Exploring the Map of the Byzantine Empire at its Height: A Historical Overview is a fascinating journey into one of the most powerful and enduring empires of the medieval world. Spanning from the 4th to the 15th centuries, the Byzantine Empire was a beacon of civilization, blending Eastern and Western influences to create a rich and dynamic society.
At its height, the Byzantine Empire reached its territorial zenith, stretching from the Mediterranean to the Black Sea, and from Italy to the Middle East. Its capital, Constantinople, was a cultural and economic hub that rivaled any city in the world. Exploring the map of this ancient empire allows us to trace the rise and fall of an extraordinary civilization, uncovering the secrets of its political, military, and cultural achievements.
Delve into the historical map of the Byzantine Empire during its height to gain a comprehensive understanding of one of the most significant empires in history. Explore the bordering regions, key cities, and notable landmarks that made up this powerful civilization. Uncover the empire’s expansion, trade routes, and strategic locations, shedding light on its political, cultural, and military influence. By studying the map, you can appreciate the vast scope and enduring legacy of the Byzantine Empire.
Contents
- The Geographical Extent of the Byzantine Empire
- Exploring the Map of the Byzantine Empire at its Height: A Historical Overview
- Key Takeaways:
- Frequently Asked Questions
- 1. What were the territorial boundaries of the Byzantine Empire at its height?
- 2. What were the major cities within the Byzantine Empire?
- 3. What were the defining characteristics of the Byzantine Empire?
- 4. How did the Byzantine Empire decline and eventually fall?
- 5. What is the significance of the Byzantine Empire in history?
- History of Byzantine Empire in 6 minutes on Map Description | Past to Future
The Geographical Extent of the Byzantine Empire
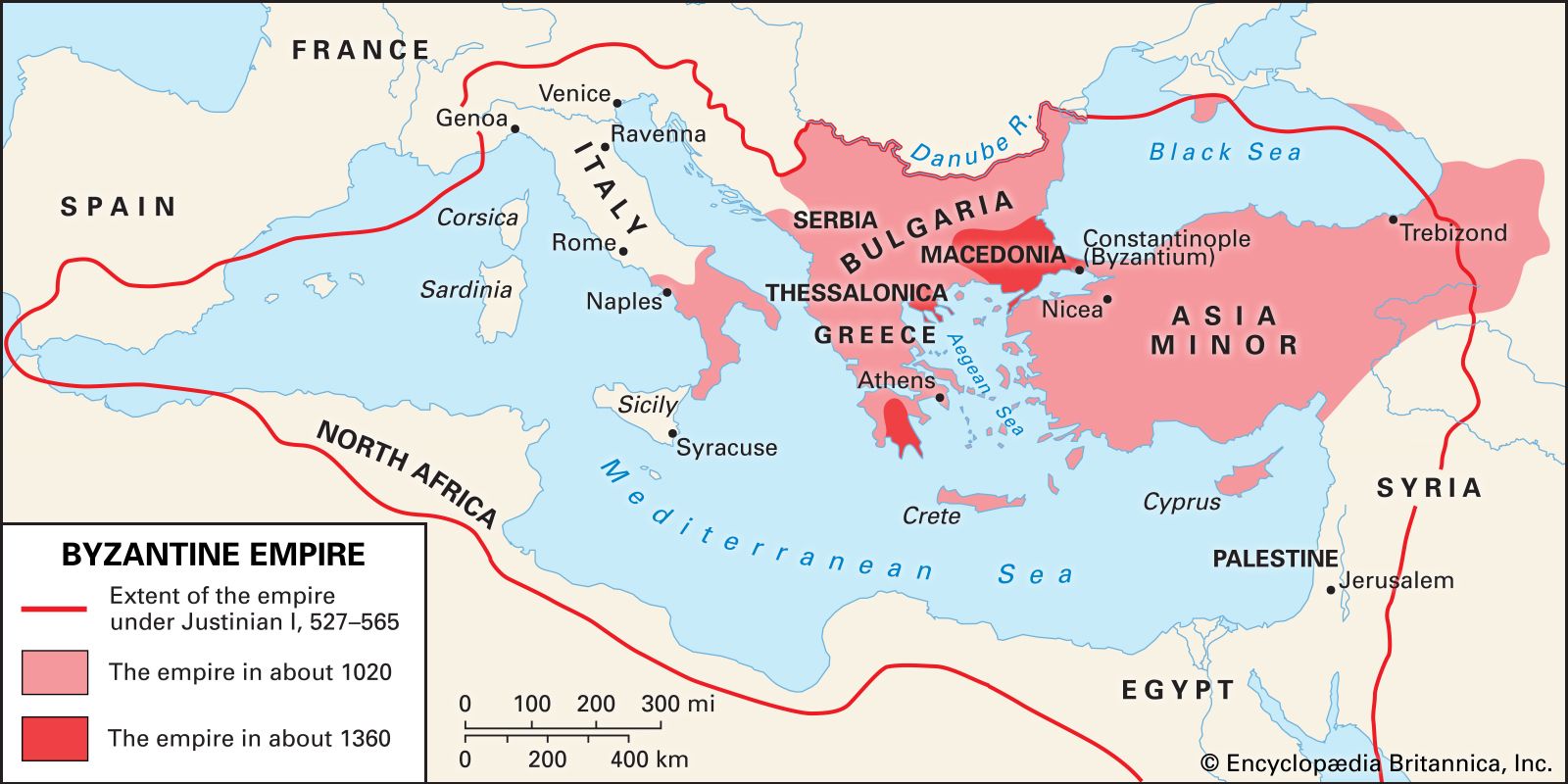
The Byzantine Empire, also known as the Eastern Roman Empire, reached its height of territorial expansion during the reign of Justinian I (527-565 CE). At its peak, the empire spanned three continents, encompassing territories in Europe, Asia, and Africa. This vast geographical extent is a testament to the empire’s military prowess and strategic diplomacy.
