The Byzantine Empire, often overlooked in World History, played a crucial role in shaping the course of civilization. Its impact extended far beyond its borders and left a lasting legacy that still influences our modern world.
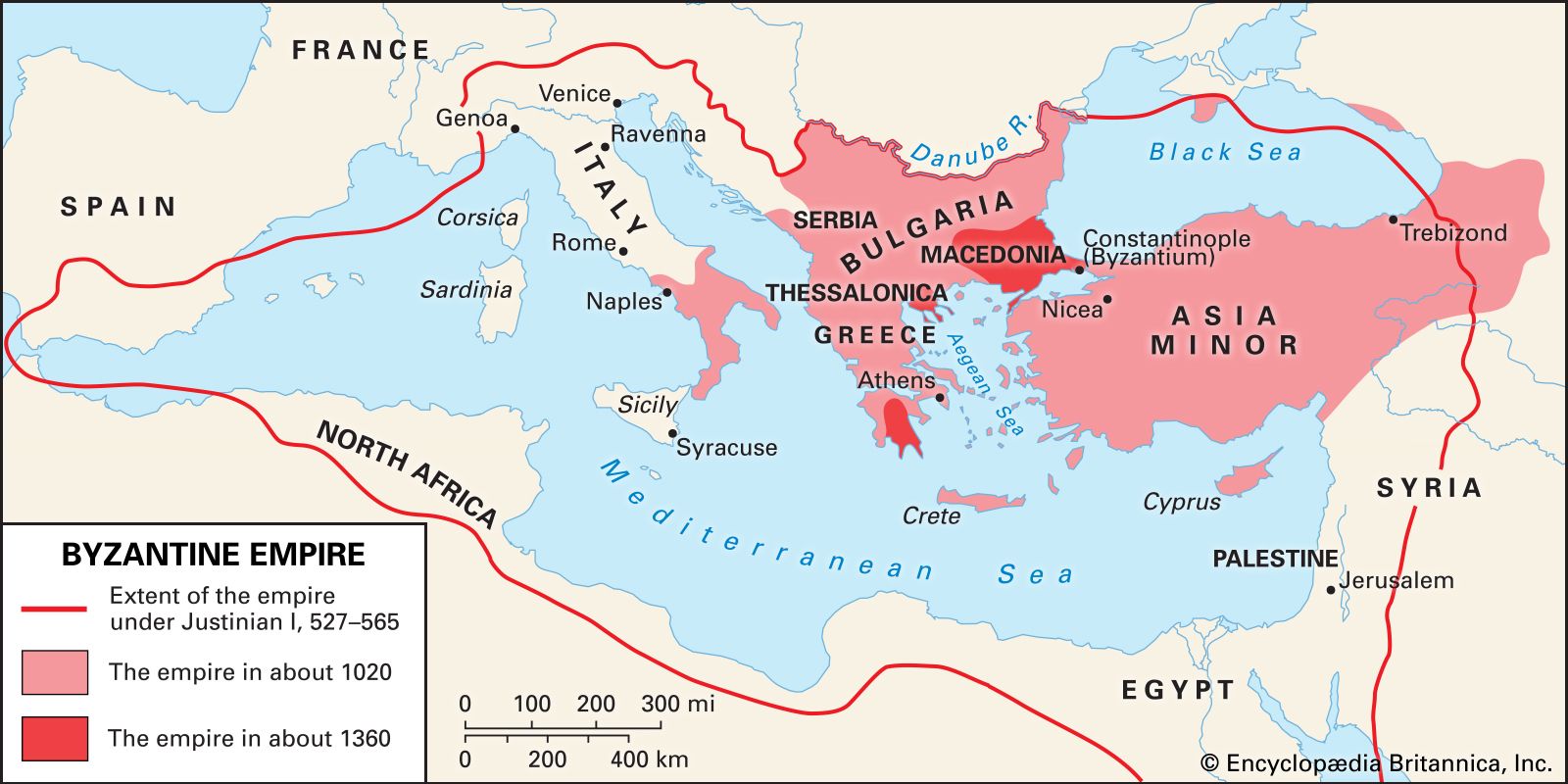
The Byzantine Empire, also known as the Eastern Roman Empire, emerged as a continuation of the Roman Empire and lasted for over a thousand years. Its capital, Constantinople, stood as a bridge between East and West, connecting Europe and Asia. This strategic location fostered cultural exchange, trade, and the spread of knowledge, helping to preserve Greek and Roman traditions and ideals during the medieval period.
