw materials.
The Byzantines were known for their production of staple crops such as wheat, barley, grapes, and olives. These crops not only provided sustenance for the empire’s population but also formed the basis of its thriving export industry. Byzantine agricultural products were highly sought after in international markets, bolstering the empire’s trade revenue and overall wealth.
In addition to crop cultivation, the Byzantine Empire was renowned for its expertise in sericulture, the production of silk. Byzantine sericulture became a highly profitable industry, with the empire monopolizing the silk trade for centuries. The Byzantines innovated silk production techniques, enhancing the quality and quantity of silk production. This valuable commodity further contributed to the empire’s economic prosperity.
Taxation and Administrative Policies: Extracting Wealth from the Empire
The Byzantine Empire implemented an effective taxation system to finance its expansive bureaucracy and military endeavors. The collection of taxes was a well-organized process, with each region having designated tax collectors. The empire imposed various taxes, including land taxes, import and export duties, and taxes on commercial transactions and professions.
The Byzantine government also controlled important industries, such as mining and manufacturing, which generated significant revenue. Gold and silver mines were a crucial source of wealth for the empire, as they provided the precious metals used to mint coins and create ornate jewelry for the elite. The Byzantines also possessed skilled craftsmen who produced luxury goods, including fine textiles, ceramics, and glassware, which were highly valued commodities.
Additionally, the empire levied tribute and imposed tariffs on conquered territories, further bolstering its economic resources. These administrative policies allowed the Byzantines to accumulate vast amounts of wealth and maintain their affluent lifestyle.
Infrastructure and Urban Development: Symbols of Wealth
The Byzantines invested heavily in infrastructure and urban development, leaving behind magnificent architectural wonders that showcased their wealth and power. The construction of grand structures such as cathedrals, palaces, and fortifications required massive financial resources, which the Byzantine Empire possessed in abundance.
Constantinople, the capital of the Byzantine Empire, was renowned for its opulence and urban planning. The city was adorned with majestic structures such as the Hagia Sophia, the Hippodrome, and the Great Palace of Constantinople. These architectural marvels served as a testament to the empire’s prosperity and aesthetic achievements.
The Byzantines also developed an extensive network of roads, aqueducts, and bridges, which facilitated trade, communication, and the movement of armies. This infrastructure not only enhanced the empire’s economic activities but also showcased its advanced engineering knowledge.
The Fall of the Byzantine Empire: A Wealth Diminished
Despite its remarkable wealth, the Byzantine Empire faced numerous challenges that ultimately led to its decline and fall. The Fourth Crusade in 1204 dealt a severe blow to Byzantine wealth, as Constantinople was sacked, and countless treasures were looted. The empire never fully recovered from this devastating event and was further weakened by internal conflicts, invasions by the Ottoman Turks, and the rise of other competing powers.
By the time of the fall of Constantinople in 1453, the once-mighty Byzantine Empire was a mere shadow of its former grandeur. Its wealth had dwindled, its economy ravaged, and its territories reduced to a fraction of what they once were. The era of Byzantine opulence had come to an end.
Although the Byzantine Empire’s wealth may have diminished over time, its legacy remains a testament to the incredible economic achievements and cultural contributions of this remarkable civilization.
The Wealth of the Byzantine Empire
The Byzantine Empire, which existed from the 4th to the 15th century, was known for its immense wealth and prosperity. As a major center of trade and commerce, the empire thrived economically and accumulated vast riches.
One of the main sources of the empire’s wealth was its control over key trade routes. Located at the crossroads between Europe and Asia, the Byzantines enjoyed a strategic position that allowed them to dominate lucrative trade networks. They collected customs duties, tolls, and taxes from the merchants passing through their territories, generating significant revenue.
The Byzantine Empire was also known for its advanced economy and strong financial institutions. The empire minted its own currency, the solidus, which was widely recognized as a stable and reliable means of exchange. Byzantine bankers, known as argentarii, facilitated international financial transactions and set the foundation for modern banking practices.
The empire’s wealth was further bolstered by its control over valuable resources and productive agricultural lands. The Byzantines had access to abundant reserves of gold, silver, and precious stones, as well as fertile lands that supported a flourishing agricultural sector.
Key Takeaways
- The Byzantine Empire was one of the wealthiest and most prosperous civilizations in history.
- Its wealth was built on a strong economy, extensive trade networks, and a strategic location.