The Byzantine Empire was centered around the city of Constantinople (modern-day Istanbul), which served as the capital and the cultural and economic hub. From this strategic location, the empire controlled key trade routes, including the Silk Road, allowing it to flourish economically. By exploring the map of the Byzantine Empire at its height, we gain insights into its influence and power across different regions.
In this article, we will delve into the geographical expansion of the Byzantine Empire, examining its presence in Europe, Asia, and Africa. We will explore the diverse cultures and peoples that were part of the empire and analyze the lasting impact of Byzantine rule in these regions.
Let us embark on a journey through the map of the Byzantine Empire at its height to unveil the historical significance of this remarkable civilization.
Europe: The Core of the Byzantine Empire
Europe was the heartland of the Byzantine Empire, where its capital Constantinople was situated. The empire’s control extended over the majority of the Balkans, including Greece, Thrace, Macedonia, and parts of modern-day Bulgaria and Albania.
The Byzantine Empire played a crucial role in shaping European history. Its strategic position enabled it to act as a defensive bulwark against invading forces. The empire successfully defended against barbarian invasions, such as those from the Goths and the Huns, preserving the Greco-Roman legacy and maintaining a Christian stronghold.
Moreover, the Byzantines left an enduring architectural and cultural legacy in Europe. The notable examples include the majestic Hagia Sophia, the grand Byzantine churches, and the intricate mosaics that adorned these structures. Byzantine artistic and architectural influences can be observed in various European countries, such as Italy, where the influence of Byzantine art can be seen in the iconic mosaics of Ravenna.
The Byzantine Empire’s connection with Europe extended beyond territorial control. The empire maintained strong diplomatic ties through intermarriages with European royal families, paving the way for cultural exchanges and the spread of Byzantine influence in various realms.
Asia: Byzantine Influence Across the East
Beyond Europe, the Byzantine Empire expanded into Asia, occupying parts of modern-day Turkey, Syria, and Israel. This region, known as Anatolia, was crucial for the empire’s economic prosperity as it provided vital agricultural resources and served as a buffer against invading forces.
The Byzantines had a complex relationship with the neighboring Islamic powers. They engaged in both conflict and trade with the Arab Caliphates, such as the Umayyad and Abbasid dynasties. The city of Antioch, for example, was a vibrant center of cultural exchange between Byzantines, Arabs, and various other groups.
Byzantine territorial control in Asia fluctuated over time due to conflicts with the Arab forces. However, the Byzantines managed to retain their influence and authority across the region, ensuring the preservation of the Byzantine cultural and political identity in this part of the empire.
Moreover, the Byzantines played a vital role in transmitting ancient Greek knowledge to the Islamic world, particularly during the translation movement in the Abbasid period. Byzantine scholars preserved and translated numerous Greek texts, including scientific, philosophical, and medical works, thus contributing to the preservation and development of knowledge in the Islamic Golden Age.
Africa: Byzantine Presence on the Mediterranean Coast
The Byzantine Empire also had a significant presence in Africa, primarily along the coast of the Mediterranean Sea. The region known as the Exarchate of Africa included territories in modern-day Tunisia, Libya, and parts of Algeria.
Carthage, once a thriving center of the ancient Phoenician civilization, became an important Byzantine stronghold in Africa. The Byzantines sought to maintain control over this region due to its strategic importance for trade and as a gateway to the Western Mediterranean.
The Byzantines faced several challenges to their control over Africa. The indigenous Berber populations, as well as invasions from Vandals and later the Arab conquests, posed significant threats. However, Byzantine influence endured in pockets along the coast, maintaining cultural links with the wider empire.
The Legacy of the Byzantine Empire
The map of the Byzantine Empire at its height showcases the empire’s extensive reach and its impact across Europe, Asia, and Africa. The influence of Byzantine culture, architecture, and art can still be observed today in various regions that were once part of the empire.
Moreover, the Byzantine Empire played a significant role in preserving and transmitting ancient classical knowledge, serving as a bridge between the Greco-Roman world and the Islamic civilizations that followed. Byzantine scholars and their works contributed to the intellectual and cultural flourishing of these subsequent civilizations.
