When considering the history of Islamic empires, one may wonder: how many of these empires actually existed? The answer may surprise you. Throughout history, there were not just a few, but in fact, a multitude of Islamic empires that rose and fell, leaving a significant mark on the world.
The history of Islamic empires stretches back centuries, with the earliest empire, the Rashidun Caliphate, establishing itself in the 7th century. From there, numerous empires emerged, including the Umayyad Caliphate, the Abbasid Caliphate, and the Ottoman Empire, just to name a few. These empires, with their wealth, military might, and cultural influence, shaped the development of Islamic civilization and left a lasting legacy across various regions. One notable statistic is that at its height, the Ottoman Empire encompassed territories spanning three continents, making it one of the largest empires in history. Understanding the history and impact of these Islamic empires is crucial in unraveling the complex tapestry of our world’s history.
Throughout history, there were various Islamic empires that left a significant impact on the world. Some of the notable ones include the Umayyad Caliphate, Abbasid Caliphate, Seljuk Empire, Mughal Empire, and Ottoman Empire. These empires spanned across different regions and time periods, contributing to the spread and development of Islamic culture, architecture, and influence. Each empire had its unique characteristics, achievements, and historical significance.
Contents
- Origins of Islamic Empires
- Islamic Empires: A Historical Overview
- Key Takeaways: How Many Islamic Empires Were There?
- Frequently Asked Questions
- 1. How many Islamic empires have there been in history?
- 2. How long did the Islamic empires last?
- 3. Which Islamic empire was the largest in terms of territory?
- 4. Did all Islamic empires follow the same political and religious structure?
- 5. What led to the decline of the Islamic empires?
- The rise and fall of the medieval Islamic Empire – Petra Sijpesteijn \u0026 Birte Kristiansen
Origins of Islamic Empires
An exploration of the history of Islamic empires reveals a rich tapestry of political, cultural, and economic achievements. From the early days of the Islamic Caliphate to the later empires that spanned across continents, the question of how many Islamic empires existed is complex and multifaceted. Each empire was shaped by its unique historical context, religious beliefs, and interactions with other civilizations. In this article, we will delve into the different Islamic empires that emerged over time, highlighting their distinctive characteristics and contributions.
The Rashidun Caliphate (632-661)
The first major Islamic empire to emerge was the Rashidun Caliphate, which lasted from 632 to 661 AD. This empire was founded by the four immediate successors of Prophet Muhammad, known as the Rashidun Caliphs. Under their leadership, the empire expanded rapidly, conquering vast territories from the Byzantine and Sassanian Empires.
The Rashidun Caliphate was characterized by a decentralized governance structure, with each caliph ruling over a specific region. Despite its short duration, this empire played a crucial role in spreading Islam across the Arabian Peninsula and beyond. It laid the foundation for future Islamic empires and served as a model for subsequent caliphates.
The Rashidun Caliphate’s legacy also includes its religious tolerance, as the conquered territories were allowed to retain their own religious practices. This approach fostered a sense of unity while preserving cultural diversity within the empire.
Through its military successes and administrative innovations, the Rashidun Caliphate established a strong foundation for the Islamic empires that followed.