The Byzantine Empire was a pivotal force in shaping world history. It preserved ancient knowledge, literature, and art, acting as a bridge between the classical world and the Renaissance. The empire’s strategic location facilitated trade routes and cultural diffusion, contributing to the spread of Christianity and the development of Europe. Its legal and administrative systems influenced future civilizations. The Byzantine Empire’s military prowess defended Christendom from numerous invasions, including the Arab expansion and the Ottoman Empire. Understanding its importance grants insight into the foundations of Western civilization.
Contents
- The Byzantine Empire: A Crucial Influence on World History
- Understanding the Importance of the Byzantine Empire in World History
- Key Takeaways: Understanding the Importance of the Byzantine Empire in World History
- Frequently Asked Questions
- 1. How did the Byzantine Empire contribute to the preservation of ancient Greek and Roman knowledge?
- 2. How did the Byzantine Empire shape the development of Christianity?
- 3. How did the Byzantine Empire contribute to the spread of trade and commerce?
- 4. How did the Byzantine Empire influence the development of art and architecture?
- 5. How did the fall of the Byzantine Empire impact world history?
- The rise and fall of the Byzantine Empire – Leonora Neville
The Byzantine Empire: A Crucial Influence on World History
1. Geographical Advantage and Strategic Importance
The Byzantine Empire, also known as the Eastern Roman Empire, emerged from the ashes of the Western Roman Empire and became a significant force in shaping world history. One of the unique aspects of understanding the importance of the Byzantine Empire lies in its geographical advantage and strategic importance. Located at the crossroads between Europe and Asia, the Byzantine Empire served as a crucial bridge between the East and the West, connecting different cultures, trade routes, and ideas.
The strategic location of the Byzantine Empire enabled it to control key trade routes such as the Silk Road and the Mediterranean Sea, which played a pivotal role in the exchange of goods, ideas, and technologies between civilizations. The empire’s capital, Constantinople, situated on the Bosporus Strait, provided easy access to both the Black Sea and the Aegean Sea, making it a hub of commerce and cultural exchange.
Moreover, the Byzantine Empire’s control over important chokepoints, such as the Bosporus and the Dardanelles, allowed it to regulate maritime traffic and maintain a monopoly over trade routes, giving it immense economic power. With its extensive network of forts, coastal defenses, and naval fleets, the empire safeguarded these vital waterways, ensuring the smooth flow of goods and protecting its interests.
The strategic position of the Byzantine Empire made it an indispensable player in world politics, as it acted as a barrier against invasions from the east while also serving as a buffer zone between rival powers. By controlling key territories in the Balkans, Anatolia, and the Levant, the Byzantines acted as a bulwark against the expansionist ambitions of various civilizations throughout history, including the Persian Empire, the Islamic Caliphates, and later, the Ottoman Turks.
Military Power and Diplomatic Influence
In addition to its geographic advantage, the Byzantine Empire’s military power and diplomatic influence were crucial in shaping world history. The empire possessed a well-trained and disciplined army, which included the feared Varangian Guard, elite Byzantine soldiers composed of Scandinavian warriors.
Constantinople, the imperial capital, was renowned for its impressive defensive walls, including the formidable Theodosian Walls, which withstood multiple sieges and protected the city for centuries. The Byzantines’ mastery of siege warfare and fortification engineering made them a force to be reckoned with, deterring any would-be invaders.
Furthermore, the Byzantines established themselves as skilled diplomats and negotiators, often using diplomacy to secure alliances and preserve their interests. Through intricate diplomatic maneuvers, the Byzantines managed to maintain a delicate balance of power between rival kingdoms and empires. The empire’s diplomatic efforts not only contributed to its survival but also prevented large-scale conflicts, thus shaping the geopolitical landscape of the Mediterranean region and beyond.
Preservation and Transmission of Knowledge
The Byzantine Empire played a pivotal role in the preservation and transmission of knowledge during the tumultuous medieval period. While Western Europe experienced a decline in intellectual and cultural achievements during the Early Middle Ages, the Byzantines upheld the traditions of the classical Greek and Roman civilizations.
The Byzantines embraced Greek philosophy, literature, and science, making significant contributions to fields such as mathematics, astronomy, and medicine. Byzantine scholars meticulously copied and preserved ancient texts, which would have otherwise been lost to history. The rediscovery of these works during the Renaissance period sparked a revival of classical knowledge in Western Europe, leading to profound advancements in various disciplines.