While the empire ultimately fell to the Ottoman Turks in 1453, the Byzantine legacy continues to captivate historians, archaeologists, and enthusiasts alike. Exploring the map of the Byzantine Empire at its height allows us to appreciate the complex and multifaceted nature of this fascinating civilization and its enduring impact on the world.
Exploring the Map of the Byzantine Empire at its Height: A Historical Overview
The Byzantine Empire, also known as the Eastern Roman Empire, was one of the most influential civilizations in history. At its height, it stretched from present-day Turkey to Egypt and encompassed parts of Europe, Asia, and Africa. The empire’s capital, Constantinople (modern-day Istanbul), was a cultural and economic hub that connected the East and West.
The Byzantine Empire experienced periods of expansion and decline throughout its existence, and its borders fluctuated over time. By exploring the map of the empire at its height, we can gain a better understanding of its territorial extent and geopolitical importance. The empire’s map reveals strong military presence along its frontiers, strategic coastal positions, and the major trade routes it controlled.
During its peak, the Byzantine Empire was characterized by a flourishing economy, rich artistic and architectural heritage, and the preservation of classical knowledge. Its influence extended beyond its borders through diplomacy, religion, and trade. Today, remnants of the Byzantine Empire can still be seen in the architecture of churches, mosaics, and manuscripts that have survived the test of time.
Key Takeaways:
- The Byzantine Empire was at its height during the reign of Emperor Justinian I in the 6th century.
- The Byzantine Empire had a strong centralized government led by the emperor.
- The empire controlled territories in Europe, Asia, and North Africa.
- Constantinople, the capital of the Byzantine Empire, was a thriving cultural and economic center.
- The Byzantine Empire made significant contributions to art, architecture, and religious theology.
Frequently Asked Questions
In this section, we will answer some frequently asked questions about exploring the map of the Byzantine Empire at its height and provide a historical overview.
1. What were the territorial boundaries of the Byzantine Empire at its height?
The Byzantine Empire reached its height of territorial expansion during the reign of Emperor Justinian I (527-565 AD). At its largest extent, it included parts of southeastern Europe, the eastern Mediterranean, and western Asia. The empire’s boundaries stretched from the Danube River in the north to the Arabian Peninsula in the south, and from the Iberian Peninsula in the west to the borders of Persia in the east.
The capital city of the Byzantine Empire, Constantinople (now Istanbul), was strategically located along the trade routes between Europe and Asia, further contributing to the empire’s wealth and influence.
2. What were the major cities within the Byzantine Empire?
The Byzantine Empire was known for its numerous thriving cities, some of which played significant roles in shaping its history and culture. Here are a few notable cities:
a) Constantinople: The capital city and the political, cultural, and economic center of the Byzantine Empire. It was a cosmopolitan city with impressive infrastructure, including the renowned Hagia Sophia.
b) Thessaloniki: A major port city in northern Greece and an important trade hub in the Balkans.
c) Alexandria: A significant city in Egypt and a gateway to trade between Europe, Africa, and Asia.
3. What were the defining characteristics of the Byzantine Empire?
The Byzantine Empire had several defining characteristics that set it apart from other medieval civilizations:
a) Greek Influence: The Byzantine Empire inherited and preserved much of the Hellenistic culture, which heavily influenced its art, literature, and education.
b) Orthodox Christianity: Byzantium was the center of Eastern Orthodox Christianity, with the emperor serving as both the political and religious leader.
c) Strong Centralized Government: The Byzantine Empire had a strong and centralized bureaucracy, with the emperor at the top of the hierarchical structure.
4. How did the Byzantine Empire decline and eventually fall?
The decline of the Byzantine Empire can be attributed to various factors:
a) External Threats: The empire faced numerous invasions from various external forces, including the Arab Caliphates, the Seljuk Turks, and the Fourth Crusade.
b) Internal Struggles: Power struggles, political instability, and economic decline weakened the empire from within.
c) Ottoman Conquest: The final blow came with the siege of Constantinople by the Ottoman Turks in 1453, leading to the fall of the Byzantine Empire.
5. What is the significance of the Byzantine Empire in history?
The Byzantine Empire played a crucial role in the development and preservation of Greek and Roman culture. It served as a bridge between the ancient world and the Renaissance period, preserving and transmitting classical knowledge, art, and literature.
The Byzantine Empire also acted as a buffer between Western Europe and the Islamic world, safeguarding Europe from Arab invasions and influencing the spread of Christianity in Eastern Europe and Russia.
History of Byzantine Empire in 6 minutes on Map Description | Past to Future
To conclude, exploring the map of the Byzantine Empire at its height provides a valuable historical overview. This empire was vast, stretching from Eastern Europe to the Middle East, and its map shows the extent of its power and influence.
By examining the map, we can see the cities, trade routes, and territories that made up the Byzantine Empire. It gives us a visual representation of the empire’s strength and wealth, as well as its connections to other regions and civilizations.