The rise of the Islamic Empire is an intriguing period of history that is filled with captivating stories, complex political dynamics, and remarkable cultural achievements. It is a time when a relatively small group of people managed to build an empire that stretched across vast lands, leaving a profound impact on the world we live in today. Exploring this historical phenomenon allows us to gain a deeper understanding of how religion, politics, and social factors can shape the course of human history.
The rise of the Islamic Empire can be traced back to the early 7th century, when the Prophet Muhammad laid the foundations of a new faith known as Islam. Over the next few centuries, Islamic empires emerged and expanded, encompassing territories as diverse as Spain in the west and India in the east. This rapid expansion was fueled by a combination of military prowess, political skill, and a unifying religious ideology. The Islamic Empire not only created a powerful and influential political entity but also fostered an environment of intellectual and cultural flourishing, making significant contributions to fields such as science, philosophy, and architecture.
The rise of the Islamic Empire was a monumental period in history. Starting in the 7th century, the empire expanded its territories through military conquest, creating an influential and prosperous civilization. It brought advancements in various fields, including science, philosophy, and architecture. The empire’s cultural and intellectual contributions left a lasting legacy, shaping the modern world. Understanding the historical overview of this empire is essential for comprehending its impact on the past and present.
Contents
- The Birth of Islamic Empire: A Historical Overview
- Architecture and the Islamic Empire: A Legacy of Grandeur
- Exploring the Rise of the Islamic Empire: A Historical Overview
- Key Takeaways – Exploring the Rise of the Islamic Empire: A Historical Overview
- Frequently Asked Questions
- 1. What led to the rise of the Islamic Empire?
- 2. What were the major achievements of the Islamic Empire?
- 3. What was the political structure of the Islamic Empire?
- 4. How did the Islamic Empire impact trade and commerce?
- 5. How did the decline of the Islamic Empire occur?
- The rise and fall of the medieval Islamic Empire – Petra Sijpesteijn \u0026 Birte Kristiansen
The Birth of Islamic Empire: A Historical Overview
The rise of the Islamic Empire stands as a pivotal moment in world history. Spanning from the 7th to the 13th century, this vast empire emerged from the Arabian Peninsula and extended its influence across the Middle East, North Africa, and parts of Europe and Asia. With its rapid expansion and the spread of Islam, the Islamic Empire left an indelible mark on various spheres, including politics, religion, culture, and scientific advancements. Exploring the journey of the Islamic Empire unveils a rich tapestry of historical events, conquests, and intellectual advancements that shaped the world as we know it today.
The Rise of Islam: From Revelation to Empire
The roots of the Islamic Empire can be traced back to the Prophet Muhammad and the revelation of the Quran in the 7th century CE. In the early years of Islam, the Arabian Peninsula was fragmented into various tribes and city-states. However, Muhammad’s teachings and the unifying principles of Islam brought a sense of cohesion among the Arab tribes. With the establishment of the first Islamic state in Medina, Muhammad laid the foundation for the future Islamic Empire.
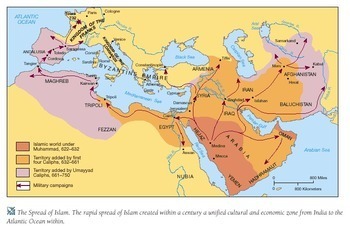
Following Muhammad’s death in 632 CE, the Rashidun Caliphate took over the reins of power. Under the leadership of the first four caliphs, known as the “Rightly Guided Caliphs,” the Islamic Empire embarked on a series of military campaigns, known as the Rashidun Expansion, to spread the message of Islam. These conquests laid the groundwork for the subsequent empires and marked the beginning of the Islamic Empire’s rise to dominance.
One of the key factors in the empire’s expansion was its military prowess and strategic alliances. The Arab armies, motivated by religious zeal and a desire for expansion, conquered vast territories, including the Byzantine Empire, Sassanian Persian Empire, and parts of Africa and Europe. The victories in these conflicts and the subsequent administrative and organizational systems established by the early caliphs propelled the Islamic Empire into becoming a powerful force in the world.
