Exploring the River Civilizations of the Ancient World: A Historical Journey takes us back in time to discover the fascinating civilizations that thrived alongside some of the world’s most famous rivers. From the ancient Egyptians along the Nile to the Mesopotamians along the Tigris and Euphrates, these river civilizations laid the foundation for human history. Delving into their rich cultures, advanced cities, and complex societies, this historical journey is a captivating exploration of the past.
As we delve into the river civilizations of the ancient world, we unravel the secrets of these remarkable societies. From the Nile Valley’s agricultural abundance that supported the mighty Egyptian civilization to the irrigation networks that sustained the city-states of Mesopotamia, the importance of rivers in shaping human development becomes evident. With each civilization leaving behind architectural marvels, intricate systems of governance, and significant cultural achievements, Exploring the River Civilizations of the Ancient World allows us to better understand our own roots and the fascinating journey of humanity throughout history.
Embark on a historical journey as you explore the river civilizations of the ancient world. Discover the mysteries of the Nile River in Egypt, the cultural significance of the Tigris and Euphrates in Mesopotamia, and the rich history of the Indus River in the Indian subcontinent. Uncover the fascinating tales of these civilizations through archaeological sites, ancient artifacts, and intriguing legends. Gain insights into their political systems, social structures, and technological advancements. Immerse yourself in the wonders of these ancient river civilizations and experience the power and beauty that once thrived along their majestic waters.
Contents
- River Civilizations: The Cradle of Ancient Societies
- Exploring the River Civilizations of the Ancient World: A Historical Journey
- Key Takeaways:
- Frequently Asked Questions
- 1. How did the river civilizations of the ancient world develop?
- 2. What were some notable river civilizations of the ancient world?
- 3. What were the key contributions of the river civilizations?
- 4. How did trade flourish in the river civilizations?
- 5. What led to the decline of the river civilizations?
- History Explored: Ancient Civilizations Around the World | EXPLORE MODE
River Civilizations: The Cradle of Ancient Societies
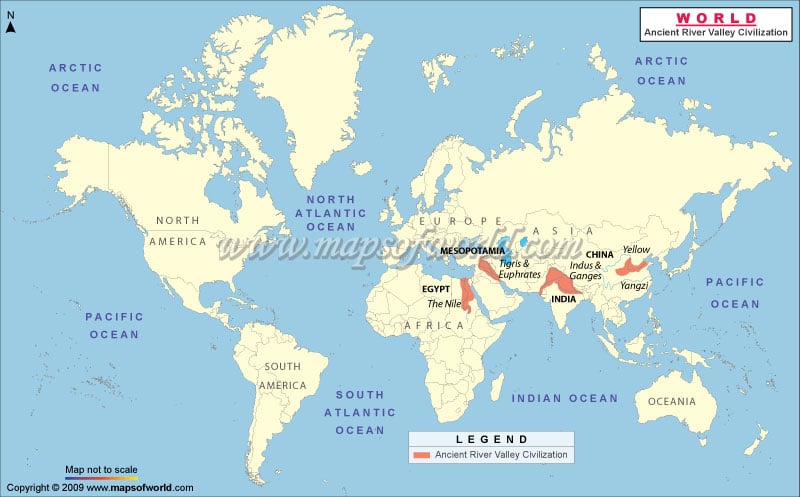
The river civilizations of the ancient world hold a special place in human history. These societies emerged and flourished along the banks of rivers, which provided them with the necessary resources for survival and growth. Exploring the river civilizations takes us on a historical journey, allowing us to discover the remarkable achievements and innovations of these ancient cultures. From the Nile in Egypt to the Tigris and Euphrates in Mesopotamia, the Indus in the Indian subcontinent, and the Yellow River in China, these riverine regions became the cradle of human civilization.
The Nile: Egypt’s Lifeline
The Nile River played a crucial role in the development of ancient Egyptian civilization. It was not just a source of water but also a lifeline for the people. The Nile flooded annually, leaving behind fertile soil that allowed for abundant agricultural production. This surplus of food supported the growth of cities, trade, and the rise of a powerful centralized state. The Nile was also a significant transportation route, facilitating trade and communication between different regions of Egypt.
