The rise of Islamic empires and states is a fascinating chapter in human history, marked by the spread of Islam, the formation of powerful dynasties, and the flourishing of Islamic culture and civilization. It is a story of conquest and diplomacy, of political and military strategies, and of the interplay between religion, power, and governance. Exploring this historical overview presents an opportunity to delve into the complexities of Islam’s impact on the world and to understand the dynamics that shaped the rise and fall of Islamic empires.
From the 7th to the 17th centuries, Islamic empires and states emerged across vast territories, leaving an indelible mark on the regions they controlled. The conquests of the Rashidun Caliphate and the subsequent Umayyad and Abbasid dynasties established a new order, bringing Islam to new lands and transforming societies. These empires were centers of cultural, scientific, and intellectual advancements, fostering trade, innovation, and artistic expression. With the decline of the Abbasid Caliphate, new Islamic states emerged, such as the Seljuks, the Mughals, and the Ottomans, further shaping the world we know today. Exploring the rise of Islamic empires and states provides insights into the political, social, and religious forces that shaped the course of history, offering a deeper understanding of the Islamic world and its contributions to humanity.
Delve into the extensive history of Islamic Empires and States, and gain a comprehensive overview of their rise and impact. From the powerful empires of the Abbasids and Umayyads to the influential states of the Seljuks and Mughals, explore the political, cultural, and religious dimensions that shaped these civilizations. Uncover the key factors that led to their dominance and understand the lasting legacies they left behind. Discover the rich tapestry of Islamic history and the empires that shaped the world.
Contents
- The Spread of Islam and the Formation of Islamic Empires
- Exploring the Rise of Islamic Empires and States: A Historical Overview
- Key Takeaways for “Exploring the Rise of Islamic Empires and States: A Historical Overview”
- Frequently Asked Questions
- 1. How did the Islamic empires and states come into existence?
- 2. Which were the notable Islamic empires and states?
- 3. What were the key achievements of Islamic empires and states?
- 4. What led to the decline of Islamic empires and states?
- 5. What is the legacy of Islamic empires and states in the modern world?
- The rise and fall of the medieval Islamic Empire – Petra Sijpesteijn \u0026 Birte Kristiansen
The Spread of Islam and the Formation of Islamic Empires
