Ancient China, known for its rich history and vast empire, has long fascinated scholars and historians. One intriguing question that arises is whether Ancient China ever conquered another civilization. Exploring this topic reveals surprising insights into the interactions and influence of Ancient China on neighboring societies, shedding light on the empire’s reach and power.
Ancient China’s history is marked by numerous military campaigns and conflicts, but the concept of conquering another civilization is complex. While China expanded its territory through imperial conquests, it primarily aimed to assimilate and incorporate neighboring regions rather than conquer them outright. The idea of conquest is often associated with complete domination and subjugation, which was not the typical approach of Ancient China. Instead, the empire sought to exert its influence and establish tributary relationships, emphasizing cultural and economic integration rather than direct control.
Ancient China was known for its powerful dynasties and military campaigns, but there is no concrete evidence to suggest that it conquered another civilization. China did expand its territory and influence through political alliances, trade, and cultural exchanges. However, it primarily focused on maintaining its own unity and stability rather than conquering other civilizations. Ancient China’s remarkable achievements in science, technology, and governance had a significant impact on other societies, but conquest was not its primary goal.
Contents
- The Influence of Ancient China on Other Civilizations
- Did Ancient China Conquer Another Civilization?
- Key Takeaways
- Frequently Asked Questions
- 1. How did Ancient China expand its empire?
- 2. Which civilizations did Ancient China conquer?
- 3. How did Ancient China’s conquests impact other civilizations?
- 4. Were there any failed attempts by Ancient China to conquer other civilizations?
- 5. Did Ancient China engage in peaceful interactions with other civilizations?
- Did Ancient Rome and China Know About Each Other? (Short Animated Documentary)
The Influence of Ancient China on Other Civilizations
China, with its rich history and cultural heritage, has been a fascinating subject for scholars and historians alike. One intriguing question that often arises is whether ancient China conquered other civilizations. While many empires and dynasties rose and fell within China, it is essential to explore the interactions and influence that ancient China had on other cultures. This article seeks to shed light on the relationships between ancient China and other civilizations, examining their impact on politics, trade, and cultural exchange.
The Expansion of Ancient China: A Prelude to Conquest
Ancient China, like many other ancient civilizations, experienced periods of expansion. However, it is important to note that China’s primary focus was often on defending its borders against nomadic tribes rather than conquering other states. The concept of “all under Heaven” (tianxia) in ancient Chinese philosophy emphasized the unity and harmony of the world under a single ruler, the Son of Heaven.
During the Zhou Dynasty (1046-256 BCE), China’s influence gradually extended beyond its borders through cultural diffusion and diplomatic relations. The Zhou Dynasty established a feudal system, where regional lords pledged loyalty to the king and received land in return. This system allowed for increased political stability and cultural exchanges with neighboring states, particularly in the form of rituals and ceremonies.
