The Byzantine Empire played a crucial role in the spread of Christianity throughout its territory and beyond. Through its political power, cultural influence, and strategic alliances, the empire effectively promoted and consolidated the Christian faith.
One of the most significant ways in which the Byzantine Empire spread Christianity was through its establishment of the Eastern Orthodox Church as the state religion. This provided a strong institutional framework for the dissemination of Christian beliefs and practices. Additionally, the Byzantines actively engaged in missionary activities, sending out monks and monastic communities to evangelize and convert people to Christianity. This combination of political support, religious infrastructure, and missionary efforts helped to expand the influence of Christianity within and beyond the borders of the Byzantine Empire.
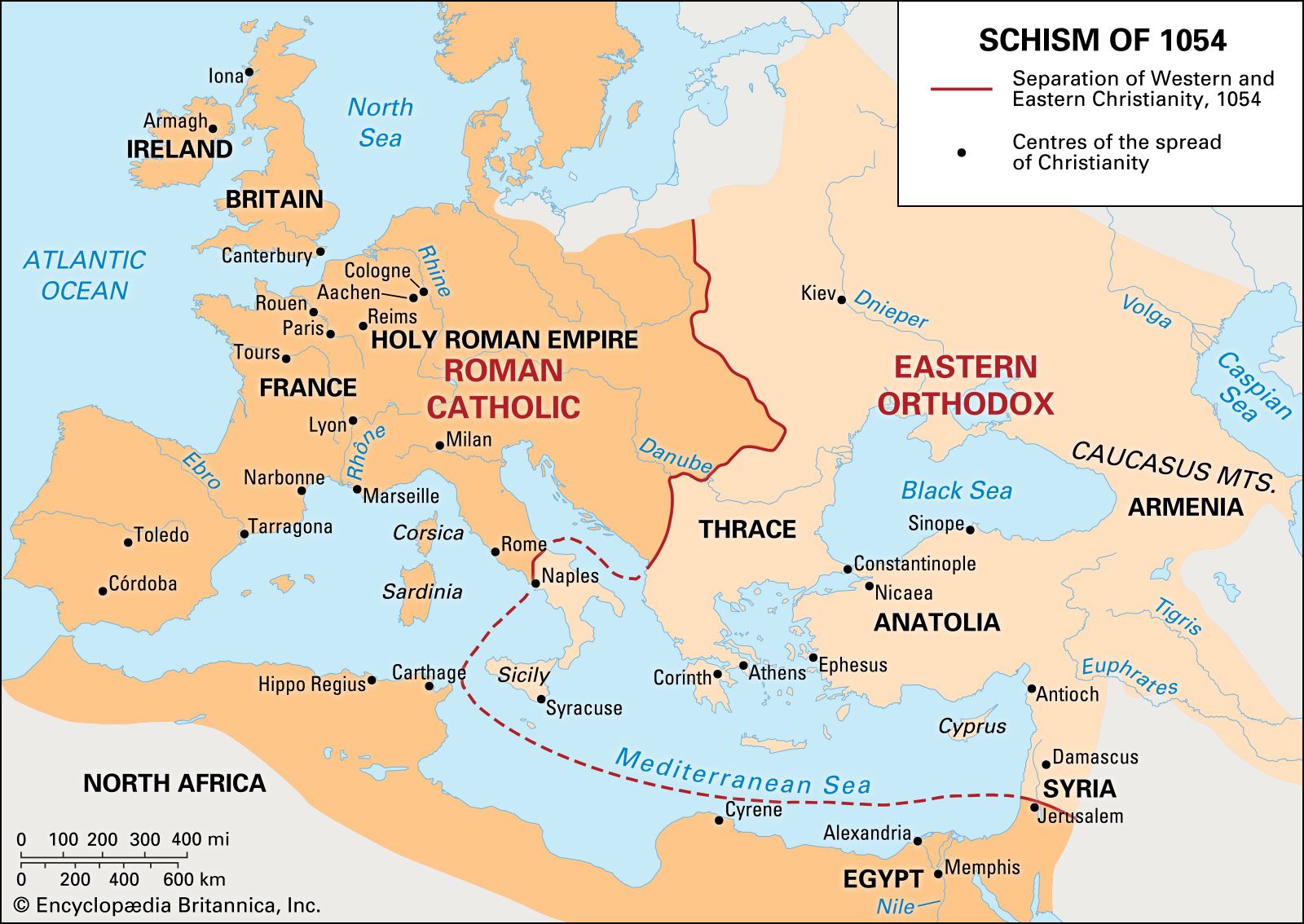
The Byzantine Empire played a crucial role in spreading Christianity. Emperor Constantine established Christianity as the empire’s official religion, leading to its widespread adoption. Byzantine missionaries and scholars were instrumental in spreading Christian teachings to neighboring regions, such as Bulgaria, Russia, and Serbia. The empire’s strategic location also facilitated the spread of Christianity through trade routes and diplomatic relations. Additionally, Byzantine art and architecture, such as magnificent churches and icons, helped to popularize Christian beliefs and teachings.