The Umayyad Caliphate (661-750)
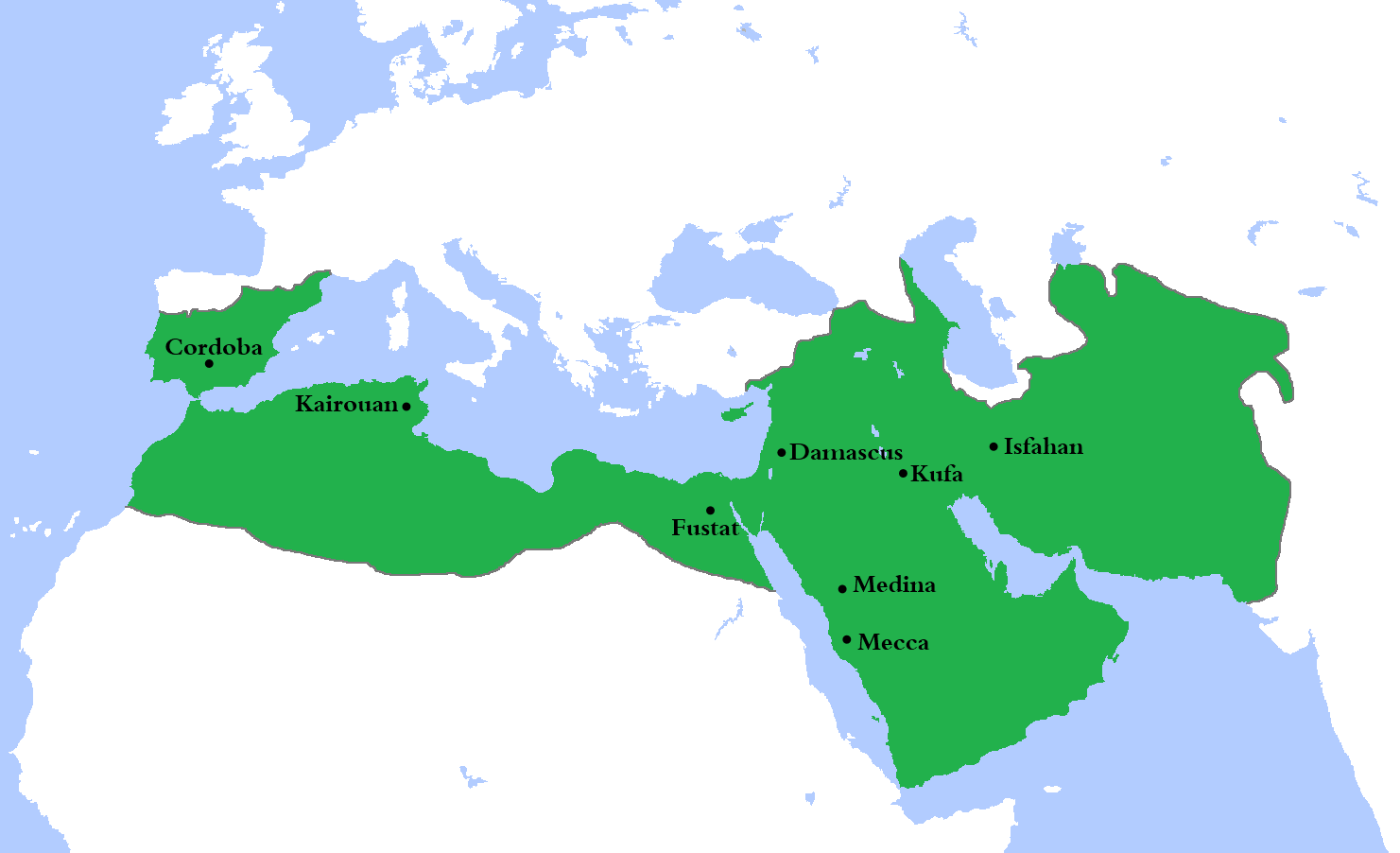
After the Rashidun Caliphate, the Umayyad Caliphate emerged as the next major Islamic empire. It lasted from 661 to 750 AD and was characterized by its expansionist policies and centralized administration. The Umayyads shifted the capital of the empire from Medina to Damascus, establishing a powerful and influential dynasty.
The Umayyad Caliphate expanded its territories through military conquests, reaching as far as Spain in the west and India in the east. It developed a sophisticated bureaucratic system, with governors overseeing provinces and collecting taxes on behalf of the central government.
The empire also witnessed the emergence of early Islamic art and architecture, with magnificent structures like the Dome of the Rock in Jerusalem and the Great Mosque of Damascus. These architectural marvels showcased the empire’s cultural and artistic achievements.
However, the Umayyad Caliphate faced internal conflicts and challenges, resulting in its decline and eventual overthrow by the Abbasid dynasty.
The Abbasid Caliphate (750-1258)
The Abbasid Caliphate, which lasted from 750 to 1258 AD, is often considered the golden age of Islamic civilization. It was founded by Abu al-Abbas al-Saffah, who overthrew the Umayyads and established a new capital in Baghdad.
