The Byzantine Empire, often overshadowed by its predecessor, the Roman Empire, played a crucial role in preserving and continuing the legacy of Rome. Its influence extended over a vast territory and spanned more than a thousand years. Through its political, cultural, and architectural achievements, the Byzantine Empire ensured that the traditions and achievements of Rome were not forgotten, leaving a lasting impact on future generations.
One significant aspect of the Byzantine Empire’s continuation of Rome’s legacy was its preservation of Roman law. The Byzantines compiled and codified the Corpus Juris Civilis, a comprehensive legal code that drew heavily from Roman legal principles. This code provided a basis for legal systems in medieval Europe and influenced the development of modern legal systems. Furthermore, the Byzantines’ emphasis on education and the arts continued the Roman tradition of intellectual pursuits, contributing to advancements in fields such as literature, philosophy, and architecture.
The Byzantine Empire continued the legacy of Rome in several significant ways. First, it preserved and expanded upon Roman law, fostering a sense of order and stability. Second, Byzantine art and architecture drew heavily from Roman influences, integrating them with Eastern styles. Third, the Byzantines continued to use Latin as the language of administration and diplomacy. Finally, the Orthodox Christianity practiced in the Byzantine Empire carried on many traditions and doctrines of the Roman Catholic Church. Through these means, the Byzantine Empire upheld Rome’s cultural, linguistic, legal, and religious heritage.
Contents
- The Byzantine Empire: Carrying Forward the Legacy of Rome
- Preserving Rome’s Legacy for Centuries
- Continuity of Rome in the Byzantine Empire
- Key Takeaways
- Frequently Asked Questions
- 1. What was the Byzantine Empire’s connection to Rome?
- 2. How did the Byzantine Empire preserve Roman laws and institutions?
- 3. How did the Byzantine Empire contribute to Roman architecture and art?
- 4. What was the Byzantine Empire’s influence on Christianity?
- 5. How did the Byzantine Empire influence medieval Europe?
- The rise and fall of the Byzantine Empire – Leonora Neville
The Byzantine Empire: Carrying Forward the Legacy of Rome
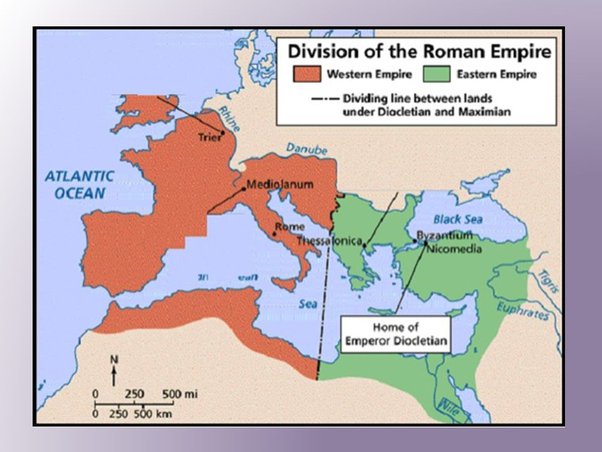
The Byzantine Empire, also known as the Eastern Roman Empire, played a significant role in preserving and continuing the legacy of the Roman Empire. While the Western Roman Empire crumbled in the 5th century CE, the Byzantine Empire emerged as a powerful successor that preserved Roman traditions, institutions, and culture. This article will explore how the Byzantine Empire continued the legacy of Rome through its governance, religion, art, and architecture, as well as its influence on the development of Western civilization.
Governance: The Continuation of Roman Institutions
The Byzantine Empire continued the Roman legacy by maintaining and adapting the administrative and legal institutions established by Rome. The Byzantines inherited Rome’s focus on bureaucracy, with a complex system of government that included imperial officials, provincial governors, and a central administration based in the capital city of Constantinople.
The most significant contribution to governance during the Byzantine Empire was the development and codification of Roman law. Emperor Justinian I, known as Justinian the Great, compiled and organized the Roman legal system into a single code, known as the Justinian Code or Corpus Juris Civilis. This code became the basis for legal systems across Europe, influencing the development of civil law.
Furthermore, the Byzantine Emperor served as both the political and religious leader, inheriting the concept of Caesaropapism from Rome. This system emphasized the close relationship between the state and the Orthodox Church, with the emperor holding authority over both secular and religious matters. The Byzantine Empire thus ensured the continuation of Rome’s fusion of politics and religion.
Finally, the Byzantine Empire’s continuation of the Roman tradition of military dominance was evident in its military organization and strategy. The Byzantines maintained a powerful army and navy, utilizing the Roman military infrastructure and adapting it to the changing warfare of the time. The Byzantine armies successfully defended the empire against numerous barbarian invasions and expanded its territories through conquest.
Religion: The Influence of Christianity and the Orthodox Church
The Byzantine Empire played a crucial role in shaping the development of Christianity and the Orthodox Church, which became a cornerstone of the empire’s identity and a continuation of Rome’s religious legacy. The Byzantines embraced Christianity and made it the empire’s official religion under Emperor Constantine the Great in the 4th century CE.
