The Byzantine Empire, known for its rich cultural heritage and strategic location, left a lasting impact on future civilizations. From its advancements in art and architecture to its preservation of classical knowledge, the Byzantine Empire played a vital role in shaping the world we know today.
One of the most significant ways in which the Byzantine Empire influenced future civilizations was through its artistic contributions. The empire’s unique blend of Roman, Greek, and Eastern influences resulted in the development of a distinct Byzantine art style characterized by intricate mosaics, vibrant icons, and stunning architecture. This artistic legacy not only inspired later Byzantine-influenced cultures but also left an indelible mark on European artistic traditions, especially during the Renaissance.
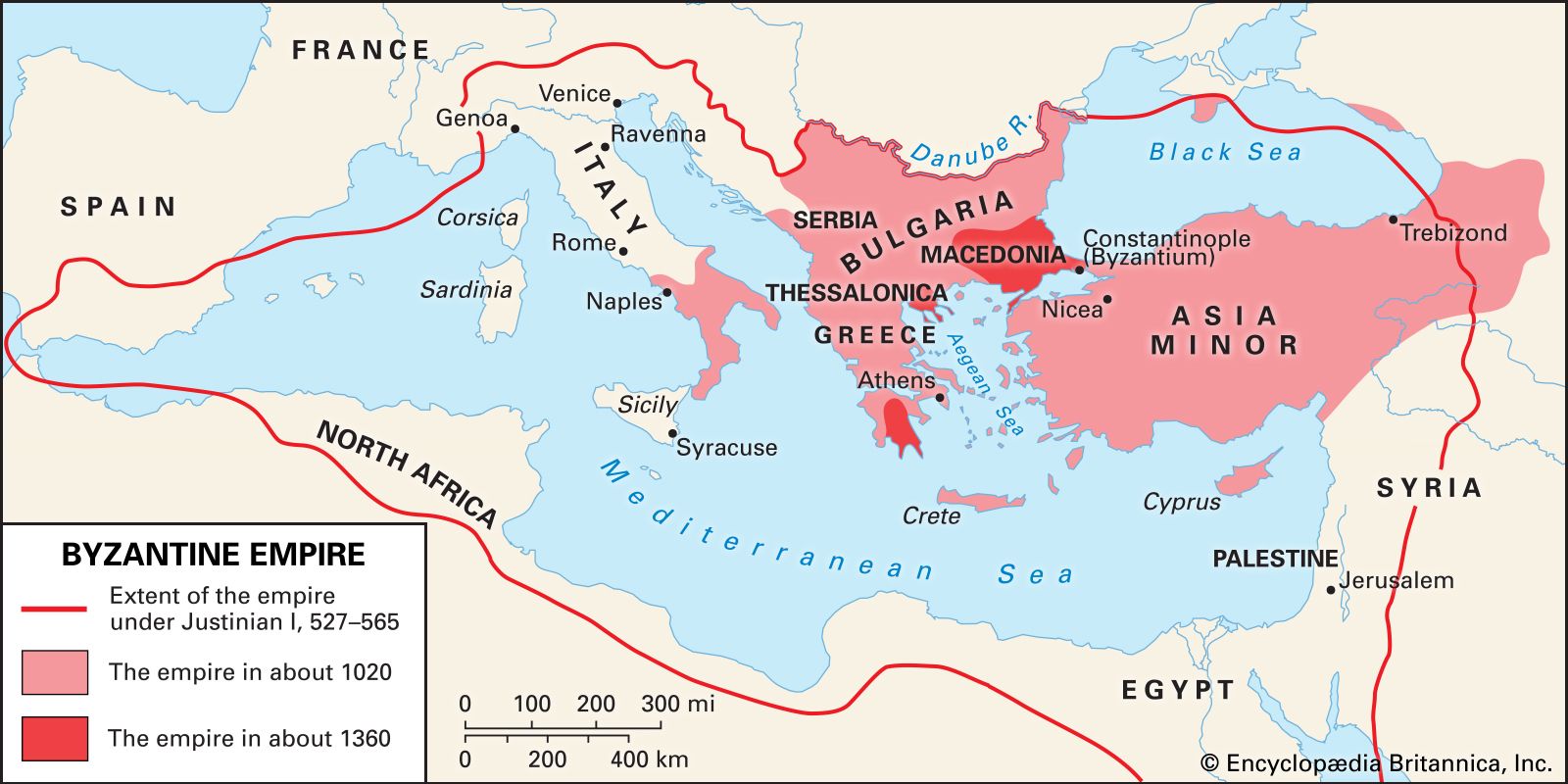
The Byzantine Empire had a significant impact on future civilizations. Its preservation of classical knowledge during the Middle Ages played a crucial role in shaping Western civilization. Byzantium’s strategic location facilitated the exchange of ideas, trade, and cultural influences between East and West. The empire’s artistic and architectural achievements, such as the Hagia Sophia, influenced later Byzantine, Islamic, and European art and architecture. Byzantine legal and administrative systems also influenced future governments. Overall, the Byzantine Empire left a lasting legacy that shaped the development of subsequent civilizations.

