The Industrial Revolution, a period of rapid industrialization and technological advancements that took place from the 18th to the 19th century, is often hailed as a turning point in human history. It brought about significant changes in various aspects of life, from the economy to the living conditions of people. But did this revolution truly improve life for individuals, or did it bring about a set of new challenges and inequalities?
The Industrial Revolution undoubtedly brought numerous advancements and improvements to various aspects of life. It led to the development of new machinery and manufacturing processes that increased productivity and efficiency. This resulted in the production of more goods and a rise in living standards for some individuals. Additionally, transportation and communication were revolutionized, allowing for easier and faster movement of goods and information. However, it is important to acknowledge that the benefits of the Industrial Revolution were not evenly distributed, as it also brought about numerous social and environmental problems.
The Industrial Revolution had a significant impact on improving life in many ways. It led to technological advancements, increased productivity, and economic growth. The revolution brought about the development of new industries, improved transportation and communication systems, and the availability of mass-produced goods. It also created employment opportunities and higher wages for workers. However, it also had negative effects, such as poor working conditions and environmental pollution. Overall, the Industrial Revolution improved life, but it came with both benefits and drawbacks.
Contents
- The Impact of Industrial Revolution on Living Conditions
- Technological Advancements and Standard of Living
- The Impact of the Industrial Revolution on Life
- Key Takeaways
- Frequently Asked Questions
- 1. How did the Industrial Revolution impact living conditions?
- 2. Did the Industrial Revolution improve transportation?
- 3. Did the Industrial Revolution lead to technological advancements?
- 4. Did the Industrial Revolution improve education opportunities?
- 5. Did the Industrial Revolution improve social equality?
- How Did the Industrial Revolution Affect People’s Lives?
The Impact of Industrial Revolution on Living Conditions
The Industrial Revolution, which took place from the 18th to the 19th century, marked a significant shift in the way people lived and worked. It was a time of rapid industrialization, technological advancements, and urbanization. While the Industrial Revolution brought about many positive changes, it also had its drawbacks, particularly in terms of living conditions for the working class. This article explores the impact of the Industrial Revolution on overall living conditions, including housing, sanitation, health, and working conditions.
Housing and Living Conditions
One of the most significant challenges during the Industrial Revolution was the lack of adequate housing for the growing population in urban areas. With the rapid influx of people moving from rural to urban areas in search of employment, the demand for housing skyrocketed. As a result, overcrowding became a rampant issue, leading to cramped and unsanitary living conditions.
Workers often lived in small, poorly constructed tenement buildings with multiple families sharing a single room. These buildings lacked basic amenities such as plumbing and ventilation, making them breeding grounds for diseases. The high population density and unsanitary living conditions led to the spread of diseases like cholera and tuberculosis, contributing to high mortality rates.
However, it is important to note that not all living conditions during the Industrial Revolution were bleak. The advancement of new technologies and industrial practices also resulted in improvements in housing for some sections of society. The middle class, for instance, experienced an increase in housing quality with the development of affordable terraced houses and improved sanitation systems. These advancements were a direct result of the technological progress brought about by the Industrial Revolution.
Overall, while the Industrial Revolution did bring about improvements in housing conditions for some sections of society, the working class faced severe challenges with overcrowding and unsanitary living conditions.
Sanitation and Public Health
The Industrial Revolution had a significant impact on sanitation and public health. The rapid urbanization and overcrowding in cities led to inadequate sanitation systems, exacerbating the spread of diseases. In the early stages of the revolution, waste disposal was often haphazard, resulting in polluted water sources, foul odors, and unsanitary living conditions.
However, as the need for improved sanitation became evident, new technologies and practices were introduced. Sewage systems were designed to remove waste from homes and dispose of it properly. The development of underground sewers and water supply networks laid the foundation for modern sanitation systems. These advancements significantly improved public health by reducing the spread of waterborne diseases and improving overall cleanliness.
