Ancient China, renowned for its rich history and influential civilization, has left a lasting impact on the world. However, amidst its many achievements, one question lingers: did Ancient China conquer another civilization? Exploring this intriguing inquiry takes us on a journey through time, uncovering tales of conquest and interaction between ancient empires.
Ancient China, known for its dynasties and technological advancements, had a complex relationship with neighboring civilizations. While China did engage in military campaigns and expand its territorial reach, the concept of conquest in the traditional sense may not fully capture the nature of its interactions. Rather than outright domination, China’s approach often included diplomatic strategies and cultural exchanges, which played a significant role in shaping the region’s history.
Ancient China was known for its strong military and expansionist ambitions. Through various military campaigns, China did conquer and assimilate several civilizations and regions, such as the regions of Xinjiang, Tibet, and Taiwan. Additionally, the Han Dynasty expanded its influence through diplomatic alliances and tributary systems. However, it’s important to note that China’s conquests were usually aimed at establishing dominance rather than complete subjugation, often resulting in the incorporation of conquered civilizations into the Chinese cultural sphere.
Contents
- Ancient China’s Conquests and Influences on Other Civilizations
- Ancient China’s Conquest: A Historical Perspective
- Key Takeaways: Did Ancient China Conquer Another Civilization?
- Frequently Asked Questions
- 1. How did Ancient China interact with neighboring civilizations?
- 2. Did Ancient China conquer any other ancient civilization?
- 3. What were the reasons for Ancient China’s military expansion?
- 4. How did Ancient China incorporate conquered regions into its empire?
- 5. What impact did Ancient China’s interactions and conquests have on other civilizations?
- Did Ancient Rome and China Know About Each Other? (Short Animated Documentary)
Ancient China’s Conquests and Influences on Other Civilizations
Ancient China, with its rich history spanning over several millennia, is often recognized for its remarkable achievements and contributions in various fields. From technological advancements to cultural innovations, the Chinese civilization has influenced numerous aspects of human development. While it is widely known that Ancient China was a dominant force in East Asia, the question of whether it conquered another civilization remains a topic of debate among historians and archaeologists.
China’s own history is filled with instances of internal conflicts, territorial expansion, and the assimilation of neighboring cultures. However, the idea of Ancient China conquering another distinct civilization is not as clear-cut as one might expect. It is crucial to examine the interactions between Ancient China and other civilizations in order to understand the extent of their conquests and influence.
Interaction with the Xiongnu Empire
The Xiongnu Empire, also known as the Huns, emerged as a powerful nomadic confederation in the Eurasian Steppe during the third century BCE. While they were not a distinct civilization in the same sense as Ancient China, they played a significant role in shaping China’s history. The Xiongnu and Ancient China engaged in frequent conflicts and negotiations, with the Han Dynasty even establishing alliances and marrying off princesses to Xiongnu leaders.
Although the Xiongnu were able to exert pressure on the Han Dynasty through military campaigns and raids, they did not conquer the Chinese civilization in a traditional sense. Instead, the relationship between Ancient China and the Xiongnu Empire involved a complex mix of diplomacy, tribute exchanges, and occasional warfare. While the Han Dynasty held the upper hand in some instances, it was never able to fully annex or assimilate the Xiongnu Empire.
Furthermore, the Xiongnu Empire eventually declined in power and dissolved, making it difficult to categorize as a civilization conquered by Ancient China. Although Ancient China’s influence on the Xiongnu is evident in some aspects of their culture and political organization, it would be inaccurate to claim that Ancient China conquered the Xiongnu Empire.
The Influence on Vietnam
Vietnam, located to the south of China, has a long history of interaction with its northern neighbor. Ancient China had a significant influence on Vietnam, particularly during the period when China was under the rule of the Han Dynasty. The Han Dynasty sought to extend its influence into the region, leading to the establishment of Chinese provinces in present-day northern Vietnam.
During this time, Chinese culture, administration, and language were introduced to Vietnam, leaving a lasting impact on its society. However, it is essential to note that the Vietnamese people also maintained a strong sense of cultural identity and resisted full assimilation into the Chinese civilization.
The period of Chinese domination in Vietnam came to an end with the collapse of the Han Dynasty. Despite subsequent attempts by different Chinese dynasties to control Vietnam, the Vietnamese people consistently fought for their independence. Eventually, Vietnam emerged as an independent civilization that integrated Chinese influences while asserting its distinct cultural heritage.
Interactions with Central Asian Empires
Ancient China’s interactions with the Central Asian empires, such as the Kushan Empire and the Western Regions, were crucial for trade, cultural exchange, and military conflicts. These regions, which encompassed parts of modern-day China, India, Pakistan, and Afghanistan, were strategic crossroads connecting different civilizations.
The Kushan Empire, centered in present-day Afghanistan and northern India, had a significant impact on Ancient China. Trade routes, such as the Silk Road, facilitated the exchange of goods, ideas, and cultural practices between the Kushans and the Chinese. However, it is essential to note that the interactions between these empires were characterized by a mix of cooperation, rivalry, and conflicts.