The rise of Islamic empires and states during the medieval period had a profound impact on world history. It marked a significant transformation in political, cultural, and intellectual spheres. This article explores the unique aspects of the rise of Islamic empires and states, shedding light on their historical significance and contributions to the world.
1. The Expansion of the Arab Empire
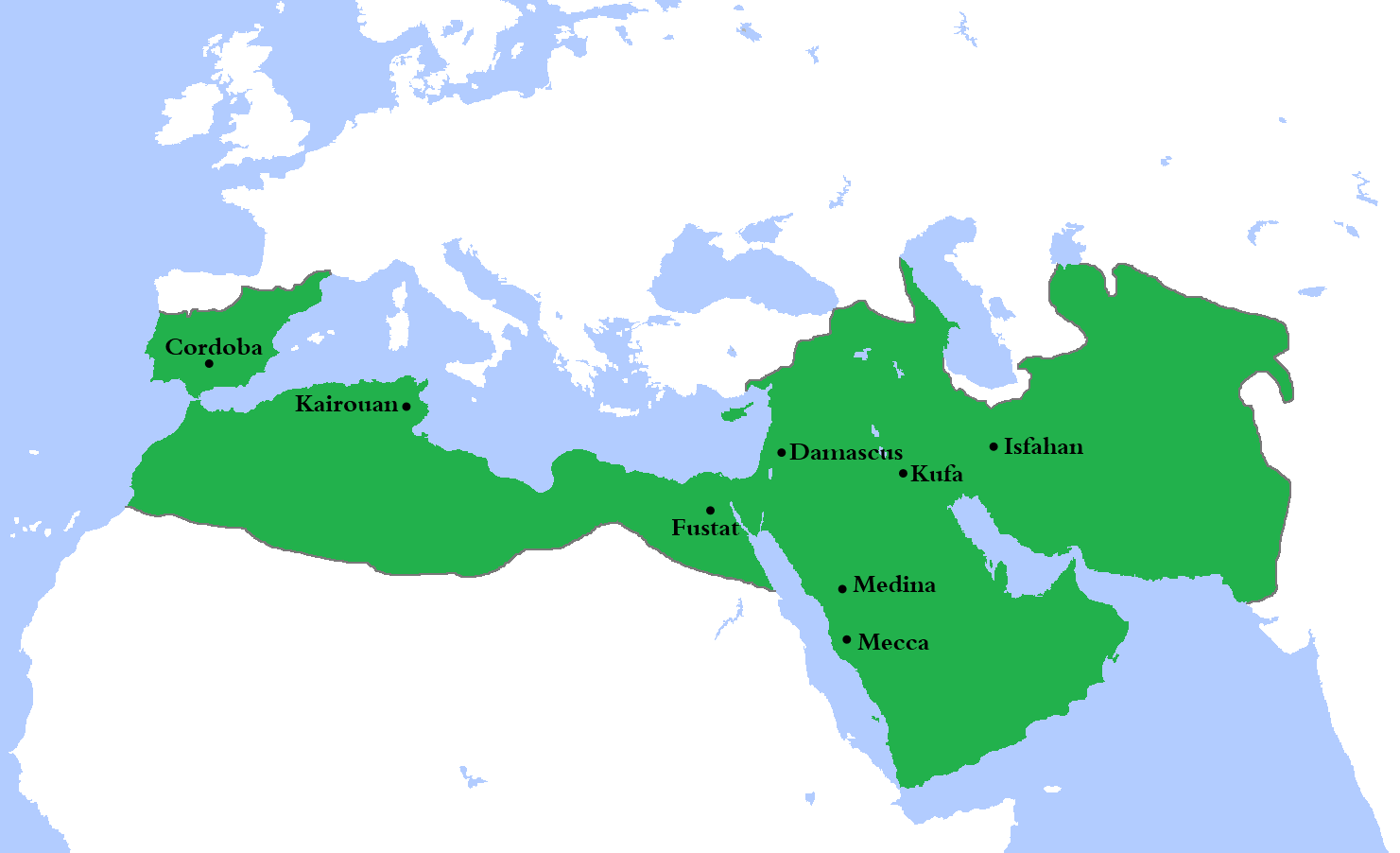
The early Islamic period witnessed the rapid expansion of the Arab Empire. Under the leadership of Prophet Muhammad and his successors, the Arab armies conquered vast territories, establishing a unified political structure known as the Caliphate. The Caliphate encompassed regions from the Arabian Peninsula to North Africa, the Levant, and even parts of Europe.
The key factors behind the success of the Arab Empire’s expansion were the unity and military prowess of the Arab armies. Additionally, the concept of jihad, which refers to the struggle or effort to spread Islam, played a crucial role in fueling the conquests. The Arab Empire’s conquests not only had political and military implications but also facilitated the spread of Islamic culture, language, and religion.
The Arab Empire’s conquests had a lasting impact on the regions it came into contact with. It led to the Arabization and Islamization of many territories, influencing their languages, customs, and social structures. Moreover, the Arab Empire served as a conduit for the transmission of knowledge and ideas, playing a vital role in the preservation and translation of classical Greek and Roman texts.
However, the Arab Empire eventually fragmented into various independent states, marking the emergence of different Islamic dynasties and kingdoms across the Muslim world.
1.1 The Umayyad Caliphate
The first and most notable Islamic dynasty to emerge after the fall of the Arab Empire was the Umayyad Caliphate. The Umayyads established their capital in Damascus and expanded their rule across a vast territory, including Spain (Al-Andalus), North Africa, the Levant, and parts of Central Asia.
The Umayyads adopted an imperial approach to governance, promoting Arab culture and establishing Arabic as the official language of administration. They also built grand structures, such as the Dome of the Rock in Jerusalem, showcasing their architectural achievements.
Despite their military successes and cultural contributions, the Umayyads faced significant challenges, particularly in the form of political and sectarian unrest. The Umayyad dynasty was eventually overthrown by the Abbasids, leading to the establishment of a new Islamic empire.
