The Islamic Empire, also known as the Caliphate, holds the distinction of being the largest Islamic empire in history. With its vast territories spanning from Spain to India, it shaped the course of history and left behind a rich legacy. From its intellectual contributions in science, medicine, and philosophy to its architectural marvels like the Dome of the Rock and the Alhambra, this empire continues to impact our world today.
One of the most significant aspects of exploring the legacy and influence of the largest Islamic empire is understanding its profound impact on knowledge and scholarship. During the Golden Age of Islam, scholars in the Islamic Empire made groundbreaking discoveries and advancements in various fields of study. They translated ancient Greek and Roman texts, preserving and expanding upon the knowledge of previous civilizations. This led to significant contributions in mathematics, astronomy, medicine, and more. For example, the numerals we use today, known as Arabic numerals, were actually developed during this time. Exploring the legacy of the largest Islamic empire allows us to appreciate the vast intellectual heritage that continues to shape our modern world.
Delve into the profound legacy and influence of the largest Islamic empire in history. From the breathtaking architectural wonders like the Hagia Sophia and Alhambra to the advancements in mathematics, medicine, and astronomy, this empire left an indelible mark on various fields. Its cultural diversity, scientific discoveries, and artistic achievements continue to shape the world we live in today.
Contents
- The Golden Age of Islamic Civilization
- Exploring the Legacy and Influence of the Largest Islamic Empire in History
- Key Takeaways
- Frequently Asked Questions
- 1. What was the largest Islamic empire in history?
- 2. What is the legacy of the largest Islamic empire?
- 3. How did the largest Islamic empire influence trade and commerce?
- 4. How did the largest Islamic empire contribute to the advancement of knowledge?
- 5. How did the largest Islamic empire shape Islamic art and culture?
- Islam – Empire of Faith (Full) | PBS Documentary (EN)
The Golden Age of Islamic Civilization
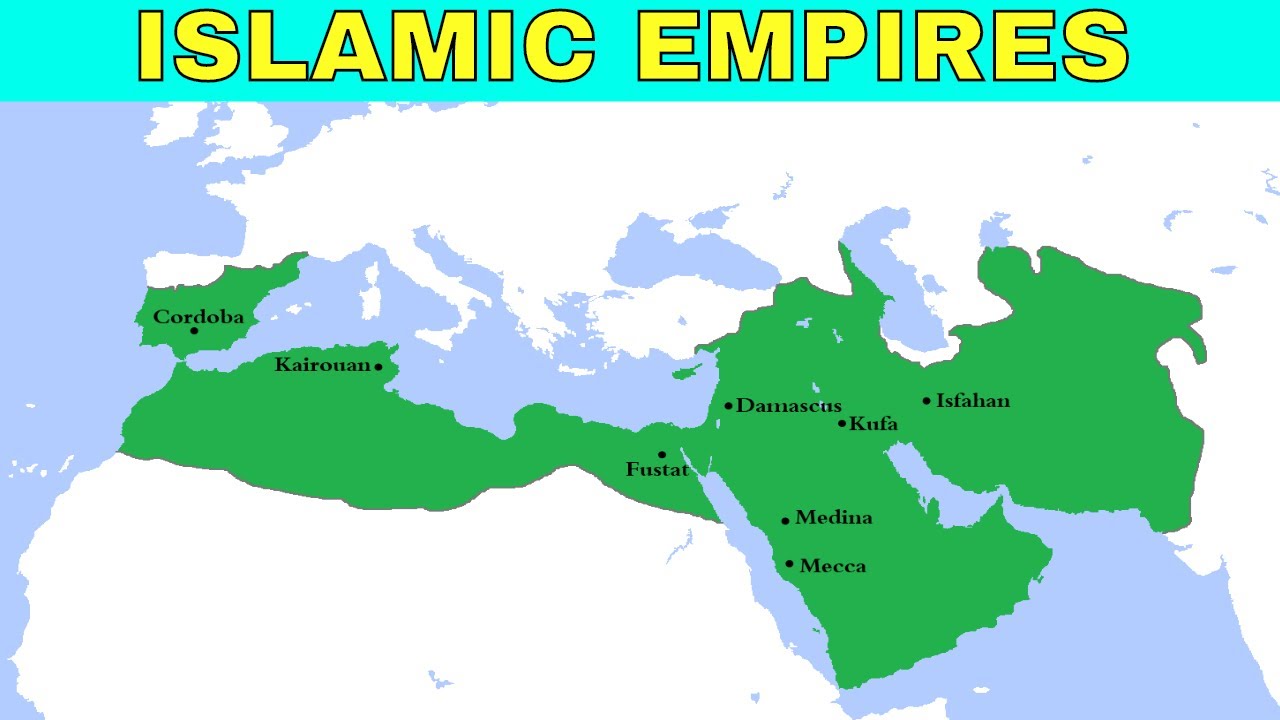
The Islamic Empire stands as one of the largest and most influential empires in history. Spanning from the 7th to the 13th century, this empire left an indelible mark on the world in terms of its legacy and influence. At its height, the Islamic Empire stretched across three continents, encompassing diverse cultures, languages, and religions. This article aims to explore the largest Islamic empire in history, delving into its legacy and the profound impact it had on various aspects of human civilization.