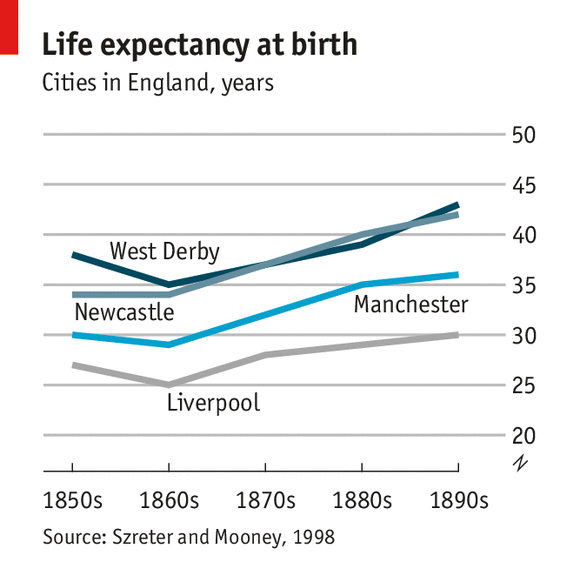
Public health initiatives, such as the establishment of public hospitals and advancements in medical science, also played a crucial role in improving living conditions. The Industrial Revolution paved the way for medical advancements, including the development of vaccines, improved surgical techniques, and the understanding of hygiene practices. These breakthroughs contributed to longer life expectancy and a reduction in mortality rates.
While sanitation and public health conditions improved over time as a response to the challenges posed by the Industrial Revolution, it is important to acknowledge that these improvements were not immediate and took time to implement on a larger scale.
Working Conditions and Labor Laws
The working conditions during the Industrial Revolution were notoriously harsh and exploitative, particularly for factory workers. Many workers, including women and children, were subjected to long working hours, dangerous working conditions, and low wages. The introduction of machinery in factories led to an increase in productivity but also resulted in dangerous working environments.
Factory workers often faced hazardous conditions without proper safety regulations or protective measures. Accidents were common, and workers were exposed to harmful substances and dangerous machinery. The lack of labor laws and worker protections meant that many workers were forced to endure these conditions to make a living.
However, as the Industrial Revolution progressed, the plight of workers became a social concern. Trade unions and labor movements emerged, pushing for better working conditions and fair wages. As a result, labor laws were gradually implemented, setting standards for working hours, child labor, and workplace safety.
The Factory Acts of the early 19th century in Britain, for example, introduced restrictions on child labor, limiting working hours for children and improving safety regulations. These legislative changes marked a significant improvement in working conditions, although it took time for them to be enforced and widely adopted.
Improvements in Education and Social Mobility
One aspect that cannot be overlooked when discussing the impact of the Industrial Revolution on living conditions is the advancements in education and social mobility. The Industrial Revolution brought about a need for skilled workers to operate machinery and perform specialized tasks.
The demand for skilled labor prompted the establishment of educational institutions aimed at providing technical training. Schools and apprenticeship programs were developed to equip workers with the necessary knowledge and skills to thrive in industrial settings. This emphasis on education played a crucial role in improving social mobility, allowing individuals to break free from the cycle of poverty.
Moreover, the rise of industrial capitalism created opportunities for social advancement. New industries and businesses emerged, creating jobs and economic growth. This, in turn, provided avenues for upward mobility, allowing individuals to improve their living conditions and social standing.
However, it is important to note that access to education and social mobility were not available to all segments of society. The working class, in particular, still faced significant barriers to education and social advancement. Nonetheless, the strides made during the Industrial Revolution laid the foundation for future developments in education and social mobility.
Technological Advancements and Standard of Living
In addition to the improvements and challenges in living conditions, the Industrial Revolution brought about significant technological advancements that had a profound impact on the standard of living.
Transportation and Communication
The advancements in transportation and communication revolutionized the way people lived and interacted. The invention of steam-powered locomotives and railways facilitated the transportation of goods and people over long distances, connecting different regions and stimulating trade and commerce. This facilitated the movement of raw materials to factories and the distribution of finished goods to markets, leading to economic growth.
