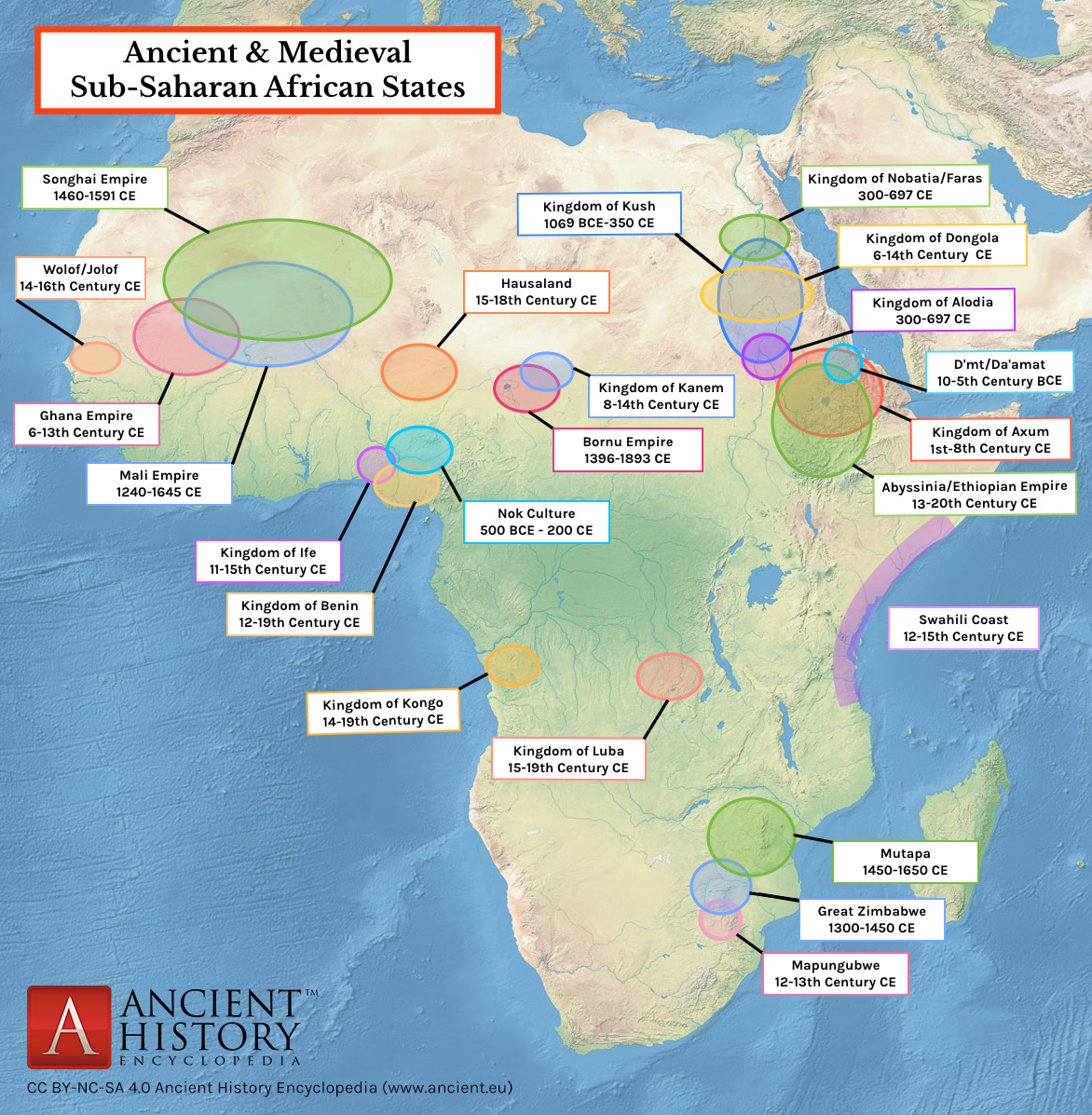
As we explore the map of ancient civilizations in Africa, we embark on a historical journey filled with fascinating discoveries and rich cultural heritage. Africa, often overlooked in mainstream narratives, is home to a diverse range of ancient civilizations that shaped the course of human history in profound ways.