Contents
- The Influence of Byzantine Art on the Spread of Christianity
- Spread of Christianity by the Byzantine Empire
- Key Takeaways: How Did The Byzantine Empire Spread Christianity?
- Frequently Asked Questions
- 1. What role did Constantine the Great play in spreading Christianity?
- 2. How did the Byzantine Empire use diplomacy to spread Christianity?
- 3. What role did Byzantine missionaries play in spreading Christianity?
- 4. Did the Byzantine Empire use art and architecture to spread Christianity?
- 5. How did the Byzantine Empire influence the spread of Christianity to neighboring regions?
- The rise and fall of the Byzantine Empire – Leonora Neville
The Influence of Byzantine Art on the Spread of Christianity
The Byzantine Empire played a crucial role in the spread of Christianity through its rich and influential art. Byzantine art, with its distinct style and religious themes, helped to communicate and affirm the Christian faith in a visually captivating manner. From the construction of magnificent churches and the use of icons to the production of illuminated manuscripts and mosaics, Byzantine art became a powerful tool for spreading Christianity throughout the empire and beyond.
The Construction of Byzantine Churches
One significant way in which the Byzantine Empire spread Christianity was through the construction of grand churches. The architectural marvels of Byzantine churches, such as the Hagia Sophia in Constantinople, showcased the wealth, power, and devotion of the empire. These elaborate structures served as physical representations of the Christian faith and attracted both believers and non-believers alike. The strategic placement of churches in prominent locations within cities and towns made it impossible to ignore the presence and influence of Christianity.
The design and layout of Byzantine churches were also significant in promoting the Christian message. The central dome, symbolizing the heavens and the presence of God, dominated the interior space and drew the eyes of worshippers upward. The extensive use of mosaic decorations, depicting scenes from the Bible and the lives of saints, further reinforced the teachings of Christianity. These vivid and intricate mosaics served as visual aids for the illiterate population, making the stories and teachings of the religion accessible to all.
Furthermore, the inclusion of relics, such as the bones or personal belongings of saints, in the consecration of churches added a sense of holiness and spiritual power to the space. The presence of these relics encouraged pilgrimage and attracted believers from far and wide, fostering a sense of devotion and unity among Christians.
The Role of Icons in Byzantine Christianity
Icons, sacred images of Christ, the Virgin Mary, and the saints, played a central role in Byzantine Christianity and its spread. These religious artworks were believed to possess a spiritual presence and were venerated by believers. Icons were present in churches, homes, and public spaces, serving as focal points for devotion and prayer.
The Byzantine Empire actively promoted the use of icons as aids to worship and expressions of faith. Iconoclasm, the debate over the use of religious images, was a significant issue during this period. While there were periods of iconoclastic policies, especially during the 8th and 9th centuries, the veneration of icons eventually prevailed, leading to the flourishing of iconography in Byzantine art.
Icons became an essential medium for conveying theological and moral teachings to the largely illiterate population of the Byzantine Empire and beyond. Through the depiction of biblical scenes and the lives of the saints, icons served as visual representations of the divine, making the teachings and stories of Christianity accessible and relatable to people of all backgrounds.
The spread of icons also facilitated the spread of Christianity through trade and cultural exchanges. Byzantine icons were highly sought after by other Christian communities, and they traveled beyond the borders of the empire, reaching regions such as Russia and the Balkans. As these regions adopted the use of icons, Christianity spread along with them, contributing to the expansion of the faith.