Ancient China’s engagement with the Central Asian empires did not result in the conquest of a distinct civilization. Instead, it involved a complex network of political alliances, economic cooperation, and military clashes. These interactions contributed to the spread of Chinese influence in the region and the exchange of ideas, technology, and trade goods.
The Legacy of Ancient China’s Influence
While Ancient China may not have conquered another distinct civilization in the traditional sense, its interactions with various cultures and empires left a lasting legacy. China’s cultural, technological, and economic influence radiated beyond its borders, shaping the development of neighboring civilizations. The spread of Chinese writing, Confucian philosophy, agriculture techniques, and tea cultivation are just a few examples of the profound impact Ancient China had on other societies.
Ancient China’s conquests and influences were not limited solely to military victories or territorial acquisitions. Its soft power and cultural exchange played a significant role in shaping the history and development of other civilizations. While the question of whether Ancient China conquered another civilization remains debated, it is undeniable that its contributions and interactions had a transformative effect on the world.
Ancient China’s Conquest: A Historical Perspective
Ancient China, throughout its vast and complex history, witnessed numerous military campaigns and territorial expansions. While China’s dynasties aimed at extending their influence, it is debatable if they ever conquered another civilization outright.
China’s most significant conquests were within its own borders, where it assimilated and integrated various ethnic groups into its cultural fabric. The Han Dynasty, for instance, successfully incorporated regions like Xinjiang into its empire, symbolizing unity through peaceful assimilation instead of conquest.
However, historians acknowledge that China did engage in conflicts and territorial expansion beyond its borders. The Han Dynasty’s military campaigns against the Xiongnu, a nomadic tribe based in present-day Mongolia, were significant but did not result in complete conquest. Similarly, the Tang Dynasty expanded into Central Asia and established strong trading networks, but did not fully assimilate the local cultures.
Despite these endeavors, China prioritized cultural exchange and trade rather than imposing its rule forcibly. Therefore, it can be concluded that while Ancient China did engage in external military campaigns and territorial expansions, it did not conquer and subjugate another civilization in the conventional sense.
Key Takeaways: Did Ancient China Conquer Another Civilization?
- Ancient China did not directly conquer another civilization, but it did have conflicts and influence over neighboring states.
- China’s main objective was to establish dominance and maintain stability within its own territories.
- Ancient China’s focus was on expanding its influence through trade, cultural exchange, and political alliances.
- The empires of China had a “tributary system” which established hierarchical relationships with neighboring states.
- China’s impact on neighboring civilizations was significant, shaping their political systems, arts, and technological advancements.
Frequently Asked Questions
Ancient China was a significant civilization with a rich history. Throughout its existence, it interacted with various other cultures and civilizations. Let’s explore some frequently asked questions about whether Ancient China conquered another civilization.
1. How did Ancient China interact with neighboring civilizations?
Ancient China had a complex relationship with its neighboring civilizations. While there were instances of territorial expansion and conflict, Ancient China also engaged in peaceful cultural exchanges and trade with neighboring regions. These interactions helped in the transmission of ideas, technologies, and goods.
Ancient China established diplomatic ties with neighboring regions through marriage alliances, tributary systems, and exchange of envoys. This allowed for the exchange of knowledge and cultural practices, fostering mutual understanding and cooperation.
2. Did Ancient China conquer any other ancient civilization?
Ancient China did engage in military conflicts and territorial expansion, but it is important to note that conquest was not the primary objective. Ancient China focused more on building and strengthening their own civilization rather than conquering others.
However, there were instances where Ancient China exerted influence over neighboring regions, such as the conquest and incorporation of the territories of present-day Tibet and Xinjiang into the Chinese empire. These regions were brought under Chinese control through a combination of military force and political alliances.
3. What were the reasons for Ancient China’s military expansion?
Ancient China’s military expansion was driven by several factors. The primary motivations were ensuring the security and protection of the Chinese empire from external threats, maintaining control over key trade routes, and safeguarding valuable resources.
Additionally, the Chinese emperors sought to establish Chinese influence and power over neighboring regions, extending their authority and maintaining political stability. Military campaigns were also launched for strategic purposes, such as securing buffer zones or annexing regions with important geographical or economic significance.
4. How did Ancient China incorporate conquered regions into its empire?
When Ancient China conquered a region, it employed various strategies to incorporate it into the empire. These included establishing administrative systems, appointing local officials, and implementing cultural assimilation policies.
Ancient China would often allow the conquered regions to retain some degree of autonomy under the overarching rule of the empire. This approach helped maintain stability and foster cooperation between different regions within the empire.
5. What impact did Ancient China’s interactions and conquests have on other civilizations?
Ancient China’s interactions and conquests had a significant impact on the civilizations it came into contact with. The cultural exchanges and trade facilitated the spread of Chinese art, technology, and philosophy to neighboring regions.