The map of ancient civilizations in Africa presents a captivating tapestry of cultures and societies that flourished across the vast continent. From the mighty kingdoms of Egypt and Kush to the trading empires of Axum and Ghana, Africa’s ancient past is a testament to the ingenuity and resilience of its peoples. By exploring this map, we gain valuable insights into the complex interactions and exchanges that occurred among these civilizations, as well as their enduring legacies that continue to shape Africa and the world today.
Embark on a historical journey through the map of ancient civilizations in Africa. This fascinating exploration takes you back in time to discover the rich history and cultural heritage of Africa’s past. From the pyramids of Egypt to the legendary Kingdom of Aksum, the map reveals the diverse empires and societies that thrived across the continent. Uncover the mysteries of Great Zimbabwe, marvel at the rock-hewn churches of Lalibela, and immerse yourself in the fascinating stories of Africa’s ancient civilizations.
Contents
- Ancient Nubia: The Land of Gold and Powerful Empires
- Exploring the Map of Ancient Civilizations in Africa: A Historical Journey
- Key Takeaways
- Frequently Asked Questions
- 1. What were the major ancient civilizations in Africa?
- 2. How did ancient African civilizations impact the world?
- 3. How were ancient African civilizations organized?
- 4. What were the main achievements of ancient African civilizations?
- 5. How can we explore the ancient civilizations in Africa today?
- Exploring Ancient African Civilizations Map
Ancient Nubia: The Land of Gold and Powerful Empires
Ancient Nubia, located in present-day Sudan and southern Egypt, was a land that flourished with trade routes, rich resources, and powerful empires. This region was referred to as the “Land of Gold” due to its abundant gold deposits, which made it a significant economic hub. The ancient civilization of Nubia had a complex political and social structure, leaving behind fascinating ruins and artifacts that offer insights into their achievements and cultural developments.
Nubia is believed to have had its first major civilization around 3500 BCE, with the emergence of the Kingdom of Kerma. The Kerma civilization was known for its advanced agricultural practices, intricate pottery, and impressive architecture. They built large mud-brick structures known as deffufas, some of which still stand today. The Kingdom of Kerma was eventually overthrown by the Egyptians in the 16th century BCE, marking the beginning of Egyptian domination in Nubia.
The Egyptian influence in Nubia can be seen in the construction of temples, such as the famous Abu Simbel temples, which were dedicated to the pharaoh Ramses II. These temples were carved out of solid rock and serve as a testament to the remarkable engineering skills of the ancient Egyptians. The Egyptians also established military forts and trading posts along the Nile River, further solidifying their control of the region.
However, Nubia was not merely a colony of Egypt. It had its own powerful Kushite Empire, which rose to prominence in the 8th century BCE. The Kushites eventually conquered Egypt and established the 25th Dynasty, also known as the Nubian Dynasty. During this period, Nubia experienced a golden age with flourishing arts, monumental architecture, and extensive trade networks.
Axum: The Ancient Ethiopian Empire
Axum, located in present-day Ethiopia, was one of the most prosperous and influential ancient civilizations in Africa. The Axumite Empire reached its peak between the 1st and 7th centuries CE and had a significant impact on the culture, religion, and trade of the region. The empire was strategically located along the Red Sea, allowing it to control important trade routes connecting Africa, Arabia, and the Roman Empire.
The Axumites were known for their advanced agricultural techniques, monumental architecture, and impressive engineering skills. One of the most iconic structures of Axum is the obelisk, which served as a representation of power and status for the empire. These tall stone pillars, some of which are still standing today, are adorned with intricate carvings and inscriptions.
Another significant aspect of Axum’s civilization was its involvement in trade. The empire controlled the lucrative trade of ivory, gold, and spices, which brought wealth and prosperity to the region. Axum also played a crucial role in the spread of Christianity in Africa, becoming one of the first Christian kingdoms in the world.