Science and Knowledge
One of the defining characteristics of the Islamic Empire was its embrace of science and knowledge. During the Islamic Golden Age, scholars from various backgrounds made significant contributions in fields such as mathematics, astronomy, medicine, and philosophy. Islamic scholars built upon the knowledge of ancient civilizations, including the Greeks, Romans, and Indians, and expanded upon it.
Islamic scholars were instrumental in preserving and translating the works of classical Greek philosophers such as Aristotle, Plato, and Socrates. These translations played a crucial role in reintroducing Greek philosophy to the Western world during the Renaissance. Additionally, Islamic scientists made groundbreaking discoveries in areas like optics, algebra, and trigonometry, which laid the foundation for modern scientific advancements.
The translation movement led by Islamic scholars also facilitated the preservation of ancient knowledge from other civilizations. Texts from ancient Babylonia, Persia, and India were translated into Arabic, ensuring that their knowledge and wisdom were not lost to history. This exchange of knowledge between different cultures during the Islamic Empire played a pivotal role in the advancement of human civilization.
Education and Libraries
Education played a central role in the Islamic Empire, and the establishment of libraries and centers of learning contributed to the advancement of knowledge. Prominent cities such as Baghdad, Cairo, and Cordoba became intellectual hubs, attracting scholars from diverse backgrounds. The House of Wisdom in Baghdad, for example, became a renowned center for academic pursuits, where scholars conducted research, translated texts, and engaged in intellectual discussions.
The Islamic Empire’s commitment to education is exemplified by the establishment of numerous libraries. Libraries like the Al-Qarawiyyin Library in Fez, Morocco, and the Great Library of Alexandria in Egypt housed vast collections of books and manuscripts. These libraries were not only repositories of knowledge but also places where scholars gathered, shared ideas, and advanced their understanding of various subjects.
Islamic scholars also emphasized the importance of education for both males and females, making significant strides in promoting education for women. Women scholars emerged during this period, contributing to the fields of literature, medicine, and philosophy. The Islamic Empire’s emphasis on education and the establishment of libraries paved the way for the preservation and dissemination of knowledge, enabling future generations to build upon the achievements of their predecessors.
Art and Architecture
The Islamic Empire witnessed a flourishing of art and architecture, characterized by intricate designs, geometric patterns, and a fusion of various artistic traditions. Islamic art and architecture drew inspiration from different cultures, including Persian, Byzantine, and Indian, resulting in a unique and distinctive style.
Mosques, in particular, became architectural marvels during the Islamic Empire. They were not only places of worship but also centers of community life and centers of learning. The Great Mosque of Cordoba in Spain, the Dome of the Rock in Jerusalem, and the Alhambra in Granada are prime examples of the architectural brilliance of the Islamic Empire.
Islamic art, on the other hand, encompassed a wide range of artistic expressions, including calligraphy, ceramics, textiles, and metalwork. Arabic calligraphy, in particular, became a highly regarded form of artistic expression, combining textual elements with aesthetic beauty. The intricate geometric designs seen in Islamic art were not only visually appealing but also symbolized the unity and harmony in the cosmos.
Trade and Commerce
The Islamic Empire had a significant impact on global trade and commerce during its reign. Trade routes such as the Silk Road and the Trans-Saharan Trade Route became vital arteries for the exchange of goods, ideas, and technologies. As a result, the Islamic Empire became a hub of economic activity, connecting the Eastern and Western hemispheres.
The establishment of stable and secure trade routes facilitated the movement of goods across vast distances. Merchants from different regions flocked to the markets of cities like Baghdad and Cairo, creating a vibrant and cosmopolitan atmosphere. Islamic merchants were known for their honesty, fairness, and adherence to ethical business practices, which further enhanced their reputation and attracted traders from far and wide.
Islamic banking and financial systems also played a crucial role in facilitating trade. The establishment of Islamic banks and the development of financial instruments such as letters of credit and bills of exchange simplified commercial transactions. These innovations in finance not only stimulated economic growth within the Islamic Empire but also influenced the development of banking systems in Europe and the rest of the world.
Cultural Exchange
The Islamic Empire’s extensive trade networks fostered cultural exchange between different regions and civilizations. As goods traveled across vast distances, so did ideas, languages, and cultural practices. The Islamic Empire served as a bridge between East and West, enabling the transmission of knowledge and cultural traditions.
The exchange of goods and ideas facilitated by the Islamic Empire led to a remarkable blending of cultures. This cultural fusion not only enriched the societies within the empire but also influenced the art, music, literature, and cuisine of other regions. Influences from the Islamic Empire can be seen in European architecture, Persian poetry, Indian music, and the culinary traditions of the Middle East.
Overall, the Islamic Empire’s legacy and influence are far-reaching and enduring. From its advancements in science and knowledge to its contributions in art, architecture, trade, and cultural exchange, the empire shaped the course of human history. The Islamic Empire’s commitment to learning, its openness to diverse cultures, and its spirit of innovation continue to inspire and inform our understanding of the world today.