1.2 The Abbasid Caliphate
The Abbasid Caliphate, founded by Abu al-Abbas, emerged as a new Islamic dynasty following the overthrow of the Umayyads. The Abbasids established their capital in Baghdad, which became a center of intellectual, cultural, and economic activity.
The Abbasids embraced Persian administrative practices and sought to create a cosmopolitan Islamic state that incorporated the diverse cultures and traditions of the territories under their rule. They promoted an atmosphere of intellectual inquiry and patronized scholars, leading to significant advancements in various fields, including mathematics, astronomy, medicine, and philosophy.
However, despite their dedication to scholarship and culture, the Abbasids faced numerous challenges, including internal power struggles, economic decline, and invasions by external forces. The empire eventually fragmented into several smaller states, marking the end of the Abbasid Caliphate as a unified political entity.
2. The Ottoman Empire: The Last Great Islamic Empire
The Ottoman Empire, founded in the 13th century by Osman I, emerged as the last great Islamic empire. From its capital in Istanbul, the Ottomans expanded their rule across three continents, including Anatolia, the Balkans, the Middle East, and parts of Eastern Europe.
The Ottoman Empire’s military strength and administrative prowess allowed it to conquer and assimilate diverse regions and peoples. The empire’s governance system, based on a centralized bureaucracy and the institution of the Sultanate, provided stability and ensured the efficient administration of the territories.
The Ottoman Empire reached its zenith under Suleiman the Magnificent, known for his military campaigns, legal reforms, and patronage of the arts and architecture. During this period, the empire controlled strategic trade routes and played a pivotal role in the geopolitics of the time.
However, the Ottoman Empire faced challenges in the form of external pressures, such as European expansionism and colonial ambitions. The empire gradually declined in power and influence, leading to its dissolution at the end of World War I.
2.1 Legacy of the Islamic Empires
The rise and fall of Islamic empires left a lasting legacy on the regions they once governed. The contributions of these empires to various fields, including architecture, art, science, and literature, have had a profound impact on world history.
The Islamic empires played a crucial role in the preservation and translation of classical Greek and Roman texts, contributing to the European Renaissance. They also advanced knowledge in various scientific disciplines, particularly medicine, astronomy, and mathematics.
Additionally, the Islamic empires promoted cultural exchange and intellectual inquiry, creating an environment conducive to the flourishing of arts and literature. They left behind magnificent architectural wonders, such as the Alhambra in Spain, the Taj Mahal in India, and the Blue Mosque in Istanbul, which continue to inspire awe and admiration.
The legacy of the Islamic empires extends beyond their cultural and intellectual contributions. These empires also shaped political and social structures, leaving a lasting impact on the regions they once governed. The rise of Islamic empires and states remains a significant chapter in world history, reflecting the diversity, complexity, and enduring influence of the Islamic civilization.
The exploration of the rise of Islamic empires and states provides valuable insights into the historical forces that shaped the Muslim world and its interactions with other civilizations. From the expansion of the Arab Empire to the grandeur of the Ottoman Empire, each period offers unique perspectives on the rise, consolidation, and eventual decline of Islamic political power. Understanding the historical context of these empires allows for a deeper appreciation of their legacies and the contributions they have made to the world.
Exploring the Rise of Islamic Empires and States: A Historical Overview
The rise of Islamic empires and states marks a crucial period in history, shaping the course of civilizations across the Middle East, North Africa, and beyond. This historical overview delves into the key events, socio-cultural influences, and political developments that contributed to the growth and dominance of Islamic empires and states.
Beginning in the 7th century with the rapid expansion of the Islamic caliphate under the leadership of Prophet Muhammad, Islamic empires and states emerged as major world powers. The Umayyad Caliphate, Abbasid Caliphate, and Ottoman Empire were among the most influential Islamic entities, spanning vast territories and exerting significant political, economic, and cultural influence.
The rise of Islamic empires and states can be attributed to various factors, including military strategies, administrative reforms, religious unity, and patronage of arts and sciences. These empires fostered cosmopolitan societies, fostering the exchange of knowledge, ideas, and innovations.
Furthermore, the Islamic empires and states played a significant role in preserving and expanding classical knowledge, including advancements in mathematics, astronomy, medicine, and literature. They also facilitated the diffusion of ideas between different civilizations through trade networks and cultural interactions.