The Abbasid Caliphate ushered in a period of cultural and intellectual flourishing, known as the Islamic Golden Age. Scholars and intellectuals from diverse backgrounds made significant advancements in various fields, including mathematics, astronomy, medicine, and philosophy. The House of Wisdom in Baghdad became a center for intellectual exchange, attracting scholars from around the world.
During this period, the Abbasids also developed a sophisticated administrative system, dividing the empire into provinces and appointing governors to oversee them. Trade flourished, facilitated by the Islamic empire’s extensive network of roads and a unified currency.
The Abbasid Caliphate’s decline began in the 9th century due to external invasions, internal conflicts, and the rise of regional power centers. However, it left a lasting legacy of knowledge and cultural exchange, shaping the development of subsequent empires.
The Seljuk Empire (1037-1194)
The Seljuk Empire was a Turkic Sunni Muslim empire that emerged in the 11th century and played a significant role in the history of Islamic empires. It originated from the Seljuk Turks, a nomadic group from Central Asia, who gradually expanded their influence throughout the Muslim world.
The Seljuks embraced Persian culture and governance systems, adopting administrative practices from the Abbasid Caliphate. They were known for their military prowess and successfully defended the Muslim territories against the Crusaders.
Under the Seljuks, Islamic art and architecture thrived, with intricate geometric patterns and calligraphy becoming defining features. The Seljuks also patronized scholars and encouraged the translation of Greek and Persian works into Arabic, preserving and disseminating knowledge.
The Seljuk Empire eventually declined due to internal conflicts and external pressure from Mongol invasions. However, its influence laid the groundwork for future Islamic empires in the region.
The Ottoman Empire (1299-1922)
The Ottoman Empire is arguably the most famous and enduring Islamic empire in history. It lasted from 1299 to 1922 AD and was founded by Osman I, a Turkish tribal leader. The empire reached its zenith under the rule of Suleiman the Magnificent and encompassed vast territories in Europe, Asia, and Africa.
The Ottoman Empire was known for its military prowess and strategic expansion. It conquered Constantinople in 1453, signaling the end of the Byzantine Empire and establishing Istanbul as the empire’s new capital.
During its long history, the Ottoman Empire adopted a flexible administrative system, known as the millet system, which allowed non-Muslim communities to govern themselves while remaining under Ottoman rule. This approach ensured a degree of religious and cultural autonomy within the empire.
The empire’s contributions to architecture, art, and literature are exemplified by iconic structures like the Hagia Sophia, Topkapi Palace, and intricate miniature paintings. The Ottoman Empire also left a lasting impact on Islamic law, as it compiled and codified existing legal systems.
The End of Islamic Empires
The end of the Islamic empires came with the decline of Ottoman power in the early 20th century. The empire faced challenges from European powers and internal political struggles, leading to its dissolution in 1922.
Although the era of Islamic empires had come to an end, their legacies continue to resonate today. The contributions of these empires in the fields of science, art, architecture, and governance have shaped the Islamic world and left an indelible mark on human civilization.
Islamic Empires: A Historical Overview
The history of Islam is marked by the rise and fall of numerous empires that spanned vast territories and significantly influenced the development of society, culture, and politics in the Islamic world. These empires were characterized by their adherence to Islamic principles and the expansion of Islamic civilization.
Some of the most notable Islamic empires include:
- The Umayyad Caliphate (661-750 CE): This empire was established after the death of the Islamic prophet Muhammad and expanded from Spain to India.
- The Abbasid Caliphate (750-1258 CE): The Abbasid dynasty ruled over territories across the Middle East, North Africa, and parts of Europe, maintaining a notable focus on education, science, and arts.
- The Ottoman Empire (1299-1922 CE): One of the longest-lasting empires in history, the Ottomans controlled major parts of Southeast Europe, Western Asia, and North Africa, including the holy city of Mecca.
- The Safavid Empire (1501-1736 CE): This empire emerged in Persia (modern-day Iran) and established Shia Islam as the dominant religion in the region.