Improved communication systems also played a significant role in the standard of living. The introduction of the telegraph and later the telephone allowed for faster and more efficient communication over long distances. This connected people and businesses, enabling faster decision-making, coordination, and the exchange of ideas. The ability to communicate effectively contributed to economic development and social cohesion.
Furthermore, the development of infrastructure, such as roads and canals, improved accessibility and reduced transportation costs. This opened up opportunities for trade and economic development in previously isolated regions.
Mechanization and Automation
The Industrial Revolution saw a shift from manual labor to mechanization and automation. The invention and use of machinery in production processes increased efficiency and productivity. Tasks that were previously done by hand could now be done more quickly and on a larger scale.
The mechanization of agriculture, for example, led to increased crop yields and reduced labor requirements. This resulted in a more abundant food supply and better nutrition for the population. In the textile industry, the invention of the spinning jenny and power loom made textile production faster and more cost-effective, leading to the availability of affordable clothing.
The use of machinery also led to the creation of new jobs, particularly in manufacturing and engineering. The demand for skilled workers to operate and maintain the machines contributed to job growth and improved employment opportunities.
Access to Goods and Services
The Industrial Revolution expanded access to goods and services, leading to an improvement in the standard of living for many. With the increase in production and the development of transportation networks, a wider range of goods became available at more affordable prices.
People had access to a variety of consumer goods that were previously out of reach. Basic necessities such as clothing, food, and household items became more accessible to the general population. This improved the overall quality of life and increased material well-being.
The improvements in transportation also facilitated the growth of the tourism industry, allowing people to travel and explore new places. This opened up opportunities for leisure and cultural exchange, enriching people’s lives and broadening their horizons.
Energy and Power Sources
An essential aspect of the Industrial Revolution was the emergence of new energy sources to power machinery and drive industrial processes. The shift from traditional energy sources, such as human and animal labor, to machines powered by coal and later oil, revolutionized productivity and production capabilities.
The use of coal as a primary energy source allowed for the operation of steam engines, which powered factories, locomotives, and ships. This led to increased industrial output and the ability to transport goods and people more efficiently.
With the discovery and utilization of oil, the availability of energy increased further. Oil became an integral part of transportation and industrial processes, powering vehicles and machinery. The increased accessibility and affordability of energy sources improved production capabilities and contributed to economic growth.
The transition to these new energy sources had a profound impact on the standard of living. It allowed for increased production, improved transportation, and the availability of goods and services that were previously unimaginable.
In conclusion, the Industrial Revolution had a mixed impact on living conditions. While it brought about significant improvements in technology, transportation, and access to goods and services, it also created challenges in terms of housing, sanitation, and working conditions for the working class. It is important to recognize that not all sections of society benefited equally from these advancements. However, the technological and societal changes brought about by the Industrial Revolution laid the foundation for further progress in improving living conditions and shaping the modern world.
The Impact of the Industrial Revolution on Life
The industrial revolution, spanning from the mid-18th to mid-19th century, brought about significant changes in societies around the world. While it undoubtedly led to advancements in technology, increased production, and economic growth, the question remains: did it truly improve people’s lives?
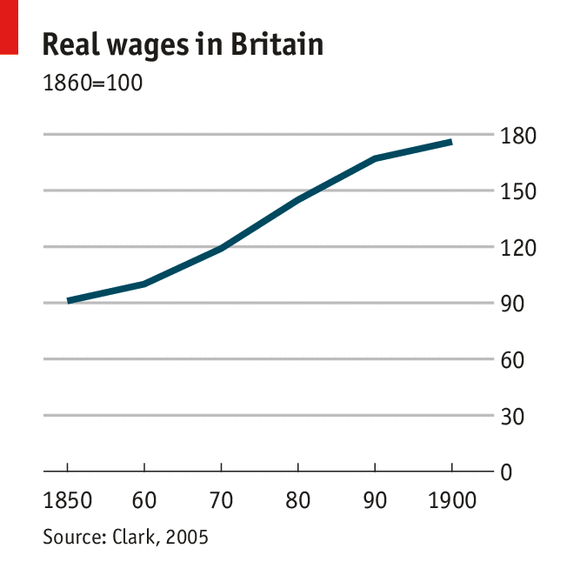
From a professional perspective, the industrial revolution had both positive and negative effects on society. On one hand, it led to the creation of jobs, improved transportation and communication systems, and increased access to goods and services. The revolution also led to scientific and technological innovations that improved healthcare, increased agricultural productivity, and enhanced living standards.
