The Byzantine Empire, known for its rich history and influence, once controlled land on three continents. Its reach extended across Europe, Asia, and Africa, making it a truly global power. This dominance over multiple continents is a testament to the empire’s strength and strategic positioning.
Spanning from the 4th century AD to the 15th century AD, the Byzantine Empire held significant territories in these three continents. In Europe, its control included regions such as Greece, Italy, and parts of Eastern Europe. In Asia, it ruled over Anatolia in modern-day Turkey and maintained a strong presence in the Middle East. Moving south into Africa, the Byzantine Empire extended its influence to Egypt and parts of North Africa.
The Byzantine Empire controlled land in three continents: Europe, Asia, and Africa. In Europe, the empire extended its reach over the Balkan Peninsula, including Greece and parts of Italy. In Asia, it held territories in Anatolia (modern-day Turkey) and the Levant, including Syria and Palestine. And in Africa, the Byzantines controlled Egypt and parts of North Africa. This expansive control over multiple continents contributed to the empire’s lasting influence and significance in history.
Contents
- The Byzantine Empire’s Control Over Three Continents
- Identifying the Three Continents where the Byzantine Empire Controlled Land
- Key Takeaways
- Frequently Asked Questions
- 1. Which continents did the Byzantine Empire control land on?
- 2. Did the Byzantine Empire have a significant presence in Europe?
- 3. How did the Byzantine Empire control land in Asia?
- 4. Was the Byzantine Empire’s presence in Africa significant?
- 5. How did the Byzantine Empire’s control over multiple continents impact its influence?
- History of The Byzantine Empire – Documentary
The Byzantine Empire’s Control Over Three Continents
The Byzantine Empire, also known as the Eastern Roman Empire, was a powerful and enduring civilization that controlled vast territories across three continents. Spanning a significant portion of history, from the 4th century to the 15th century, the Byzantine Empire witnessed remarkable cultural, political, and military achievements. One key aspect that defined the Byzantine Empire was its sprawling territorial control. In this article, we will explore the three continents where the Byzantine Empire held land: Europe, Asia, and Africa.
Europe: The Heartland of the Byzantine Empire
Europe formed the core of the Byzantine Empire’s territories, encompassing major parts of the Mediterranean and the Balkans. The empire’s capital, Constantinople (modern-day Istanbul), was strategically located in Europe, serving as the political, economic, and cultural center of the empire. From this stronghold, the Byzantine Empire exerted control over various regions of Europe through a combination of military might, diplomacy, and administrative efficiency.
One of the notable features of Byzantine control in Europe was the strategic fortifications that safeguarded its borders. The empire constructed impressive defensive structures such as the Theodosian Walls, which surrounded Constantinople, protecting it from external threats. These fortifications symbolized the empire’s commitment to territorial control and served as a symbol of Byzantine power.
Furthermore, the Byzantine Empire maintained a network of provinces and territories throughout Europe, ensuring its presence extended beyond Constantinople. These territories included Greece, Thrace, Macedonia, Italy, and various regions in Eastern Europe. The Byzantine administration effectively governed these territories, fostering economic prosperity, preserving cultural heritage, and propagating the influence of the empire.
Trade routes also played a vital role in Byzantine control over Europe. The empire’s strategic location allowed it to control major trade routes connecting Europe, Asia, and Africa. The Byzantines monopolized trade in the region, facilitating commerce and accumulating wealth. Through these commercial networks, the Byzantine Empire expanded its influence and maintained its grip on European territories.
The Byzantine Empire’s Reach in Asia
While Europe formed the heartland of the Byzantine Empire, the empire also extended its dominion into Asia. One of the key regions under Byzantine control in Asia was Anatolia, which is present-day Turkey. Anatolia held immense significance due to its strategic location bridging Europe and Asia. Byzantine control over Anatolia allowed the empire to protect its eastern territories, maintain trade routes, and exert influence in the broader Asian region.