Pyramids: Architectural Marvels of Ancient Egypt
The pyramids of Egypt are iconic symbols of the ancient world. These structures were monumental tombs built for the pharaohs, the ruling elite of ancient Egypt. The pyramids were designed to be grand and imposing, reflecting the power and divinity of the pharaoh. Constructed with precision and expertise, they stand as a testament to the advanced engineering knowledge of the ancient Egyptians. The most famous pyramid, the Great Pyramid of Giza, is the oldest and largest of the three pyramids in the Giza complex.
Hieroglyphs: A Window into Ancient Egyptian Culture
Ancient Egyptian civilization is known for its unique system of writing known as hieroglyphs. Hieroglyphs were a complex combination of pictorial symbols and phonetic signs that represented words and sounds. They were used to record important religious, historical, and administrative texts. Decoding hieroglyphs was a long-standing mystery until the discovery of the Rosetta Stone, which provided the key to deciphering the ancient script. Hieroglyphs offer valuable insights into the beliefs, achievements, and daily life of the ancient Egyptians.
The Legacy of Ancient Egypt
Ancient Egypt’s legacy extends beyond its monuments and hieroglyphs. The civilization’s advancements in medicine, mathematics, architecture, and agriculture set the stage for future civilizations. Egyptian medical practices, including elaborate surgical procedures and the use of medicinal plants, were highly advanced for their time. In mathematics, the Egyptians developed a decimal numbering system and were among the first to solve mathematical problems algebraically. Their architectural techniques, such as the use of columns and the mortarless construction of structures like the Temple of Karnak, influenced later civilizations.
Mesopotamia: The Land Between Two Rivers
Mesopotamia, known as the “land between two rivers,” was located between the Tigris and Euphrates rivers. This region gave birth to some of the earliest complex societies in human history, including the Sumerians, Assyrians, and Babylonians. The fertile soil of Mesopotamia supported agriculture, allowing these civilizations to flourish.
Cuneiform: The World’s First Writing System
The Sumerians of Mesopotamia were the first to develop a system of writing known as cuneiform. This script involved wedge-shaped marks made on clay tablets using a stylus. Cuneiform was used to record various aspects of life, including economic transactions, laws, literature, and religious texts. This invention was a significant advancement in human communication and paved the way for the development of other writing systems in the ancient world.
Hammurabi’s Code: A Landmark Legal System
Hammurabi’s Code, named after King Hammurabi of Babylon, is one of the earliest known legal codes in history. The code consisted of a set of laws that governed various aspects of Babylonian society, including commerce, marriage, and criminal justice. It established a sense of order and justice and influenced legal systems of future civilizations. The famous principle “an eye for an eye, a tooth for a tooth” originated from Hammurabi’s Code.
Ziggurats: Sacred Temples of Mesopotamia
Ziggurats were massive stepped structures built in ancient Mesopotamia. These towering temples were dedicated to the worship of various gods and served as centers of religious and administrative activities. The most famous ziggurat is the Tower of Babel, believed to have inspired the biblical story. Ziggurats showcased the architectural prowess of the Mesopotamians and were symbols of the power and authority of the ruling elite.
The Indus Valley Civilization: Mystery of an Urban Culture
The Indus Valley Civilization, also known as the Harappan Civilization, emerged in the flood plains of the Indus River in present-day Pakistan and northwest India. This ancient urban culture thrived from around 2600 BCE to 1900 BCE and is one of the most enigmatic civilizations of the ancient world.
Urban Planning: A Testament to Organized Society
The cities of the Indus Valley Civilization were meticulously planned, with a well-defined grid layout and sophisticated drainage systems. Major cities like Mohenjo Daro and Harappa featured large, multi-roomed houses made of brick, public baths, granaries, and even a complex water management system. The level of urban planning displayed by the Indus Valley Civilization is a testament to their organized society and advanced knowledge of city governance.