Administration and Governance: The Umayyad Dynasty
The Umayyad Dynasty, which emerged after the Rashidun Caliphate, further solidified the Islamic Empire’s authority. The reign of the Umayyad caliphs marked a shift in the empire’s structure, with a centralization of power and the establishment of a hereditary monarchy. The Umayyads expanded the empire’s borders, reaching Spain in the west and Central Asia in the east.
The administration of the Islamic Empire during the Umayyad period was characterized by a hierarchical bureaucracy, with provinces governed by walis (governors) who reported to the caliph. The empire’s vast territories were united under a single system of law, known as Sharia, which provided guidelines for governance, commerce, and personal conduct. This uniform legal system contributed to the empire’s stability and facilitated trade and cultural exchange.
The Umayyad Dynasty also witnessed the transformation of important cities into major centers of political and cultural significance. Damascus, the empire’s capital, became a thriving hub of trade, learning, and architectural innovation. The Umayyads’ patronage of the arts and architecture led to the construction of iconic structures such as the Umayyad Mosque, which still stands as a testament to the empire’s grandeur.
A Golden Age: The Abbasid Caliphate
The Abbasid Caliphate, which lasted from 750 to 1258 CE, is often regarded as the Islamic Empire’s golden age. With its capital in Baghdad, the Abbasid dynasty ushered in a period of unparalleled intellectual and cultural achievements. It was during this time that the Islamic Empire made significant contributions to various fields, including science, mathematics, astronomy, philosophy, and literature.
The Abbasid Caliphs embraced knowledge from diverse sources, including Greek, Persian, and Indian cultures, fostering a spirit of intellectual curiosity and exploration. The House of Wisdom, a renowned center of learning in Baghdad, translated and preserved ancient texts, making them accessible to scholars across the empire. Scholars such as Al-Khwarizmi, known as the “Father of Algebra,” and Ibn Sina, known as Avicenna, made groundbreaking advancements in math and medicine.
The Abbasids’ patronage of art and architecture resulted in the development of unique styles influenced by the empire’s multicultural heritage. Islamic art and architecture, characterized by intricate geometric patterns and calligraphy, flourished during the Abbasid era. This period saw the construction of iconic structures like the Great Mosque of Samarra and the Palace of the Lions at Alhambra, showcasing the empire’s architectural ingenuity.
Trade and Commerce: The Silk Road and Beyond
The Islamic Empire’s rise to prominence was closely linked with its thriving trade and commerce networks. Situated at the crossroads of the Eastern and Western worlds, the empire connected diverse regions and facilitated the exchange of goods, ideas, and cultures. The Silk Road, a vast network of trade routes that linked China to the Mediterranean, played a crucial role in the empire’s economic growth and cultural exchange.
The Islamic Empire’s control over key trade routes brought significant economic benefits, as it served as a bridge between Asia, Europe, and Africa. This allowed for the flow of commodities such as silk, spices, precious metals, and textiles. Trade flourished in major cities like Basra, Cairo, and Damascus, which became bustling commercial centers attracting merchants from far and wide.
The empire’s economic prosperity also resulted from innovations in finance and banking. Islamic financial practices, such as the development of the first forms of checks and bills of exchange, laid the foundation for modern banking systems. The establishment of the first banks by Muslim merchants facilitated long-distance trade and fostered economic growth.
Cultural Exchange: The Spread of Islamic Civilization
As the Islamic Empire expanded, it brought about a significant exchange of ideas and cultures. The empire’s conquests introduced Islam to diverse societies, leading to the spread of Islamic civilization. The Islamic Empire’s policy of religious tolerance allowed different religious and ethnic communities to coexist, contributing to the preservation and translation of ancient texts and the sharing of scientific and philosophical knowledge.
The translation movement, initiated by Caliph Al-Ma’mun, played a crucial role in transmitting knowledge from the Greek and Roman civilizations to the Islamic world. Islamic scholars translated classical works by Aristotle, Plato, and others, sparking intellectual debates and shaping the development of various disciplines.
The Islamic Empire is also credited with preserving and expanding upon various scientific and mathematical works. Scholars made significant advancements in fields such as astronomy, medicine, alchemy, and optics. The Islamic numerical system, including the concept of zero and decimal fractions, revolutionized mathematics and laid the foundation for modern arithmetic.