The establishment of Constantinople as the new capital of the Roman Empire further reinforced the Byzantine Empire’s connection to Christianity. The city became a center of Christian power and culture, housing magnificent churches, such as the Hagia Sophia, which showcased the empire’s devotion to the Christian faith and its desire to rival the grandeur of Rome.
The Byzantine Empire’s influence on Christianity extended beyond its architectural and cultural achievements. The empire played a pivotal role in shaping the doctrinal decisions of Christianity through various ecumenical councils, including the First Council of Nicaea in 325 CE. These councils resolved theological debates and defined important aspects of Christian belief, ultimately shaping the course of Christianity for centuries to come.
Moreover, the Byzantine Empire’s preservation of Greek and Roman manuscripts helped safeguard Christian literature, including the Bible, from destruction during the chaotic period following the fall of Rome. The translation and dissemination of these texts across Europe contributed to the spread of Christianity and the preservation of ancient knowledge.
Art and Architecture: The Byzantine Aesthetic
The Byzantine Empire continued the legacy of Rome through its distinctive artistic and architectural style, which blended Roman, Greek, and Eastern influences. Byzantine art was characterized by its emphasis on religious themes, with icons and mosaics depicting Christian figures and stories. The use of vibrant colors, gold leaf, and intricate details conveyed the empire’s devotion to Christianity.
One of the most iconic examples of Byzantine architecture is the Hagia Sophia in Constantinople. This monumental structure, built in the 6th century CE, showcases the fusion of Roman and Eastern architectural elements. The massive dome, intricate mosaics, and soaring arches reflect the empire’s commitment to grandeur and beauty, paralleling the achievements of Rome’s architectural marvels.
The Byzantine Empire’s architectural influence extended far beyond its borders. Byzantine architectural styles influenced the development of Islamic architecture, particularly in the construction of mosques. The use of domes, minarets, and geometric patterns in Islamic architecture can be traced back to Byzantine influences.
Influence on Western Civilization: Transmitting Knowledge and Ideas
The Byzantine Empire played a vital role in transmitting the knowledge and ideas of the ancient world to Western Europe during the Middle Ages. As the Western Roman Empire crumbled, the Byzantine Empire remained a center of learning and intellectual pursuits.
One of the most significant contributions of the Byzantine Empire was its role in preserving Greek philosophy and literature. Byzantine scholars meticulously copied and preserved ancient Greek texts, including the works of Aristotle, Plato, and other influential philosophers. These texts were later rediscovered and translated during the Renaissance, sparking a renewed interest in classical Greek thought and culture in Western Europe.
The Byzantine Empire also served as a cultural bridge between the East and the West, facilitating the exchange of ideas, technologies, and goods. Its strategic location at the crossroads of Europe and Asia allowed for the transmission of knowledge between different civilizations, including the Islamic world, and Western Europe.
The Byzantine Empire’s legacy continued to shape Western civilization through its architectural and artistic influences. The Byzantine aesthetic inspired the development of Romanesque and Gothic styles in Western European architecture, leaving a lasting imprint on medieval Europe.
Preserving Rome’s Legacy for Centuries
The Byzantine Empire admirably carried forward the legacy of Rome by preserving and adapting its administrative institutions, codifying the Roman legal system, embracing and shaping Christianity, leaving a lasting impact on art and architecture, and transmitting knowledge and ideas to Western Europe. Through its governance, religion, art, and culture, the Byzantine Empire ensured Rome’s legacy lived on, influencing the development of Western civilization for centuries to come.

Continuity of Rome in the Byzantine Empire
The Byzantine Empire, a successor to the Roman Empire, preserved and continued many aspects of Rome’s legacy. Firstly, the Byzantines maintained the administrative structure established by the Romans. They adopted a centralized government system, with an Emperor controlling both political and religious affairs. This continuity in governance ensured stability and continuity in the empire.
The Byzantine Empire also held onto the Roman legal system, known as Justinian’s Code. This legal framework was crucial in maintaining order and justice within the empire. Additionally, the Byzantines continued to use the Latin language initially, but later shifted to Greek, ensuring the preservation and transmission of Roman literature, philosophy, and culture.
Furthermore, the Byzantine Empire inherited Rome’s infrastructure. They maintained and expanded upon the impressive architectural achievements of the Romans, constructing grand churches and buildings such as the Hagia Sophia, showcasing their architectural prowess.
The Byzantine Empire’s continuation of Roman practices and traditions allowed it to thrive for over a thousand years after the fall of the Western Roman Empire. This legacy of Rome in the Byzantine Empire enabled the preservation of knowledge, architecture, and culture that profoundly influenced the future development of Europe and beyond.
Key Takeaways
- The Byzantine Empire continued the legacy of Rome through its adoption of Roman political, legal, and administrative systems.