Byzantine control in Asia also extended beyond Anatolia. The empire maintained a presence in regions such as the Levant, which includes modern-day Lebanon, Israel, Jordan, and Syria. These territories provided the Byzantine Empire with access to vital trade routes linking Asia to Europe, reinforcing the empire’s economic power and overall control in the region.
Additionally, the Byzantine Empire maintained influence over parts of the Caucasus, including Georgia and Armenia, further expanding its reach in Asia. The empire strategically controlled these regions to protect its eastern frontiers and counter external threats from the neighboring Persian and Arab empires.
Africa: Byzantine Presence in the Northern Region
Africa formed the third continent where the Byzantine Empire held land. The empire’s presence in Africa was centered around the northern regions, primarily comprising Egypt and parts of modern-day Libya and Tunisia. Alexandria, the iconic Egyptian city, served as an important administrative and economic center under Byzantine rule.
The Byzantine Empire’s control over Egypt was significant due to the region’s economic and agricultural prominence. Egypt was one of the empire’s key breadbaskets, providing a steady supply of grain. The Nile River, traversing through Egypt, facilitated agricultural productivity and enabled the Byzantine Empire to maintain its dominance in the region.
Further beyond Egypt, the Byzantine Empire also controlled territories in North Africa, including the region of Cyrenaica, which encompassed modern-day eastern Libya. These territories served as valuable outposts, extending the Byzantine Empire’s influence along the northern African coast and securing its trade routes in the Mediterranean.
The Strategic Importance of the Byzantine Empire’s Territorial Control
The Byzantine Empire’s territorial control over three continents carried immense strategic importance. It ensured the empire’s stability, security, and economic prosperity. By exerting control over Europe, Asia, and Africa, the Byzantine Empire maintained a vast network of territories, trade routes, and defensive fortifications.
The empire’s territorial control acted as a buffer against external threats, safeguarding Byzantine interests from neighboring kingdoms and empires. The administration and governance of these territories displayed the empire’s organizational prowess, preserving law and order, promoting cultural diversity, and facilitating economic growth.
Ultimately, the Byzantine Empire’s expansive territorial control played a crucial role in shaping its identity, influence, and longevity. It solidified the empire’s position as a significant force in the medieval world, leaving a lasting impact on the regions it governed.
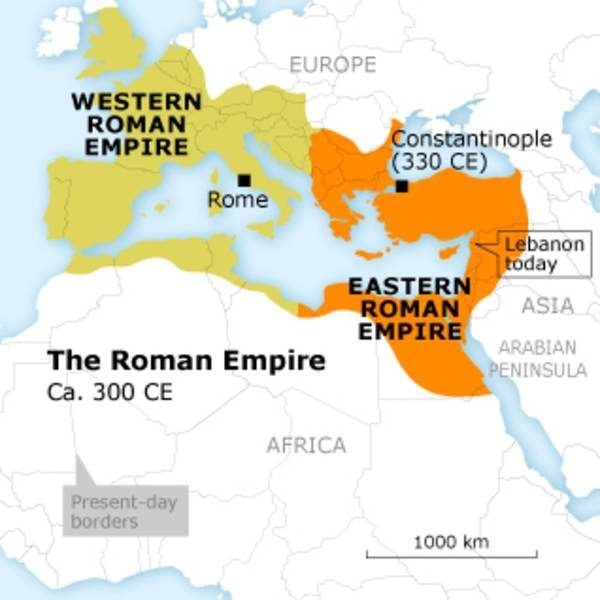
Identifying the Three Continents where the Byzantine Empire Controlled Land
The Byzantine Empire, also known as the Eastern Roman Empire, was a vast empire that existed from the 4th century until the 15th century. At its height, the Byzantine Empire controlled territories in three continents: Europe, Asia, and Africa.