Indus Script: Yet to be Deciphered
One of the greatest mysteries of the Indus Valley Civilization is their script. The Indus script, which remains undeciphered, consists of symbols and signs found on various artifacts such as seals, pottery, and amulets. Despite numerous attempts to decode the script, its meanings and purpose remain a mystery. Unlocking the Indus script could provide insights into the culture, language, and civilization of the ancient Indus Valley people.
Trade and Commerce: The Indus Valley’s Economic Network
The Indus Valley Civilization had a robust system of trade and commerce, evidenced by the discovery of seals and artifacts from the civilization in regions as far as Mesopotamia and the Persian Gulf. They engaged in long-distance trade, exchanging goods such as textiles, pottery, precious stones, and metals. The existence of a well-developed economic network indicates the prosperity and sophistication of the Indus Valley Civilization.
China’s Yellow River Civilization: Land of Ancient Dynasties
The Yellow River, also known as the “Cradle of Chinese Civilization,” played a significant role in the rise and development of ancient Chinese dynasties. This river provided fertile soil for agriculture and facilitated communication and trade.
Oracle Bone Script: Ancient Chinese Writing
One of the earliest forms of writing in ancient China was the Oracle Bone Script. This script was inscribed on oracle bones, which were used for divination purposes in the Shang Dynasty (around 1600 BCE to 1046 BCE). These inscriptions provide valuable information about the religious beliefs, political events, and daily life of the ancient Chinese.
Terracotta Army: Guardians of the First Emperor
The Terracotta Army is one of the most remarkable archaeological discoveries in the world. Discovered near the mausoleum of the first emperor of China, Qin Shi Huang, the army consists of thousands of life-sized terracotta soldiers, horses, chariots, and weapons. This vast army was crafted to protect the emperor in the afterlife and reflects the military might and grandeur of the Qin Dynasty.
Great Wall of China: An Engineering Marvel
The Great Wall of China is an architectural marvel that stretches over thousands of miles and was built to protect the Chinese empire from invasions. Construction of the wall began over two millennia ago and continued for centuries, with each dynasty adding to its length and fortifications. The Great Wall stands as a testament to the engineering feats and strategic prowess of the ancient Chinese.
Conclusion
Exploring the river civilizations of the ancient world takes us on a captivating historical journey. These civilizations, such as Egypt, Mesopotamia, the Indus Valley, and China, laid the foundation for human progress with their advancements in agriculture, writing systems, architectural marvels, and innovative governance. The legacy of these ancient river civilizations continues to shape our understanding of the past and inspires us in the present.
Exploring the River Civilizations of the Ancient World: A Historical Journey
Throughout history, civilizations have thrived along river banks, benefiting from the fertile land and abundance of water. Some of the most notable river civilizations of the ancient world include the Nile Valley in Egypt, the Mesopotamian civilization between the Tigris and Euphrates rivers, the Indus Valley civilization in present-day Pakistan and India, and the Yellow River civilization in ancient China.
Each of these river civilizations made significant contributions to human history in terms of technology, culture, and governance. The ancient Egyptians developed advanced farming techniques and constructed magnificent pyramids and temples. Mesopotamia, often considered the cradle of civilization, gave birth to the first written language, cuneiform, and established the world’s earliest known legal code, the Code of Hammurabi.
The Indus Valley civilization had a highly organized urban system and sophisticated sanitation systems, with planned cities like Mohenjo-daro. Meanwhile, the Yellow River civilization saw the rise of early Chinese dynasties, such as the Shang and Zhou, and developed a complex system of writing known as oracle bone script.
Exploring the river civilizations of the ancient world offers a glimpse into their remarkable achievements and enduring legacies. These civilizations laid the foundation for later societies and continue to fascinate scholars and historians with their rich history and cultural heritage.
Key Takeaways:
- The river civilizations of the ancient world were pivotal in shaping human history.
- The Nile River civilization in ancient Egypt was characterized by the construction of impressive monuments and the development of hieroglyphic writing.
- The Mesopotamian civilization, situated between the Tigris and Euphrates Rivers, gave rise to advancements in astronomy, mathematics, and the invention of writing.