Moreover, the Byzantine Empire acted as a bridge between the Islamic world and Western Europe, translating and transmitting Arabic works into Latin. This exchange of knowledge introduced Arab mathematics, astronomy, and philosophy to Europe, revolutionizing intellectual pursuits and contributing to the Scientific Revolution.
Art, Architecture, and Cultural Influence
The Byzantine Empire’s rich artistic and architectural heritage left an indelible mark on world history. Byzantine art, characterized by its distinctive fusion of Christian religious symbolism and classical aesthetics, became a major influence on subsequent artistic movements across Europe, Russia, and the Middle East.
Iconography, the use of religious icons and mosaics to convey spiritual messages, became a hallmark of Byzantine art. The mosaics adorning Byzantine churches and palaces, such as the Hagia Sophia, showcased intricate designs, vibrant colors, and a sense of divine transcendence. These artistic achievements not only adorned religious structures but also served as didactic tools, conveying complex theological concepts to the masses.
Furthermore, Byzantine architecture influenced the development of the Romanesque and Gothic styles in Western Europe. The iconic domed structures, innovative use of arches and vaults, and elaborate ornamentation found in Byzantine buildings left a lasting architectural legacy that can still be seen in modern-day landmarks.
In addition to art and architecture, the Byzantine Empire’s cultural influence extended to literature, law, and even fashion. Byzantine legal codes, such as the Justinian Code, had a profound impact on European legal systems, providing a foundation for modern jurisprudence.
Legacy and Enduring Influence
The Byzantine Empire left a lasting legacy on world history that transcends its eventual decline and fall. Its cultural, political, and religious influence can still be seen today, particularly in regions that were once part of the Byzantine sphere of influence.
The city of Constantinople, renamed Istanbul after the Ottoman conquest in 1453, continues to be a vibrant and cosmopolitan metropolis where Byzantine art, architecture, and traditions are celebrated and preserved. The historical impact of the Byzantine Empire can also be witnessed in the Orthodox Christian Church, which traces its origins back to the Byzantine era and continues to thrive worldwide.
Understanding the importance of the Byzantine Empire in world history is paramount to grasp the intricacies of geopolitical shifts, religious developments, and cultural exchanges that shaped the course of civilizations. From its strategic advantage and military power to its preservation of knowledge and cultural influence, the Byzantine Empire left an indelible mark that continues to resonate in our modern world.
Understanding the Importance of the Byzantine Empire in World History
The Byzantine Empire, also known as the Eastern Roman Empire, played a crucial role in shaping world history. Its significance can be seen in several aspects:
- Preservation of Greco-Roman Culture: The Byzantines preserved and transmitted the classical knowledge of ancient Greece and Rome, safeguarding valuable texts, philosophy, and sciences.
- Spread of Christianity: The Byzantine Empire served as a major center for the spread of Christianity, promoting its influence throughout Europe and beyond.
- Medieval Trade and Economic Power: Constantinople, the Byzantine capital, was a crucial trade hub that connected Europe and Asia, facilitating economic growth and cultural exchange.
- Military Innovations: The Byzantines revolutionized warfare with their innovative tactics and powerful military, protecting Europe from invasions and securing the empire’s borders.
- Legal and Administrative Legacy: Byzantine legal and administrative systems influenced subsequent civilizations, including the development of the Justinian Code, which laid the foundation for modern legal systems.
The Byzantine Empire’s enduring impact on art, architecture, literature, education, and religious practices cannot be overstated. Its contributions continue to influence and shape modern society, making it an invaluable part of world history.
Key Takeaways: Understanding the Importance of the Byzantine Empire in World History
- The Byzantine Empire played a significant role in preserving and transmitting Greek and Roman culture.
- Byzantium served as a crucial bridge between the East and the West, connecting Europe and Asia.
- The Byzantine Empire’s military strength and strategic location allowed it to defend Europe from invasions.
- By promoting Christianity, the Byzantine Empire helped shape the development of Christianity in Europe.
- The Byzantine Empire’s rich artistic and architectural legacy still influences our modern world.
Frequently Asked Questions
The Byzantine Empire played a significant role in shaping world history. From its establishment in the 4th century until its fall in the 15th century, it left an indelible mark on several aspects of civilization. In this section, we will explore some frequently asked questions about the importance of the Byzantine Empire in world history.1. How did the Byzantine Empire contribute to the preservation of ancient Greek and Roman knowledge?