In Europe, the Byzantine Empire controlled significant portions of the Balkans, including modern-day Greece, Bulgaria, and parts of Albania and North Macedonia. They also controlled areas along the Mediterranean coast, such as southern Italy and Sicily.
In Asia, the Byzantine Empire held territories that encompassed modern-day Turkey, including the region of Anatolia. They also controlled parts of the Levant, including Syria and Palestine.
In Africa, the Byzantine Empire had control over the province of Egypt, along with the surrounding areas of Libya and Tunisia.
With their extensive control over these three continents, the Byzantine Empire played a crucial role in shaping the history and culture of the Eastern Mediterranean region for over a millennium.
Key Takeaways
- The Byzantine Empire controlled land in Europe, Asia, and Africa.
- Europe was the continent where the Byzantine Empire had the largest percentage of controlled land.
- Asia was also a significant continent where the Byzantine Empire had control over land.
- Africa was the continent where the Byzantine Empire had the smallest amount of controlled land.
- The Byzantine Empire’s control over these three continents contributed to its economic and political power.
Frequently Asked Questions
The Byzantine Empire was a powerful and influential state that controlled significant land throughout its existence. Here are some frequently asked questions about identifying the three continents where the Byzantine Empire controlled land.1. Which continents did the Byzantine Empire control land on?
The Byzantine Empire controlled land on three continents: Europe, Asia, and Africa. This expansive empire had a diverse territory that included parts of modern-day Turkey, Greece, Egypt, Italy, and more.
By ruling over territories on three different continents, the Byzantine Empire held a crucial position in terms of trade, political influence, and cultural exchange in the medieval world.
2. Did the Byzantine Empire have a significant presence in Europe?
Yes, the Byzantine Empire had a significant presence in Europe. It controlled vast territories in southeastern Europe, including the Balkans, Greece, and portions of Italy. The empire’s capital, Constantinople, was located in modern-day Istanbul, Turkey, which served as a crucial hub connecting Europe and Asia.
The Byzantines had a major influence on European history, shaping political, religious, and artistic developments. Their influence can still be seen today in the architecture, art, and religious traditions of countries like Greece and Russia.
3. How did the Byzantine Empire control land in Asia?
The Byzantine Empire controlled land in Asia primarily through its control of Anatolia, which is present-day Turkey. Anatolia was a crucial region, serving as a buffer zone between the Byzantines and various Muslim empires and kingdoms.
Although the Byzantines faced many invasions and struggled to maintain control over Anatolia, they were able to retain their presence in the region for centuries. This allowed them to exert influence over trade routes and maintain connections with other Asian powers.
4. Was the Byzantine Empire’s presence in Africa significant?
While the Byzantine Empire’s presence in Africa was not as extensive as its holdings in Europe and Asia, it did control some territories in North Africa. The Byzantines held parts of Egypt and Libya, including the city of Alexandria, which was a vital center of trade and culture.
The Byzantines’ control over Egypt allowed them to maintain control over the lucrative trade routes of the Red Sea and the Mediterranean, further enhancing their economic and political power.
5. How did the Byzantine Empire’s control over multiple continents impact its influence?
The Byzantine Empire’s control over multiple continents gave it immense influence and power in the medieval world. It allowed the empire to trade with and interact with various civilizations, fostering cultural exchange and economic growth.
The empire’s position at the crossroads of Europe, Asia, and Africa made it a central player in international politics. It acted as a bridge between different regions and civilizations, shaping the course of history through its alliances, wars, and diplomatic endeavors.
History of The Byzantine Empire – Documentary
To sum up, the Byzantine Empire exerted control over land in three continents: Europe, Asia, and Africa. This demonstrates their vast territorial reach and influence during their reign.
In Europe, the Byzantine Empire controlled areas such as Greece, Italy, and parts of the Balkans. In Asia, they held sway over present-day Turkey, Syria, and Egypt. Finally, in Africa, the Byzantine Empire controlled regions like Libya and Tunisia.