Illuminated Manuscripts: Preserving and Spreading Christian Knowledge
In addition to architectural marvels and icons, Byzantine illuminated manuscripts played a crucial role in preserving and spreading Christian knowledge. Monastic scriptoria, where scribes meticulously copied and illustrated sacred texts, were centers of intellectual and artistic activity. The painstaking process of producing these manuscripts ensured the accuracy and preservation of the Christian Scriptures and theological writings.
Illuminated manuscripts were highly valued and were often commissioned by the imperial court, churches, and wealthy individuals. The intricate illustrations and decorations that adorned these manuscripts brought the written word to life, making it more engaging and accessible to readers. These religious texts played a vital role in the education of clergy and the dissemination of Christian teachings to the wider population.
The portability of illuminated manuscripts allowed them to reach far-flung regions beyond the Byzantine Empire. As Byzantine missionaries and traders traveled to neighboring territories, they carried these manuscripts with them, introducing Christianity and its teachings to new audiences. The Byzantine Empire’s commitment to the production of illuminated manuscripts ensured the continued spread of Christianity and the preservation of its core beliefs and practices.
Byzantine Mosaics: The Splendor of Divine Worship
The use of mosaic art in Byzantine churches served as a powerful tool for spreading Christianity and enhancing the worship experience. Mosaics, comprised of tiny colored stones or glass pieces, adorned the walls, vaults, and domes of churches, creating awe-inspiring visual displays.
Byzantine mosaics depicted scenes from the Bible, the lives of saints, and the earthly and heavenly realms. These intricate and vibrant artworks served as visual representations of the divine and immortality. The sheer magnificence of mosaic decoration in churches had a profound impact on worshippers and visitors, drawing them into the world of divine worship.
Although the Byzantine Empire spread Christianity through various means, the beauty and exquisiteness of its art, be it in churches, icons, illuminated manuscripts, or mosaics, had a profound impact on the spiritual lives of believers and non-believers. The visual language of Byzantine art transcended barriers, communicating the core beliefs of Christianity and leaving an indelible mark on the spread of the faith.
Spread of Christianity by the Byzantine Empire
The Byzantine Empire played a significant role in spreading Christianity throughout its territories and beyond. Through a combination of political, cultural, and religious factors, the Byzantines ensured the growth and influence of Christianity in their realm.
One of the main methods employed by the Byzantine Empire to spread Christianity was through its close association with the Eastern Orthodox Church. Emperors actively promoted and protected the church, establishing it as the state religion. This enabled the church to wield considerable influence over the population and spread Christian teachings.
The Byzantines also engaged in missionary activities to evangelize neighboring regions. Missionaries were sent to various areas, such as the Balkans, Russia, Ethiopia, and the Arab lands, to convert people to Christianity. These efforts helped to extend the reach of Byzantine Christianity beyond the empire’s borders. Additionally, the Byzantines provided support to other Christian communities facing persecution, aiding in the preservation and spread of the faith.
The liturgical practices and artistic traditions of the Byzantine Empire also played a crucial role in the dissemination of Christianity. Byzantine liturgical texts and music, as well as religious artwork, influenced the development of Christian worship and iconography in other regions.
In conclusion, the Byzantine Empire spread Christianity through its close association with the Eastern Orthodox Church, missionary efforts, support for persecuted Christian communities, and the influence of its liturgical practices and artistic traditions. These factors paved the way for the expansion and enduring impact of Christianity within and beyond the Byzantine realm.
Key Takeaways: How Did The Byzantine Empire Spread Christianity?
- The Byzantine Empire spread Christianity through missionary activities and conversion efforts.
- Emperor Constantine played a crucial role in the spread of Christianity by adopting it as the official religion of the empire.
- The Byzantine Empire used its political power and influence to promote Christianity.
- The Byzantine Empire built impressive churches and religious structures to showcase the grandeur of Christianity.
- Byzantine missionaries and monks traveled to surrounding regions to spread the teachings of Christianity.