Contents
The Byzantine Empire’s Influence on Trade and Economy
The Byzantine Empire had a significant impact on future civilizations, particularly in terms of trade and economy. As a bridge between East and West, the Byzantines played a crucial role in facilitating the exchange of goods, ideas, and technologies. Their strategic location along major trade routes such as the Silk Road and Mediterranean Sea made Constantinople (present-day Istanbul) a vibrant center of commerce, attracting merchants, artisans, and scholars from various parts of the world. This influx of resources and knowledge greatly influenced the development of future civilizations.
Silk and Spice Trade
One of the most significant contributions of the Byzantine Empire to future civilizations was its involvement in the silk and spice trade. Byzantine merchants played a key role in the distribution of these valuable commodities, creating a booming trade network that connected Europe, Asia, and Africa. The empire’s control over strategic ports and the establishment of trade agreements with neighboring regions allowed for the steady flow of silk, spices, and other luxurious goods.
The Byzantines also developed their own silk industry, which became a major source of wealth and innovation. They closely guarded the secret of silk production, which was initially only known to the Chinese. By monopolizing the silk trade and exporting their own products, the Byzantines amassed considerable wealth. The demand for silk in Europe and other parts of the world created a continuous flow of trade, fostering economic growth and cultural exchange.
The impact of Byzantine trade on future civilizations cannot be overstated. The introduction of silk and spices from the East revolutionized fashion, cuisine, and medicine in Europe and other regions. These luxurious goods became symbols of wealth and power, influencing social hierarchies and establishing new markets. Moreover, the trade routes established by the Byzantines laid the foundation for future exploration and globalization, shaping the economic landscape for centuries to come.
Technological and Scientific Advancements
Another significant impact of the Byzantine Empire on future civilizations lies in its contributions to technology and science. The Byzantines were known for their innovative engineering projects, such as the construction of Hagia Sophia, one of the greatest architectural achievements of the time. The empire’s emphasis on education and learning also led to advancements in various scientific fields, including medicine, astronomy, and mathematics.
The Byzantines preserved and translated numerous ancient Greek and Roman texts, safeguarding knowledge that would have otherwise been lost. These translations served as the foundation for the development of science and philosophy in the Western world during the Renaissance. Byzantine scholars also made significant contributions to medical knowledge, including the establishment of hospitals and the development of medical treatments.
Furthermore, their knowledge of astronomy and mathematics influenced future civilizations, as evidenced by the adoption of the Byzantine numeral system, which eventually evolved into the modern-day Arabic numerals used globally. The Byzantines’ dedication to scholarship and scientific inquiry laid the groundwork for scientific progress in Europe and other parts of the world.
Preservation of Classical Learning
The Byzantine Empire played a crucial role in preserving and transmitting classical learning to future generations. While Western Europe experienced a decline in education and literacy during the Early Middle Ages, Byzantine scholars diligently preserved ancient Greek and Roman texts, ensuring the continuity of knowledge. This intellectual preservation was critical for the revival of classical learning during the Renaissance, directly influencing the development of art, literature, and philosophy.