- By preserving and promoting Roman culture and education, the Byzantine Empire helped to keep the ideals of Rome alive.
- The Byzantine Empire’s influence extended beyond its borders through trade, diplomacy, and missionary activities.
- The preservation of Roman law and the codification of legal principles in Justinian’s Code ensured the continuity of Roman legal traditions.
- The Byzantine Empire’s architectural and artistic achievements continued the grandeur of Roman aesthetics.
Frequently Asked Questions
The Byzantine Empire played a crucial role in preserving and continuing the legacy of Rome. Here are some frequently asked questions about how the Byzantine Empire continued the legacy of Rome.
1. What was the Byzantine Empire’s connection to Rome?
The Byzantine Empire was a direct continuation of the Eastern Roman Empire, which emerged after the fall of the Western Roman Empire. The Byzantines considered themselves as the true inheritors of the Roman Empire, maintaining Roman cultural traditions, laws, and institutions. The capital of the Byzantine Empire, Constantinople, was once the thriving city of Byzantium, which the Romans had transformed into a magnificent cosmopolitan center.
Furthermore, the Byzantine emperors used the title “Roman Emperor” and claimed authority over the entirety of the Roman Empire, even after the fall of the Western Roman Empire. This connection to Rome helped legitimize the Byzantine Empire’s political and cultural identity as a continuation of the Roman legacy.
2. How did the Byzantine Empire preserve Roman laws and institutions?
The Byzantine Empire continued the legal tradition of Rome by codifying and preserving Roman laws. Emperor Justinian I, known for his codification efforts, established the Corpus Juris Civilis (Body of Civil Law) which collected and organized all existing Roman laws. This legal code served as the foundation for legal systems in many European countries and was influential in shaping modern legal principles.
In addition to legal institutions, the Byzantine Empire maintained a bureaucratic administrative system inherited from Rome. Administrative officials, such as the praetorian prefects and provincial governors, oversaw governance and ensured the functioning of the empire. The Byzantine emperors also inherited the Roman concept of the divine right to rule, emphasizing their authority and legitimacy as the successors of Rome.
3. How did the Byzantine Empire contribute to Roman architecture and art?
The Byzantine Empire continued the Roman tradition of monumental architecture and grandiose artistic forms. The most renowned example is the Hagia Sophia in Constantinople, which combines elements of Roman architecture with Byzantine innovation. The use of domes, arches, and intricate mosaics became distinctive features of Byzantine architecture.
Byzantine art also evolved from Roman art, adopting and transforming classical motifs into a distinct Byzantine style. Byzantine artists often depicted religious subjects, creating stunning icons and frescoes that adorned churches and palaces. The exquisite craftsmanship and use of vibrant colors in Byzantine art influenced artistic developments in Europe.
4. What was the Byzantine Empire’s influence on Christianity?
The Byzantine Empire played a significant role in the development and spread of Christianity. The Byzantines embraced Christianity as the state religion under Emperor Constantine, who founded Constantinople as the new Christian capital. The Byzantine emperors became protectors and promoters of Orthodox Christianity.
The Byzantine Empire also contributed to the theological and doctrinal debates of Christianity. Iconoclasm, the controversy over the use of religious images, emerged in the Byzantine Empire and shaped the understanding of religious art. Additionally, Byzantine theologians, such as St. John Chrysostom and St. Basil the Great, made significant contributions to Christian theology and ethics.
5. How did the Byzantine Empire influence medieval Europe?
The Byzantine Empire played a crucial role in transmitting Greek and Roman culture and knowledge to medieval Europe. Byzantine scholars preserved and translated ancient texts, including works of philosophy, science, and literature. These Greek and Roman classics had a profound impact on the development of European intellectual thought during the Middle Ages.
The Byzantine Empire also served as a bridge between Europe and the Islamic world, facilitating cultural exchange and trade. Byzantine art, architecture, and music influenced medieval European culture, leading to the emergence of unique styles and forms. The Byzantine Empire’s influence on medieval Europe can be seen in aspects such as religious art, Byzantine-inspired churches, and the assimilation of Byzantine administrative practices.
The rise and fall of the Byzantine Empire – Leonora Neville
The Byzantine Empire played a significant role in continuing the legacy of the Roman Empire. It inherited many aspects of Roman culture, such as language, law, and governance. In fact, the Byzantines referred to themselves as Romans and saw their empire as the continuation of Rome. This continuity was demonstrated in various ways.
One way the Byzantine Empire continued the legacy of Rome was through the preservation of ancient knowledge and the promotion of education. Byzantine scholars collected and translated ancient Greek and Roman texts, preserving important works that would have otherwise been lost. They also established schools and universities, ensuring the dissemination of knowledge and the preservation of intellectual traditions. This commitment to education and the preservation of the past allowed Byzantine society to flourish and contribute to the development of Western civilization.