The Byzantine Empire played a vital role in preserving the works of ancient Greek and Roman civilizations. While Europe experienced a decline in intellectual pursuits during the early Middle Ages, the Byzantines safeguarded and copied numerous classical texts. These texts included works of philosophy, science, medicine, and literature. The Byzantine scholars diligently translated and transcribed these works, ensuring their survival during a time of turmoil in Western Europe. As a result, the Byzantine Empire became a center of learning and intellectual progress, preserving the legacy of ancient Greek and Roman civilizations.
Moreover, the Byzantine Empire also contributed to the continuation of the Roman legal system, known as Roman law. Byzantine legal scholars collected and synthesized Roman laws into a comprehensive legal code known as the Justinian Code. This legal code served as the basis for legal systems in many European countries and had a profound impact on the development of Western civilization.
2. How did the Byzantine Empire shape the development of Christianity?
The Byzantine Empire played a crucial role in the development and spread of Christianity. It served as a bridge between the eastern and western branches of Christianity and played a significant role in defining orthodox Christian theology. The Byzantines convened several important ecumenical councils, such as the Council of Nicaea and the Council of Chalcedon, where key doctrinal issues were debated and resolved. These councils established the foundations of orthodoxy and shaped the Christian faith.
Additionally, the Byzantine Empire had a profound impact on the art and architecture of Christianity. Byzantine churches, such as the Hagia Sophia, showcased intricate mosaics, vibrant frescoes, and Byzantine-style icons. These artistic expressions not only served as a visual representation of religious beliefs but also influenced the art and architecture of subsequent Christian civilizations.
3. How did the Byzantine Empire contribute to the spread of trade and commerce?
The Byzantine Empire was a vibrant hub of trade and commerce, connecting Europe, Asia, and Africa. Its strategic location at the crossroads of major trade routes facilitated the exchange of goods, ideas, and cultures between different regions. Constantinople, the capital of the Byzantine Empire, thrived as a bustling center of economic activity. The empire’s wealth and prosperity were fueled by its control over lucrative trade routes, especially the Silk Road.
The Byzantines also promoted trade through their naval power. The Byzantine navy protected merchant ships from piracy, ensuring safe passage for traders. Emperor Justinian’s efforts to revive the Roman Empire included the construction of a massive navy that controlled the eastern Mediterranean. This maritime power significantly facilitated trade and commerce in the region.
4. How did the Byzantine Empire influence the development of art and architecture?
The Byzantine Empire had a profound influence on the development of art and architecture. Byzantine art was characterized by religious subjects, rich colors, and intricate details. Icon painting, mosaics, and frescoes adorned Byzantine churches and reflected the empire’s religious devotion. These artistic expressions influenced the aesthetics of subsequent artistic movements, such as the Renaissance.
Moreover, Byzantine architecture introduced innovative design elements that had a lasting impact on the architectural traditions of Europe and the Middle East. The iconic dome structure, exemplified by the Hagia Sophia, became synonymous with Byzantine architecture. This architectural innovation influenced the construction of later religious and secular buildings, including mosques, churches, and palaces.
5. How did the fall of the Byzantine Empire impact world history?
The fall of the Byzantine Empire in 1453 to the Ottoman Turks marked the end of an era and had far-reaching consequences. The fall of Constantinople not only ended the Byzantine Empire but also led to the decline of Byzantine cultural and intellectual influence in Europe. As a result, many Byzantine scholars and artists sought refuge in Western Europe, bringing with them a rich legacy of knowledge and artistic traditions.
The fall of the Byzantine Empire also had geopolitical implications. It paved the way for the expansion of the Ottoman Empire, which later threatened and encroached upon European territories. This led to conflicts such as the Siege of Vienna and shaped the geopolitical landscape of Europe for centuries to come.
The rise and fall of the Byzantine Empire – Leonora Neville
In conclusion, the Byzantine Empire played a significant role in shaping world history. Through its preservation of Greek and Roman culture, the empire became a cultural and intellectual bridge between the ancient world and the Middle Ages. Its strategic location allowed it to control trade routes and serve as a bulwark against invaders.
The Byzantine Empire’s political, military, and economic achievements greatly influenced neighboring civilizations, such as the Slavs, Arabs, and the Ottoman Empire. The empire’s religious influence, particularly through the spread of Orthodox Christianity, also had a lasting impact on the development of Europe and Russia.