The impact of these empires on world history is undeniable, and their contributions continue to shape the cultural, political, and social landscape of the regions they once ruled. By exploring the rise of Islamic empires and states, we gain a deeper understanding of the historical forces that have shaped our world.
Key Takeaways for “Exploring the Rise of Islamic Empires and States: A Historical Overview”
- The Islamic empires and states rose to power through conquest and expansion.
- Their strong military forces and efficient administration helped them establish and maintain their dominance.
- Islamic empires such as the Abbasids and the Ottomans made significant contributions to science, art, and culture.
- The spread of Islam played a crucial role in the expansion of these empires.
- Trade routes and economic prosperity were key factors in the rise of Islamic empires and states.
Frequently Asked Questions
In this historical overview, we will explore the rise of Islamic empires and states. Here are some frequently asked questions about this topic:
1. How did the Islamic empires and states come into existence?
The Islamic empires and states emerged during the medieval period following the rise of Islam in the Arabian Peninsula in the 7th century. The expansion of Islam through military conquests, known as the Islamic conquests, played a significant role in the formation of these empires and states. As the Arab armies conquered territories, they established Islamic rule and introduced Islamic laws and customs.
The first Islamic empire, the Rashidun Caliphate, was established after the death of Prophet Muhammad in 632 CE. It was followed by the Umayyad Caliphate, Abbasid Caliphate, and several other Islamic dynasties and states that ruled different regions of the world.
2. Which were the notable Islamic empires and states?
Several notable Islamic empires and states emerged throughout history. Some of the most renowned ones include:
- The Umayyad Caliphate (661-750 CE)
- The Abbasid Caliphate (750-1258 CE)
- The Ottoman Empire (1299-1922 CE)
- The Safavid Empire (1501-1736 CE)
- The Mughal Empire (1526-1857 CE)
These empires played a significant role in shaping the political, cultural, and economic landscapes of their respective regions.
3. What were the key achievements of Islamic empires and states?
The Islamic empires and states made significant contributions in various fields, leaving a lasting impact on history. Some of their key achievements include:
- Advancements in science, medicine, and astronomy
- Development of intricate architectural styles, such as the Taj Mahal and Alhambra
- Preservation and translation of ancient Greek and Roman texts
- Promotion of trade and establishment of extensive trade networks
- Development of beautiful literary works, such as poetry and epic tales
These achievements showcased the intellectual and cultural richness of the Islamic empires and states.
4. What led to the decline of Islamic empires and states?
The decline of Islamic empires and states can be attributed to various factors. Some of the significant factors include:
- Internal conflicts and power struggles within the ruling dynasties
- Invasions and attacks by external forces
- Socioeconomic challenges and declining trade routes
- The rise of European powers and colonialism
- Internal divisions and religious tensions
These factors gradually weakened the empires and states, leading to their eventual decline and fragmentation.
5. What is the legacy of Islamic empires and states in the modern world?
The legacy of Islamic empires and states can still be seen in various aspects of the modern world. Some of the notable legacies include:
- The spread of Islam as a major world religion
- The influence of Islamic architecture and art styles
- The establishment of educational institutions and centers of learning
- The preservation and dissemination of scientific and philosophical knowledge
- The impact of Islamic legal principles on modern legal systems
Overall, the rise and decline of Islamic empires and states have left an indelible mark on history and continue to shape our world today.
The rise and fall of the medieval Islamic Empire – Petra Sijpesteijn \u0026 Birte Kristiansen
To sum up, the rise of Islamic empires and states was a significant historical phenomenon. It shaped the course of history and had a profound impact on various aspects of society, culture, and politics. The Islamic empires and states emerged from the expansion of Islamic civilization, spreading across different regions from the 7th to the 16th centuries.
These empires and states, such as the Abbasids, Umayyads, and Ottomans, established powerful political structures and contributed to the development of science, arts, and trade. They fostered intellectual and cultural exchange, contributing to the preservation and transmission of knowledge from ancient civilizations. Furthermore, the Islamic empires and states had a lasting influence on the religion, as they codified Islamic law and institutions, spreading the faith to new regions.