Ancient China’s administrative systems, such as the tributary system, had a lasting influence on the political structures of the regions it conquered or established diplomatic ties with. The economic exchanges also contributed to the growth and development of these civilizations.
Did Ancient Rome and China Know About Each Other? (Short Animated Documentary)
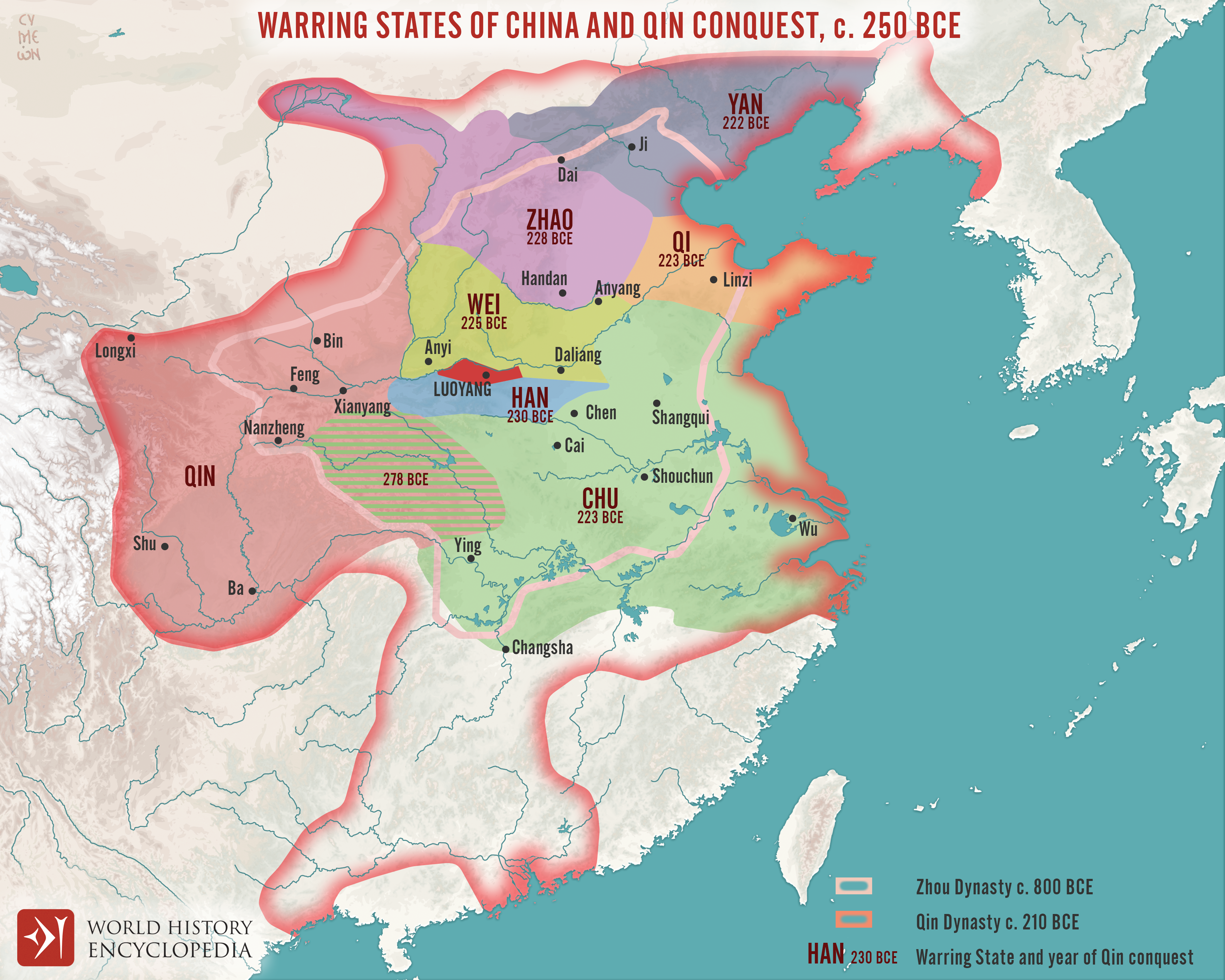
In conclusion, there is evidence to suggest that Ancient China did conquer other civilizations. The Qin Dynasty, under the reign of Emperor Qin Shi Huang, successfully united several warring states and established the first centralized empire in Chinese history. Through military conquest and diplomatic alliances, ancient Chinese leaders expanded their territories and brought surrounding regions under their control.
Ancient China’s conquests were driven by a desire for power, resources, and strategic dominance. The Great Wall of China, built primarily as a defensive fortification, is a symbol of their efforts to protect their newly acquired territories from external threats. While there may be differing interpretations and arguments, the historical record suggests that Ancient China did engage in conquests and exerted influence over other civilizations in its quest for expansion and control.