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are some frequently asked questions about how the Byzantine Empire spread Christianity:
1. What role did Constantine the Great play in spreading Christianity?
Constantine the Great played a significant role in spreading Christianity in the Byzantine Empire. In the early 4th century, he became the first Roman emperor to convert to Christianity and issued the Edict of Milan, granting tolerance and legal protection to Christians. Through his patronage and support, Christianity gained prominence in the empire. Constantine also convened the First Council of Nicaea in 325 AD, which established the Nicene Creed and resolved theological disputes, further solidifying Christian doctrine.
Constantine’s conversion and support for Christianity symbolized a major shift in the religious landscape of the Byzantine Empire. His policies encouraged the conversion of the populace and the construction of Christian churches, contributing to the spread and establishment of Christianity as the dominant religion in the empire.
2. How did the Byzantine Empire use diplomacy to spread Christianity?
The Byzantine Empire employed diplomacy as a means to spread Christianity. Byzantine emperors and officials engaged in diplomatic missions, establishing alliances and fostering relationships with neighboring kingdoms and empires. Through these diplomatic efforts, they promoted the spread of Christianity by encouraging the conversion of rulers and their subjects.
By providing incentives such as economic and military support, the Byzantines enticed rulers to embrace Christianity. They also sent Christian missionaries to regions outside the empire’s borders, spreading the faith to new territories. This diplomatic approach not only expanded the influence of the Byzantine Empire but also facilitated the dissemination of Christianity to various parts of Europe, the Middle East, and North Africa.
3. What role did Byzantine missionaries play in spreading Christianity?
Byzantine missionaries played a crucial role in spreading Christianity beyond the borders of the empire. These missionaries, often monks or clergy, traveled to regions with a significant non-Christian population and sought to convert the locals to Christianity.
They employed various strategies, including preaching, teaching, and translating religious texts, to communicate the principles and teachings of Christianity. Byzantine missionaries also established monastic communities in newly converted areas, serving as centers for religious education and practice. These efforts contributed to the gradual expansion of Christianity and the establishment of local Christian communities in regions influenced by the Byzantine Empire.
4. Did the Byzantine Empire use art and architecture to spread Christianity?
Yes, the Byzantine Empire used art and architecture as powerful tools in spreading Christianity. Byzantine artists and architects created magnificent churches, adorned with intricate mosaics, frescoes, and religious icons. These artworks served as visual representations of Christian beliefs and narratives.
Byzantine religious art depicted scenes from the life of Jesus, the Virgin Mary, and other saints, aiming to inspire and educate both the literate and illiterate population. The grandeur and beauty of Byzantine architecture and artwork attracted people’s attention and served as a testament to the power and importance of Christianity. This artistic expression contributed to the popularity and acceptance of Christianity in the Byzantine Empire and beyond.
5. How did the Byzantine Empire influence the spread of Christianity to neighboring regions?
The Byzantine Empire’s influence played a crucial role in the spread of Christianity to neighboring regions. As a major power in the eastern Mediterranean, the Byzantine Empire exerted political, cultural, and religious influence over neighboring kingdoms and empires.
Through trade routes, diplomatic missions, and cultural exchanges, the Byzantines spread their religious beliefs and practices to regions like the Balkans, Italy, and the Slavic lands. The establishment of Byzantine churches, monasteries, and educational institutions in these areas helped solidify the presence of Christianity. Additionally, the Byzantine Empire’s political alliances and military campaigns often involved the conversion of territories under their control, further propagating the faith.
The rise and fall of the Byzantine Empire – Leonora Neville
To summarize, the Byzantine Empire played a significant role in the spread of Christianity. Its strategic location, along with strong political and military power, allowed the empire to propagate the message of Christianity across various regions. Byzantine emperors actively promoted Christianity as the state religion and supported the construction of churches and monasteries. Through religious art, such as icons and mosaics, the Byzantines visually expressed their faith and attracted people to the Christian religion.
The Byzantine Empire also contributed to the spread of Christianity through diplomatic and cultural exchanges. Byzantine missionaries, such as Cyril and Methodius, successfully converted Slavic communities using their own language and developing the Cyrillic alphabet. Moreover, the Byzantines had strong ties with other Christian communities, such as the Armenians and Georgians, leading to the dissemination of Christianity to these regions. Overall, the Byzantine Empire’s influence and efforts were instrumental in the expansion and establishment of Christianity as a prominent religion in the medieval world.