Architecture and the Islamic Empire: A Legacy of Grandeur
One of the enduring legacies of the Islamic Empire is its architecture. Islamic architecture is characterized by its distinctive features, such as intricate geometric designs, calligraphy, and the effective use of light and space. The architectural achievements of the empire continue to inspire and awe people across the globe.
Mosques, with their domes, minarets, and prayer halls, are the most prominent examples of Islamic architecture. The Great Mosque of Mecca, known as the Masjid al-Haram, and the Great Mosque of Al-Masjid an-Nabawi in Medina, hold immense religious significance for Muslims worldwide. These mosques exemplify the empire’s focus on creating sacred spaces that facilitate communal worship.
The Alhambra Palace in Granada, Spain, is an architectural masterpiece that showcases the fusion of Islamic and European styles. Its intricate carvings, geometric patterns, and lush gardens reflect the empire’s emphasis on harmonizing nature and human spaces.
The Taj Mahal in India, one of the Seven Wonders of the World, is another magnificent testament to Islamic architecture. Built by Emperor Shah Jahan in memory of his wife, this mausoleum is renowned for its elegant design, delicate marble inlays, and symmetrical gardens.
The Decline and Legacy of the Islamic Empire
The Islamic Empire’s decline can be attributed to various factors, including internal conflicts, external invasions, and the emergence of regional powers. The empire faced internal divisions between different factions, leading to power struggles and weakening central authority.
External forces, such as the Crusades and the Mongol invasions, also played a significant role in the empire’s decline. The Crusades, a series of religious wars, disrupted trade routes and strained the empire’s resources. The Mongol invasions, particularly the sacking of Baghdad in 1258, dealt a severe blow to the Abbasid Caliphate, further fracturing the once-mighty empire.
Despite its decline, the Islamic Empire’s legacy continues to shape the world. Its contributions to architecture, science, mathematics, and philosophy laid the foundation for future advancements. The spread of Islam and the empire’s cultural influence left an indelible mark on societies across Asia, Africa, and Europe, forging connections and shaping the diverse world we live in today.
Exploring the rise of the Islamic Empire provides us with a deeper understanding of the historical events, cultural exchange, and intellectual achievements that unfolded during this transformative period. It serves as a reminder of the enduring impact of empires and the power of intercultural exchange in shaping the course of human history.
Exploring the Rise of the Islamic Empire: A Historical Overview
The rise of the Islamic Empire marks a significant period in world history. Beginning in the 7th century, the empire experienced extraordinary growth and influence, shaping the political, social, and cultural landscapes of the regions it conquered. This historical overview sheds light on the key events and factors that contributed to the empire’s rise.
- Founding of Islam by the Prophet Muhammad
- Expansion of the Islamic Empire through military campaigns
- Development of an advanced administrative system
- Islamic Golden Age of art, science, and literature
The Islamic Empire’s rise was propelled by an effective military, a centralized governance system, and a unifying faith. The successful military campaigns, led by skilled Muslim commanders, led to the rapid expansion of the empire across the Middle East, North Africa, and parts of Europe. Islamic scholars and thinkers made remarkable contributions during the Islamic Golden Age, advancing fields such as mathematics, medicine, and architecture.
The empire’s cultural and intellectual achievements left a lasting impact on subsequent civilizations. The Islamic Empire’s advanced architectural styles and techniques, such as the use of arches and domes, influenced later architectural developments. Additionally, its preservation and translation of ancient Greek and Roman texts helped disseminate classical knowledge to Europe during the Renaissance.
Key Takeaways – Exploring the Rise of the Islamic Empire: A Historical Overview
- The Islamic Empire was founded by Prophet Muhammad in the 7th century.
- The empire rapidly expanded through military conquests and savvy diplomacy.
- The Islamic Empire’s golden age saw advancements in science, philosophy, and art.
- The empire’s decline was marked by internal conflicts and external invasions.
- The legacy of the Islamic Empire shaped the modern world, influencing culture, architecture, and legal systems.
Frequently Asked Questions
Welcome to our FAQ section on exploring the rise of the Islamic Empire! Here, we have compiled some commonly asked questions about the historical overview of this significant empire and provided detailed answers for your understanding. Let’s dive in!