The Byzantines also actively engaged in scholarly pursuits, producing notable philosophers, theologians, and historians. Figures such as Procopius, John of Damascus, and Anna Komnene significantly contributed to intellectual discourse and inspired future thinkers. Byzantine scholars and their works became a bridge between the ancient world and the future, shaping the course of Western civilization.
Legal Systems and Governance
The Byzantine legal system and governance had a lasting impact on future civilizations. The empire developed a comprehensive legal code known as the Corpus Juris Civilis, or the Justinian Code, which served as the basis for legal systems in many European countries. The Justinian Code collected and organized Roman laws, ensuring the uniform application of justice throughout the empire.
The Byzantines also established a bureaucratic administrative system that influenced the governance structure of subsequent civilizations. Their emphasis on centralized authority and efficient governance provided a model for future empires and states. The concept of divine right, in which the emperor was seen as the representative of God and possessed absolute power, influenced the development of monarchical systems of government in Europe.
In addition, the Byzantine Empire’s approach to diplomacy and foreign relations set a precedent for future civilizations. The empire maintained diplomatic relations with neighboring powers, negotiated treaties, and forged alliances to secure their interests. These diplomatic practices influenced the conduct of international relations in the medieval and modern eras.
Cultural and Artistic Legacy
The Byzantine Empire’s cultural and artistic legacy continues to influence future civilizations. Byzantine art, characterized by its iconic mosaics, frescoes, and religious iconography, left an indelible mark on the art of subsequent eras. The distinctive style of Byzantine architecture, with its domes, columns, and intricate ornamentation, can be seen in buildings around the world, including Orthodox churches and mosques.
Byzantine music, particularly its religious chants and hymns, became the basis for the development of Eastern Christian liturgical music. The tradition of Byzantine chant spread throughout the Eastern Orthodox Church and influenced the musical traditions of neighboring regions.
The Byzantines also played a significant role in the preservation and spread of Christianity. As the eastern branch of the Christian Church, the Byzantine Empire contributed to the development of Orthodox Christianity, which has had a profound impact on the religious and cultural identity of numerous nations, including Russia, Greece, and Serbia.
The Byzantine Empire’s influence on future civilizations cannot be overstated. Its contributions to trade and economy, technology and science, preservation of classical learning, legal systems and governance, and cultural and artistic legacy shaped the course of history. The impact of the Byzantines continues to be felt in various aspects of modern society, from global trade networks to architectural styles and religious practices.
Byzantine Empire’s Impact on Future Civilizations
The Byzantine Empire had a profound impact on future civilizations through its preservation and transmission of Greek and Roman culture, advancements in art and architecture, and its role as a bridge between East and West.
The Byzantines preserved ancient Greek and Roman texts, allowing this knowledge to survive through the Middle Ages. Their scholars also made significant contributions to fields such as philosophy, medicine, and astronomy. The Byzantine Empire’s artistic achievements, such as the Byzantine architectural style, influenced later civilizations, including the Renaissance in Europe. Additionally, the empire’s strategic location at the crossroads of trade routes between Europe and Asia facilitated cultural exchange and economic growth.
Moreover, the Byzantine Empire’s legal and administrative systems influenced future civilizations. The Justinian Code, a collection of laws established by Emperor Justinian, became a basis for legal systems in Europe and beyond. The Byzantines also maintained a strong centralized government, which inspired later autocratic rulers. Furthermore, the Byzantine’s practice of Orthodox Christianity shaped the religious beliefs and rituals of future Orthodox Christian communities.
Key Takeaways
- The Byzantine Empire had a significant impact on future civilizations.
- It preserved and passed on ancient Greek and Roman knowledge and culture.
- The Byzantines developed a unique blend of Greek, Roman, and Eastern influences.
- The empire served as a bridge between Europe and Asia, facilitating cultural exchange.
- The Byzantine Empire influenced art, architecture, and literature in future civilizations.