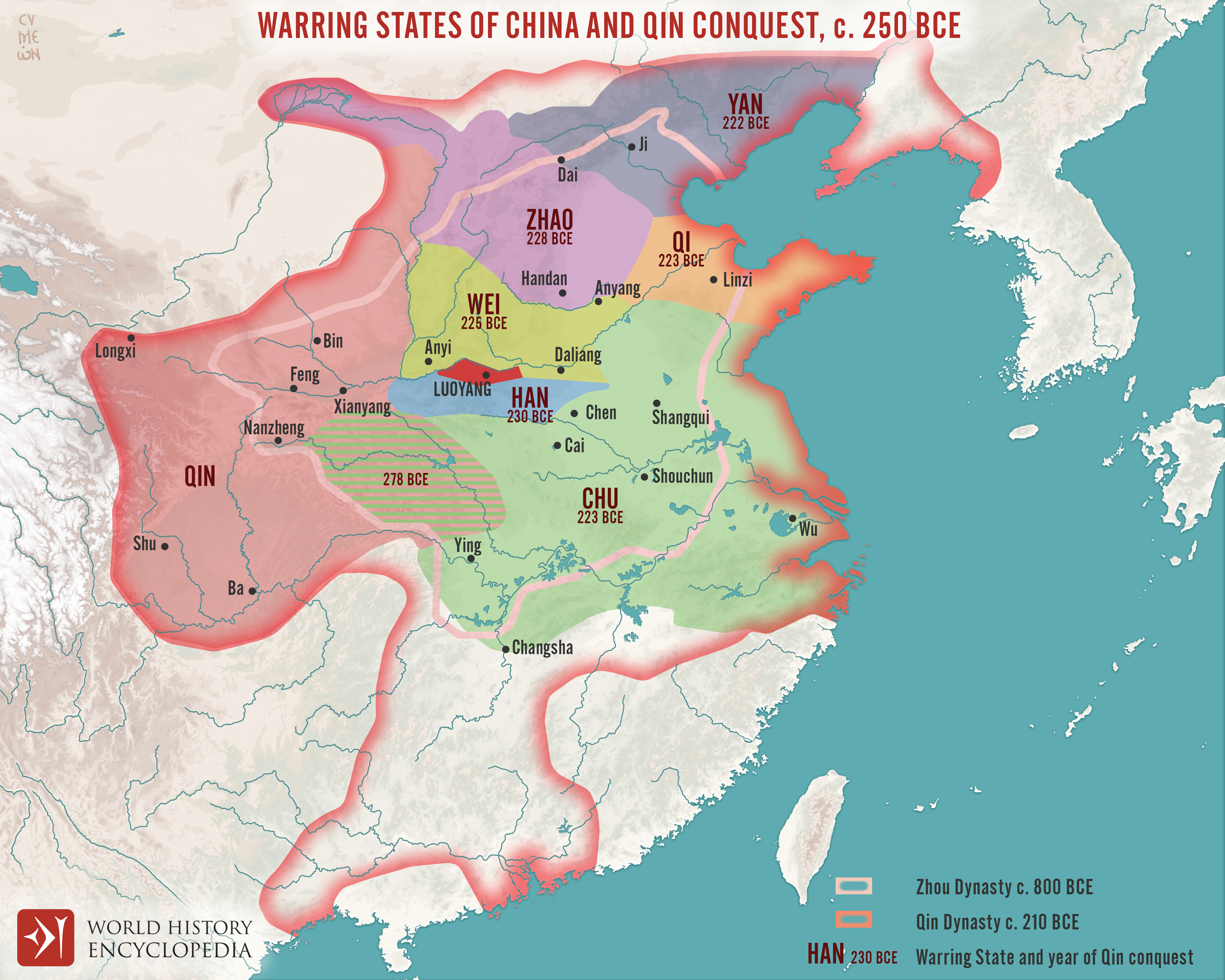
The Warring States period (475-221 BCE) witnessed an era of intense military conflicts between various states within China. While this period did involve territorial conquest within China, it did not result in the permanent incorporation of other civilizations into Ancient China.
Despite the absence of outright conquest, the expansion of ancient China often led to the establishment of tributary relationships with neighboring states. These relationships were based on the recognition of China’s cultural and political superiority, rather than conquest through military force.
China’s Influence on East Asia: The Spread of Culture and Ideas
Did Ancient China Conquer Another Civilization?
Ancient China, known for its rich history and vast empire, had a significant impact on neighboring civilizations. While China did not necessarily conquer another civilization in the traditional sense, it did exert its influence and extend its reach through political, economic, and cultural means.
China’s influence extended to regions such as Korea, Japan, Vietnam, and parts of Central Asia. Through diplomatic relations, trade routes, and cultural exchanges, China exported its customs, technologies, and ideas to these regions, influencing their political systems, art, architecture, and even language.
For instance, the influence of Chinese imperial bureaucracy and Confucianism can be seen in the political systems and social structures of neighboring civilizations. China’s advancements in agriculture, engineering, and medicine also spread, leading to technological advancements in these regions.
While China did not outright conquer these civilizations, its influence and cultural dominance were significant. The impact of Ancient China’s civilization can still be seen today in the traditions, customs, and languages of the countries it interacted with.