However, the industrial revolution also resulted in numerous challenges. Workers endured poor working conditions, long hours, and low wages, leading to social unrest and the rise of labor movements. The rapid urbanization brought overcrowding, pollution, and inadequate housing. The revolution also contributed to income inequality and the exploitation of natural resources.
In conclusion, the industrial revolution undoubtedly reshaped societies and brought about significant advancements, but its impact on overall life quality is more complex. It improved certain aspects of life, such as access to goods and technological innovations, but also contributed to social and environmental challenges. Understanding these complexities and evaluating the overall effects is essential to have a comprehensive understanding of the industrial revolution’s impact on life.
Key Takeaways
- The industrial revolution brought about significant advancements in technology and production.
- It led to the establishment of factories and mass production, increasing the availability of goods.
- Worker conditions, however, were often harsh and unsafe during this time.
- The industrial revolution also led to urbanization and the growth of cities.
- Despite its challenges, the industrial revolution laid the foundation for modern industrial societies.
Frequently Asked Questions
The Industrial Revolution had a profound impact on society, introducing new technologies, industries, and economic systems. However, its effects on quality of life were complex and varied. Here are some commonly asked questions about whether the Industrial Revolution improved life:
1. How did the Industrial Revolution impact living conditions?
The Industrial Revolution brought about significant changes in living conditions, but not all were positive. As factories and industries emerged, people migrated from rural areas to cities in search of employment. Unfortunately, urban areas became overcrowded with insufficient housing, resulting in cramped and unsanitary living conditions. The working class had to endure long hours, low wages, and unsafe working conditions, leading to poor health and a lower standard of living.
2. Did the Industrial Revolution improve transportation?
Yes, the Industrial Revolution revolutionized transportation. The development of railways, steamships, and canals allowed for faster and more efficient movement of people and goods. This facilitated trade, boosted economic growth, and connected remote regions, improving communication and accessibility. As a result, individuals had greater mobility and access to markets, which enhanced their quality of life and expanded economic opportunities.
3. Did the Industrial Revolution lead to technological advancements?
Absolutely. The Industrial Revolution was characterized by rapid technological advancements that transformed various industries. Innovations such as the steam engine, textile machinery, and the telegraph revolutionized production, manufacturing processes, and communication. These technological advancements increased productivity, reduced labor-intensive tasks, and paved the way for further technological progress. However, it’s essential to note that these advancements primarily benefited the industrial elite rather than the broader population.
4. Did the Industrial Revolution improve education opportunities?
The Industrial Revolution had a mixed impact on education opportunities. On one hand, the expansion of industries created a demand for a skilled workforce, leading to the establishment of schools and educational institutions. Technical schools and vocational training programs emerged to provide the necessary skills for industrial jobs. However, the working class often could not afford to send their children to school, and many children had to work to contribute to the family’s income. It wasn’t until later reforms that access to education became more widespread.
The Industrial Revolution did not lead to immediate social equality. In fact, it initially exacerbated social inequalities as the wealth gap between the industrial elite and the working class widened. While some workers managed to improve their economic standing, many fell into precarious working conditions and poverty. Over time, however, social and labor reforms emerged, leading to improvements in worker rights, social welfare programs, and the gradual reduction of inequality. It took several decades and ongoing efforts to address the social disparities brought about by the Industrial Revolution.
How Did the Industrial Revolution Affect People’s Lives?
Overall, it can be concluded that the Industrial Revolution had a significant impact on improving life. It brought about many changes that transformed societies and economies.
The introduction of new technologies and machinery led to increased productivity and efficiency in industries, resulting in economic growth. This, in turn, created new job opportunities and increased the standard of living for many individuals. Additionally, advancements in transportation and communication made it easier to connect people and goods, fostering trade and expanding markets.