Frequently Asked Questions
The Byzantine Empire had a lasting impact on future civilizations through its contributions to art, architecture, law, religion, and education. Here are some frequently asked questions about how the Byzantine Empire influenced the development of other societies.
1. What are the artistic contributions of the Byzantine Empire?
The Byzantine Empire was known for its rich artistic tradition, particularly in the form of religious art. Iconography, the use of religious images, played a significant role in Byzantine art. The empire also developed unique architectural styles, such as the domed churches and mosaics found in the Hagia Sophia in Constantinople. These artistic contributions influenced the development of art in future civilizations, including the Renaissance in Europe.
Additionally, Byzantine artisans were renowned for their skill in producing intricate and highly detailed works, such as illuminated manuscripts and metalwork. These artistic techniques and styles were passed down through generations and influenced the artistic traditions of later civilizations, leaving a lasting mark on the history of art.
2. How did the Byzantine Empire influence architecture?
The Byzantine Empire had a profound influence on architecture, particularly in Eastern Europe and the Middle East. The most famous example is the Hagia Sophia, which served as a model for many churches and mosques in the region. The use of the dome, arches, and mosaics in Byzantine architecture set the standard for future architectural styles.
The influence of Byzantine architecture can be seen in structures like the Basilica of San Marco in Venice and the Church of the Holy Wisdom in Kiev. The Byzantine architectural style also influenced the development of Islamic architecture, especially during the Umayyad and Abbasid periods.
3. What role did the Byzantine Empire play in the development of law?
The Byzantine Empire was known for its organized legal system, which had a considerable impact on the development of law. Emperor Justinian’s codification of Roman law in the Corpus Juris Civilis, also known as Justinian’s Code, served as the foundation for legal systems in many European countries. It influenced the development of civil law, canon law, and common law, shaping the legal systems of Western civilization.
Justinian’s Code also introduced the concept of legal universality, where laws applied equally to all people regardless of their status. This idea had a profound influence on the development of human rights and the concept of justice in future civilizations.
4. How did the Byzantine Empire impact religion?
The Byzantine Empire played a significant role in the spread and preservation of Christianity. The empire served as a bridge between the Eastern and Western branches of Christianity and played a crucial role in defining and developing Christian theology and doctrine. The Byzantine Emperor was often seen as the protector and defender of the Orthodox Christian faith.
The Byzantine Empire also had a lasting impact on the development of religious art and iconography. Icons, religious images used in worship, became an essential part of Byzantine Christianity and influenced the religious art of subsequent civilizations. The Byzantine Empire’s influence on religion can still be seen in the Orthodox Church, which traces its roots back to the Byzantine era.
5. What was the Byzantine Empire’s contribution to education?
The Byzantine Empire placed great importance on education and intellectual pursuits. The empire established several renowned centers of learning, such as the University of Constantinople, where subjects like philosophy, astronomy, and literature were taught. The Byzantines preserved and translated many ancient Greek and Roman texts, ensuring their survival and influencing the intellectual development of future civilizations.
Byzantine scholars also made significant contributions to fields like medicine, mathematics, and theology. Their works were studied and built upon by scholars in later civilizations, contributing to the advancement of knowledge and the shaping of future intellectual traditions.
11. Byzantium – Last of the Romans (Part 1 of 2)
The Byzantine Empire had a profound impact on future civilizations. Through its cultural, political, and religious influence, it shaped the development of Europe, the Middle East, and beyond.
One of the key legacies of the Byzantine Empire was its preservation of ancient knowledge. Its scholars translated and preserved important texts from Greek and Roman civilizations, including works of philosophy, science, and literature. This knowledge would later be rediscovered and contribute to the Renaissance in Europe. Additionally, the Byzantine Empire’s art and architecture influenced subsequent civilizations, with its iconic domes and mosaics inspiring later structures such as the Hagia Sophia in Istanbul. Lastly, the empire’s strategic location and powerful military made it a major player in diplomacy and warfare, shaping the geopolitical landscape of the medieval world.