Key Takeaways
- Ancient China is known for its many conquests and colonization of neighboring territories.
- Historical records suggest that China did conquer and assimilate some foreign civilizations.
- The Han Dynasty expanded its empire by conquering and incorporating various regions.
- The Tang Dynasty established control over parts of Central Asia and the Korean Peninsula.
- Ancient China’s conquests were driven by geopolitical, economic, and cultural factors.
Frequently Asked Questions
Ancient China has a rich history, but did they conquer other civilizations? Learn more about this intriguing topic with these frequently asked questions.
1. How did Ancient China expand its empire?
Ancient China expanded its empire through a combination of military conquests, diplomatic alliances, and cultural assimilation. The first major expansion occurred during the Qin Dynasty (221-206 BC) when Emperor Qin Shi Huang unified China through military campaigns and built the Great Wall as a defense against nomadic invaders.
Subsequent dynasties, such as the Han, Tang, and Yuan, further expanded Chinese territory through military conquests, establishing tributary states, and integrating neighboring regions into their empires. The Silk Road also played a significant role in facilitating cultural and economic exchanges, allowing China to exert influence on other civilizations.
2. Which civilizations did Ancient China conquer?
Ancient China conquered various civilizations throughout its history. Some notable conquests include:
- The Xiongnu Empire: The Han Dynasty defeated and absorbed the Xiongnu Empire in the 2nd century BC, expanding their control over the northern steppes of Central Asia.
- The Northern Wei: The Northern Wei Dynasty annexed the Northern Qi Dynasty in the 6th century AD, consolidating their rule over northern China.
- The Southern Han: The Song Dynasty conquered the Southern Han Dynasty in the 12th century AD, effectively unifying China under their rule.
These conquests allowed Ancient China to expand its territory and influence over neighboring civilizations, shaping its cultural and political landscape.
3. How did Ancient China’s conquests impact other civilizations?
Ancient China’s conquests had significant impacts on the civilizations it conquered. The absorption of the Xiongnu Empire allowed the Han Dynasty to secure its northern borders, protecting China from incursions by nomadic tribes. The annexation of the Northern Qi Dynasty by the Northern Wei Dynasty enhanced their control over northern China and contributed to the Sinicization of the region.
The conquest of the Southern Han Dynasty by the Song Dynasty consolidated their power and paved the way for the golden age of Chinese poetry, painting, and porcelain during the Song Dynasty.
4. Were there any failed attempts by Ancient China to conquer other civilizations?
Ancient China did experience failed attempts to conquer other civilizations. One well-known example is the Mongol Empire’s invasions of China during the Song Dynasty. Despite initially successful campaigns, the Song Dynasty managed to resist Mongol conquest for several decades, ultimately leading to the establishment of the Yuan Dynasty, which was ruled by the Mongols.
5. Did Ancient China engage in peaceful interactions with other civilizations?
Ancient China had not only engaged in military conquests but also fostered peaceful interactions with other civilizations. The concept of the “tribute system” allowed China to establish diplomatic relations with neighboring states, where they recognized China’s dominance and paid tribute in exchange for trade and protection.
Furthermore, the Silk Road served as a vital economic and cultural link between China and the rest of the world, facilitating trade and exchanges of ideas and technologies.
Did Ancient Rome and China Know About Each Other? (Short Animated Documentary)
In conclusion, it can be stated that Ancient China did not conquer another civilization in the same way that the Western powers did. While China did expand its territories through military campaigns, its approach was more focused on assimilation rather than conquering. The Chinese civilization sought to incorporate other societies into its own through cultural, economic, and political integration, rather than simply overpowering and subjugating them.
However, it is important to note that China did have conflicts and wars with neighboring civilizations, such as the Xiongnu and the Mongols. These conflicts were often driven by territorial disputes and clashes of power. Nonetheless, the objective of these conflicts was not necessarily to conquer and dominate another civilization, but rather to safeguard Chinese borders and maintain stability within the region.