- The Indus Valley civilization, located along the Indus River in present-day Pakistan and India, had well-planned cities with advanced drainage systems.
- The ancient Chinese civilization along the Yellow and Yangtze Rivers thrived due to innovations in agriculture, such as irrigation and the use of fertilizer.
Frequently Asked Questions
Exploring the River Civilizations of the Ancient World: A Historical Journey is an intriguing topic that takes us back in time to discover the vibrant and advanced ancient civilizations that thrived along major river systems. Here are some frequently asked questions about this fascinating journey.1. How did the river civilizations of the ancient world develop?
The river civilizations of the ancient world developed due to the favorable conditions provided by major rivers. These rivers, such as the Nile in Egypt, the Tigris and Euphrates in Mesopotamia, the Indus in the Indian subcontinent, and the Yellow and Yangtze in China, offered abundant water resources for agriculture, trade opportunities, and transportation.
The availability of fertile soil along the riverbanks allowed civilizations to practice agriculture and develop a surplus of food, leading to the establishment of permanent settlements. As these settlements grew, complex societies emerged with organized governments, social structures, and technological advancements.
2. What were some notable river civilizations of the ancient world?
Some notable river civilizations of the ancient world include:
– Ancient Egypt: Flourished along the Nile River, known for its pyramids, pharaohs, and rich cultural heritage.
– Mesopotamia: Developed in the region between the Tigris and Euphrates Rivers, known for its city-states like Sumer and Babylon, and the invention of writing.
– Indus Valley Civilization: Thrived along the Indus River in modern-day Pakistan and India, known for its well-planned cities and advanced sanitation systems.
– Ancient China: Developed along the Yellow and Yangtze Rivers, known for its dynasties, Great Wall, and contributions to philosophy and technology.
3. What were the key contributions of the river civilizations?
The river civilizations made significant contributions that shaped human history. Some key contributions include:
– Advancements in agriculture: They developed irrigation systems, crop cultivation techniques, and domesticated livestock, leading to surplus food production.
– Development of writing systems: The ancient river civilizations, such as Mesopotamians and Egyptians, created written scripts to record information, document laws, and preserve historical records.
– Technological inventions: They introduced innovations like wheel, sail, calendar systems, and early forms of mathematics.
– Art and architecture: They built majestic pyramids, palaces, temples, and sculptures, showcasing their artistic and architectural prowess.
4. How did trade flourish in the river civilizations?
The river civilizations laid the foundation for extensive trade networks due to their strategic locations along major rivers. The rivers provided a natural transportation network, enabling the movement of goods and people over long distances.
These civilizations developed trade routes that connected different regions and facilitated the exchange of goods, ideas, and cultural influences. For example, the Nile River in Ancient Egypt served as a trade route connecting Africa with the Mediterranean, while the Indus River played a crucial role in trade between the Indus Valley Civilization and other regions.
5. What led to the decline of the river civilizations?
The decline of the river civilizations can be attributed to various factors:
– Natural disasters: Floods, droughts, and other natural calamities disrupted agricultural systems and led to food shortages.
– Invasion and conquest: The river civilizations faced invasions by foreign powers, leading to political instability and the downfall of empires.
– Environmental degradation: Over time, unsustainable agricultural practices and deforestation caused soil erosion and land degradation, affecting agricultural productivity.
– Socioeconomic factors: Rising inequality, social unrest, and economic challenges also contributed to the decline of these civilizations.
History Explored: Ancient Civilizations Around the World | EXPLORE MODE
In summary, exploring the river civilizations of the ancient world takes us on a fascinating journey through history. These civilizations, including the Nile in Egypt, the Tigris and Euphrates in Mesopotamia, the Indus in India, and the Yellow River in China, played a crucial role in the development of human civilization.
We learned how these river civilizations relied on the fertile land provided by the rivers for agriculture, which in turn led to the growth of complex societies and the establishment of key features like cities, writing systems, and centralized governments. Moreover, the river civilizations had a significant impact on future civilizations and continue to influence our world today.