The decline of the Axumite Empire is still shrouded in mystery, with various factors such as the rise of Islam and changing trade routes contributing to its downfall. However, the legacy of Axum continues to shape Ethiopian culture and identity to this day.
The Great Zimbabwe: A Monumental Stone City
The Great Zimbabwe, located in present-day Zimbabwe, was once a thriving ancient city and the political and economic center of the Kingdom of Zimbabwe. This stone city, built between the 11th and 15th centuries CE, is a testament to the architectural and engineering skills of its inhabitants. The city was constructed entirely of stone, with massive walls and intricate passageways.
The Great Zimbabwe was renowned for its gold trade, which brought great wealth and prosperity to the kingdom. It was strategically located along the trade routes of the Indian Ocean, enabling the Kingdom of Zimbabwe to establish strong trading relationships with other African civilizations and with Arab and Indian merchants.
One of the most iconic structures in the Great Zimbabwe is the Great Enclosure, a sprawling complex consisting of a massive stone wall with a conical tower. The purpose of this enclosure is still debated by historians, with theories ranging from it being a royal palace to a religious center or a symbol of political power.
The decline of the Great Zimbabwe is believed to be linked to factors such as environmental changes, political instability, and shifts in trade routes. However, its ruins remain an important archaeological site and a testament to the once-great civilization that thrived in the region.
Societal Structure and Cultural Achievements
Ancient African civilizations had complex societal structures that varied across different regions. In Nubia, for example, the Kushite Empire had a hierarchical structure with the king as the central figure of authority. They had a strong military and controlled extensive trade networks.
In Axum, the empire was ruled by a king who held significant religious and political power. The society was stratified, with the ruling elite enjoying privileges and the common people engaging in agricultural activities and trade.
The Great Zimbabwe had a more decentralized political structure, with power dispersed among different ruling families. The society was organized around the production and trade of commodities such as gold, ivory, and cattle.
These ancient civilizations made remarkable cultural achievements in fields such as architecture, art, religion, and literature. They built awe-inspiring structures, created intricate artwork, practiced diverse religious beliefs, and developed sophisticated systems of writing and communication.
Legacy and Historical Significance
The legacy of these ancient African civilizations extends beyond their historical significance. They serve as a source of inspiration and pride for present-day African nations, highlighting the rich and diverse cultural heritage of the continent. The ruins and artifacts left behind provide valuable insights into the advancements and achievements of these civilizations, challenging preconceived notions of Africa’s history and showcasing the continent’s contributions to human civilization.
Exploring the map of ancient civilizations in Africa takes us on a historical journey through a continent that was home to thriving societies, complex political structures, and remarkable cultural achievements. From the gold-rich lands of Nubia to the monumental stone city of Great Zimbabwe, each civilization has its unique story to tell. These ancient civilizations shaped the course of African history and continue to shape the identity and cultural heritage of the continent today.
Exploring the Map of Ancient Civilizations in Africa: A Historical Journey
Africa is home to a rich and diverse history of ancient civilizations. From the powerful kingdoms of Kush and Axum to the great empires of Mali and Songhai, the continent has a fascinating past that stretches back thousands of years. Exploring the map of ancient civilizations in Africa takes us on a historical journey, shedding light on the achievements, culture, and trade routes of these advanced societies.
The map of ancient civilizations in Africa reveals the geographical diversity of these societies. The Nile River, for example, was the lifeblood of Egypt, sustaining its agricultural and economic prosperity. West Africa, with its vast grasslands and access to the Saharan trade routes, was home to thriving empires like Ghana and Mali. The Swahili Coast of East Africa was a hub of trade and commerce, connecting the interior kingdoms to the Indian Ocean.
Each civilization left behind remarkable architectural wonders, such as the ancient pyramids of Egypt, the rock-hewn churches of Ethiopia, and the Great Mosque of Djenné in Mali. These structures showcase the advanced engineering and cultural achievements of ancient African societies.