1. What led to the rise of the Islamic Empire?
The rise of the Islamic Empire can be attributed to several key factors. One major factor was the military conquests led by the early Muslim leaders, such as Abu Bakr and Caliph Umar, who expanded Muslim territories and brought more regions under Islamic rule. Another important factor was the appeal of the Islamic faith, which attracted many converts and supporters across different regions. Additionally, the Islamic Empire benefitted from its efficient administration, including its system of governance and laws, which helped maintain social order and stability.
Furthermore, the Islamic Empire’s policies of tolerance towards non-Muslims and the encouragement of trade and commerce also played a crucial role in its rise. The empire became a center of intellectual, cultural, and scientific advancements, attracting scholars, artisans, and merchants from various parts of the world. These combined factors contributed to the rapid expansion and prominence of the Islamic Empire.
2. What were the major achievements of the Islamic Empire?
The Islamic Empire witnessed remarkable achievements in various spheres, influencing the course of history. One of its notable achievements was the preservation and translation of ancient knowledge from diverse civilizations, including Greek, Roman, Persian, and Indian, into Arabic. This intellectual tradition, known as the Islamic Golden Age, led to advancements in fields such as mathematics, astronomy, medicine, and philosophy.
Moreover, the Islamic Empire made significant contributions to architecture, with the construction of magnificent structures like the Dome of the Rock and the Alhambra. Islamic art, particularly in the form of calligraphy and geometric patterns, flourished, leaving a lasting impact on visual arts and design. The empire also played a crucial role in the development and dissemination of Islamic literature, poetry, and music, enriching Islamic culture and influencing the world at large.
3. What was the political structure of the Islamic Empire?
The political structure of the Islamic Empire was primarily based on a theocratic system, where the Caliph, as the successor of the Prophet Muhammad, held both religious and political authority. The Caliphate served as the central governing institution, with multiple Caliphates established throughout the empire’s history, including the Rashidun, Umayyad, Abbasid, and Fatimid Caliphates.
Under the Caliphate, the empire was divided into provinces, each governed by a governor or emir who was responsible for maintaining law and order and collecting taxes. The Caliphate also had a council of advisors, known as the Shura, which provided counsel to the Caliph. However, over time, the political structure of the Islamic Empire evolved, with regional and local rulers gaining more autonomy and power.
4. How did the Islamic Empire impact trade and commerce?
The Islamic Empire played a significant role in facilitating trade and commerce, connecting regions and promoting economic growth. The empire’s expansive trade network, including the famous Silk Road, allowed for the exchange of goods, ideas, and cultural influences between the East and the West.
Islamic merchants, known as the Mamluks, became renowned for their expertise in trade, establishing trade routes and commercial centers in major cities like Baghdad, Cairo, and Damascus. The Islamic Empire introduced innovations in finance and banking, including the development of early forms of banking such as the letters of credit and partnership contracts. These advancements in trade and finance stimulated economic prosperity and cultural exchange within the empire and beyond.
5. How did the decline of the Islamic Empire occur?
The decline of the Islamic Empire can be attributed to several factors. One significant factor was internal conflicts and political rivalries within the empire, leading to the fragmentation of political power and the emergence of independent regional powers.
The external pressures of invasions by the Mongols, Crusaders, and European powers also weakened the empire. Additionally, economic decline, including inflation and fiscal mismanagement, contributed to the empire’s deterioration. The rise of new powers in Europe, such as the Ottoman Empire, further challenged the Islamic Empire’s influence and eventually led to its downfall.
The rise and fall of the medieval Islamic Empire – Petra Sijpesteijn \u0026 Birte Kristiansen
In conclusion, the rise of the Islamic Empire marked a significant turning point in history. From its humble beginnings in the 7th century, the empire expanded rapidly, encompassing vast territories and establishing a rich and diverse cultural legacy.
Through the spread of Islam, the empire brought about profound political, social, and economic transformations, creating a new order that would shape the course of history for centuries to come. The rise of the Islamic Empire stands as a testament to the power of faith, conquest, and the enduring impact of a civilization that continues to influence the world today.