- The empire was known for its production of luxury goods, such as silk, gold, and spices.
- Constantinople, the capital of the Byzantine Empire, was a major center of commerce and attracted merchants from all over the world.
- The Byzantine Empire’s wealth was also reflected in its impressive architecture and infrastructure.
Frequently Asked Questions
The Byzantine Empire was renowned for its wealth and prosperity. As a prominent economic and political center in the Middle Ages, it amassed vast riches through trade, taxation, and control of valuable resources. Here are some frequently asked questions about the wealth and prosperity of the Byzantine Empire.
1. How did the Byzantine Empire accumulate its wealth?
The wealth of the Byzantine Empire was derived from a combination of factors. Firstly, it had control over important trade routes, connecting the East and the West. This allowed it to profit from the exchange of goods and commodities. The empire also levied taxes on its subjects, which provided a significant source of revenue. Additionally, the Byzantines had access to valuable resources such as gold, silver, and precious stones, which further added to their wealth.
The Byzantine Empire also had a strong bureaucracy that effectively administered taxation and trade. This ensured that the imperial treasury was well-funded and enabled the Byzantines to accumulate vast wealth over the centuries.
2. What were some of the key economic activities of the Byzantine Empire?
The Byzantine Empire engaged in a variety of economic activities that contributed to its wealth. One of the most important was trade. Byzantine merchants were renowned for their involvement in long-distance trade, importing luxury goods from the East and exporting commodities such as silk, spices, and precious metals to Europe. This trade network extended as far as China, Africa, and Scandinavia, ensuring a steady flow of wealth into the empire.
Agriculture was another crucial economic activity. The Byzantines cultivated a wide range of crops, including wheat, barley, olives, and grapes. The surplus produce was not only consumed locally but also exported, further boosting the empire’s economy. The Byzantines also engaged in manufacturing, particularly in the production of luxury items such as textiles, ceramics, and jewelry.
3. How did the Byzantine Empire’s wealth compare to other medieval empires?
The Byzantine Empire was one of the wealthiest and most prosperous empires of the medieval period. Its economic strength surpassed many of its contemporaries, including Western European kingdoms. The empire’s strategic location at the crossroads of Europe and Asia, along with its extensive trade networks, contributed significantly to its wealth. The Byzantines’ control over key trade routes allowed them to accumulate and maintain considerable economic power.
The Byzantine Empire’s wealth was also reflected in its grand architecture, lavish court life, and the patronage of the arts. The emperors and wealthy elites displayed their opulence through the construction of magnificent buildings, the commissioning of elaborate mosaics, and the collection of precious artworks.
4. How did the wealth of the Byzantine Empire impact its society?
The wealth of the Byzantine Empire had a profound impact on its society. It allowed for the flourishing of a sophisticated and cosmopolitan culture. The Byzantine court was known for its luxurious lifestyle, with extravagant banquets, elaborate ceremonies, and a vibrant social scene. The empire’s wealth also supported a well-educated and cultured elite class, fostering intellectual pursuits, patronage of the arts, and the preservation of ancient knowledge.
Furthermore, the wealth of the Byzantine Empire enabled the empire to maintain a formidable military, which played a crucial role in its defense and expansion. The army was well-equipped, and the soldiers were paid relatively well, ensuring their loyalty and effectiveness in defending the empire’s borders.
5. What were some challenges to the wealth of the Byzantine Empire?
Despite its wealth, the Byzantine Empire faced several challenges that impacted its economic prosperity. One significant challenge was the constant threat of invasion. The empire had to dedicate a substantial amount of resources to defend its borders against various invaders, including Arab armies and European powers.
Internal instability and political conflicts also posed challenges to the Byzantine Empire’s wealth. Succession struggles, civil wars, and corruption within the government sometimes hindered effective governance and economic policies.
The rise and fall of the Byzantine Empire – Leonora Neville
In conclusion, the Byzantine Empire was considered one of the wealthiest and most prosperous empires in history. Its wealth can be attributed to various factors such as its strategic location, extensive trade networks, and efficient administration.
The empire’s wealth was evident in its opulent capital city of Constantinople, which boasted magnificent buildings, grand palaces, and luxurious goods. The Byzantine Empire’s wealth enabled it to achieve great military and cultural accomplishments, maintaining its status as a dominant power in the Mediterranean for over a thousand years.