Exploring the map of ancient civilizations in Africa allows us to appreciate the contributions of these societies to the development of human civilization. It is a testament to the rich history and cultural heritage of the African continent.
Key Takeaways
- Ancient civilizations in Africa have a rich and diverse history.
- Exploring the map of ancient civilizations in Africa takes us on a fascinating historical journey.
- These civilizations left behind impressive architectural structures and artifacts.
- The Nile Valley, including Egypt, was home to one of the most advanced ancient civilizations in Africa.
- Ancient trade routes connected different civilizations across Africa, facilitating cultural exchange.
Frequently Asked Questions
Welcome to our frequently asked questions section on exploring the map of ancient civilizations in Africa. Here, we will answer some common questions about the historical journey through Africa’s rich past.
1. What were the major ancient civilizations in Africa?
Africa is home to several significant ancient civilizations that left an indelible mark on history. Some of the major ancient civilizations in Africa include:
The Egyptians: Known for their impressive pyramids and advancements in art, architecture, and engineering.
The Carthaginians: A maritime civilization that excelled in trade and exploration.
Ghana Empire: A powerful West African empire known for its vast wealth and control over the gold trade.
Zimbabwe: A kingdom revered for its well-planned stone architecture, particularly the Great Zimbabwe ruins.
Axum Empire: An ancient civilization in modern-day Ethiopia that thrived as a major trading center.
2. How did ancient African civilizations impact the world?
Ancient African civilizations made significant contributions that influenced global history. These civilizations:
1. Advanced knowledge and practices in agriculture, architecture, and engineering.
2. Developed innovative trade routes that connected different regions of the world.
3. Contributed to advancements in art, science, and literature.
4. Preserved and transmitted knowledge, leading to the enrichment of future civilizations.
3. How were ancient African civilizations organized?
Ancient African civilizations had diverse organizational structures, varying from centralized monarchies to decentralized societies. Some key aspects of ancient African civilizations’ organization were:
1. Ruling elite: Monarchs and nobility held significant power in centralized states like Egypt and Axum.
2. Social classes: Ancient African societies had hierarchies based on wealth, occupation, and birth.
3. Religious institutions: Religious beliefs and practices played a central role in organizing societies.
4. Family units: Kinship and extended family ties formed the basis of social organization.
4. What were the main achievements of ancient African civilizations?
Ancient African civilizations achieved remarkable feats that left a lasting legacy. Some of their main achievements include:
1. Monumental architecture: Structures like the pyramids of Egypt and the Great Zimbabwe ruins showcase their architectural prowess.
2. Advancements in science and medicine: Ancient Africans developed knowledge in herbal medicine and made significant contributions to astronomy.
3. Artistic excellence: Intricate sculptures, vibrant paintings, and pottery demonstrate their artistic skill.
4. Trade networks: Ancient African civilizations played a vital role in global trade, connecting diverse regions.
5. How can we explore the ancient civilizations in Africa today?
To explore the ancient civilizations in Africa today, you can:
1. Visit archaeological sites: Many ancient sites, such as the Pyramids of Giza and the ruins of Great Zimbabwe, are open to visitors.
2. Explore museums: Museums across Africa house valuable artifacts and exhibits that provide insights into ancient civilizations.
3. Study ancient texts: Learning about ancient African civilizations through scholarly books and writings helps gain a deeper understanding.
4. Engage with local communities: Interacting with local communities can provide valuable cultural insight and opportunities to learn about ancient traditions.
Exploring Ancient African Civilizations Map
In conclusion, exploring the map of ancient civilizations in Africa is a fascinating historical journey. It allows us to uncover the rich and diverse cultures that flourished on the continent thousands of years ago.
By studying the ancient civilizations of Africa, we gain a deeper appreciation for the contributions they made to human history, from the impressive architecture of Egypt to the intricate metalwork of Nok. It is important to continue exploring and preserving the remnants of these ancient civilizations, as they provide valuable insights into our shared past.