Exploring the Legacy and Influence of the Largest Islamic Empire in History
The Islamic Empire, also known as the Caliphate, was the largest empire in history, spanning from the 7th to the 13th centuries. With its origins in the Arabian Peninsula, it quickly expanded under the leadership of the Prophet Muhammad and his successors, known as the caliphs. This empire had a profound impact on various aspects of human civilization, leaving behind a lasting legacy that continues to influence the world today.
One of the most notable contributions of the Islamic Empire was in the field of science and technology. During this time, scholars made significant advancements in areas such as astronomy, mathematics, medicine, and architecture. Many of the scientific discoveries and innovations made by these scholars were later transmitted to Europe, laying the foundation for the Renaissance and shaping the modern world.
The Islamic Empire also had a profound influence on art and culture. Islamic art is characterized by intricate geometric patterns, calligraphy, and vibrant colors, reflecting the empire’s diverse cultural heritage. Islamic architecture, with its iconic structures such as the Dome of the Rock and the Alhambra, showcases the empire’s mastery of design and engineering.
Furthermore, the Islamic Empire was an important center of trade, connecting the East and the West. It facilitated the exchange of goods, ideas, and knowledge between different civilizations, contributing to the development of global commerce and cultural exchange.
Key Takeaways
- The Islamic Empire was the largest in history and spanned across three continents.
- Its legacy includes significant contributions to mathematics, science, and architecture.
- The influence of the Islamic Empire can be seen in various regions, such as the Middle East, North Africa, and Europe.
- Trade and cultural exchange flourished under the Islamic Empire, leading to advancements in commerce, literature, and the arts.
- The Islamic Empire’s religious and cultural practices have profoundly shaped the Muslim world.
Frequently Asked Questions
Are you curious to learn more about the largest Islamic empire in history? Discover its legacy and influence with these frequently asked questions.
1. What was the largest Islamic empire in history?
The largest Islamic empire in history was the Abbasid Caliphate, which spanned from the 8th century to the 13th century. It grew to cover a vast territory, extending from the Iberian Peninsula in the west to India in the east.
The Abbasid Caliphate is known for its strategic advancements, cultural achievements, and flourishing trade networks. It played a crucial role in the spread and preservation of Islamic knowledge and made significant contributions to mathematics, astronomy, medicine, and other fields.
2. What is the legacy of the largest Islamic empire?
The legacy of the largest Islamic empire is immense and far-reaching. It has had a profound impact on various aspects of human civilization. Firstly, the empire’s promotion of learning and scholarship led to the preservation and translation of ancient Greek, Persian, and Indian texts, contributing to the Renaissance in Europe later on.
Additionally, the empire’s architectural achievements, such as the iconic mosques and palaces, still stand today as awe-inspiring examples of Islamic art and design. The empire’s legal and administrative systems, influenced by Islamic principles, heavily influenced subsequent governments and legal systems.
3. How did the largest Islamic empire influence trade and commerce?
The largest Islamic empire played a pivotal role in facilitating and expanding trade and commerce across vast regions. It established an extensive network of trade routes, such as the Silk Road and the Spice Route, connecting Asia, Europe, and Africa.
The empire’s stable governance, standardized currency, and protection of merchants created a favorable environment for economic growth. This led to the establishment of bustling trade cities like Baghdad and Cairo, which became renowned centers for commerce, innovation, and intellectual exchange.
4. How did the largest Islamic empire contribute to the advancement of knowledge?
The largest Islamic empire made significant contributions to the advancement of knowledge. It established prestigious centers of learning, such as the House of Wisdom in Baghdad, where scholars from diverse backgrounds gathered to advance various fields of study.
The empire’s scholars translated and preserved ancient Greek, Roman, and Persian texts, making them accessible to a wider audience. Islamic scholars also made pioneering discoveries in mathematics, astronomy, medicine, and philosophy, which greatly influenced future scientific advancements.
5. How did the largest Islamic empire shape Islamic art and culture?
The largest Islamic empire played a pivotal role in shaping Islamic art and culture. Islamic art is characterized by its intricate geometric patterns, calligraphy, and arabesque designs, which were influenced by various cultures and artistic traditions of the empire’s diverse regions.
The empire’s patronization of art and the development of architectural marvels like the Great Mosque of Cordoba and the Taj Mahal exemplify the empire’s contributions to the world of art. Islamic poetry, literature, and music also flourished during this time, leaving a lasting impact on the cultural heritage of the Islamic world.
Islam – Empire of Faith (Full) | PBS Documentary (EN)
In this deep dive into the largest Islamic empire in history, we have explored its legacy and influence. We have learned about the empire’s vast territorial expansion, its promotion of Islamic culture and scholarship, and its advancements in various fields.
The empire’s legacy can be seen in its architectural wonders, such as the grand mosques and palaces that still stand today. Its influence extends to the fields of science, medicine, and mathematics, where scholars made significant contributions that shaped the world we live in.