These are just a few examples of the many Islamic empires that shaped the course of history. Each empire had its unique contributions and impact, creating a rich and diverse Islamic civilization.
Key Takeaways: How Many Islamic Empires Were There?
- There were a total of four major Islamic empires in history.
- The first Islamic empire was the Rashidun Caliphate, which lasted from 632 to 661 AD.
- The Umayyad Caliphate was the second Islamic empire, ruling from 661 to 750 AD.
- The Abbasid Caliphate was the third Islamic empire, reigning from 750 to 1258 AD.
- The fourth and final Islamic empire was the Ottoman Empire, which lasted from 1299 to 1922 AD.
Frequently Asked Questions
Islamic empires have played a significant role in shaping the history of the world. Here are some commonly asked questions about the number of Islamic empires that have existed throughout history.
1. How many Islamic empires have there been in history?
The number of Islamic empires in history is a subject of debate among historians. However, there have been several notable Islamic empires that ruled vast territories and exerted significant influence over various regions.
Starting with the Rashidun Caliphate in the 7th century, other prominent Islamic empires include the Umayyad Caliphate, the Abbasid Caliphate, the Seljuk Empire, the Fatimid Caliphate, and the Ottoman Empire, among others. Each of these empires played a crucial role in spreading Islam, expanding their territories, and leaving a lasting impact on the societies they ruled.
2. How long did the Islamic empires last?
The duration of Islamic empires varied depending on several factors such as internal conflicts, external invasions, and changes in political dynamics. Some Islamic empires, like the Rashidun Caliphate, lasted for a relatively short period, while others, like the Ottoman Empire, spanned several centuries.
For instance, the Abbasid Caliphate, one of the longest-lasting Islamic empires, lasted for approximately five centuries from 750 CE to 1258 CE. On the other hand, the Timurid Empire, though short-lived, had a significant impact during its existence from 1370 CE to 1507 CE.
3. Which Islamic empire was the largest in terms of territory?
The largest Islamic empire in terms of territory was the Abbasid Caliphate, which, at its height, stretched from Spain in the west to Central Asia in the east. The Abbasid Caliphate covered a vast expanse, including parts of Africa, Europe, and Asia.
Another notable Islamic empire in terms of territorial size was the Umayyad Caliphate, which encompassed regions ranging from Spain to India, during its peak in the 8th century.
4. Did all Islamic empires follow the same political and religious structure?
No, Islamic empires had various political and religious structures based on the time period and the ruling dynasty. While they all shared the common foundation of Islam as their religion, the governance, administration, and power structure varied.
For example, the Rashidun Caliphate and the early Islamic empires relied on a form of Islamic governance known as caliphate, where the caliph held both religious and political authority. However, later empires, like the Ottoman Empire, had a more complex bureaucracy and governmental structure.
5. What led to the decline of the Islamic empires?
There were several factors that contributed to the decline of Islamic empires. These factors include internal conflicts, external invasions, economic instability, social unrest, and political corruption.
The rise of European powers and the colonization of Islamic regions also had a significant impact on the decline of Islamic empires. Additionally, the changing geopolitical landscape and advancements in warfare technology played a role in diminishing the power and influence of these empires over time.
The rise and fall of the medieval Islamic Empire – Petra Sijpesteijn \u0026 Birte Kristiansen
To conclude, there were several Islamic empires throughout history. These empires played a significant role in shaping the development of Islamic civilization and had a major impact on regions they ruled. The most notable Islamic empires include the Rashidun Caliphate, the Umayyad Caliphate, the Abbasid Caliphate, the Fatimid Caliphate, and the Ottoman Empire.
The Rashidun Caliphate, established after the death of Prophet Muhammad, was the first Islamic empire. The Umayyad Caliphate followed, expanding their territory and promoting Arab culture. The Abbasid Caliphate marked a golden age for Islamic civilization, encouraging advancements in science, art, and philosophy. The Fatimid Caliphate was based in North Africa and had a strong influence on the Mediterranean region. Lastly, the Ottoman Empire emerged as a powerful Islamic state, ruling over a vast territory and leaving a lasting legacy in the Middle East.