Ancient Chinese civilization, one of the oldest and most influential in the world, has its origins shrouded in mystery and legends. The question of where it all began is a topic of much debate and speculation among historians and archaeologists. However, there are some fascinating discoveries and theories that provide insights into the possible origins of ancient Chinese civilization.
According to archaeological evidence, the earliest known signs of civilization in ancient China can be traced back to the Neolithic period around 10,000 BCE. The Yellow River, also known as the Huang He, is considered by many as the birthplace of Chinese civilization. This mighty river, flowing through the heartland of China, provided fertile grounds for agricultural development, which laid the foundation for settled communities and the development of complex societies.
The ancient Chinese civilization began along the Yellow River in China. This region, also known as the Yellow River Valley, was the cradle of Chinese civilization. It is believed that the first farming communities and settlements emerged in this area around 7000 BCE. The fertile soil and abundant water resources of the Yellow River provided the ideal conditions for agricultural development, which laid the foundation for the ancient Chinese civilization to flourish.
Contents
- The Origins of Ancient Chinese Civilization
- Ancient Chinese Civilization Origins
- Key Takeaways – Where Did Ancient Chinese Civilization Begin?
- Frequently Asked Questions
- 1. What is the origin of ancient Chinese civilization?
- 2. When did ancient Chinese civilization first emerge?
- 3. How did ancient Chinese civilization spread and evolve?
- 4. What were the major achievements of ancient Chinese civilization?
- 5. What is the legacy of ancient Chinese civilization?
- How did Chinese Civilization begin? (Shang and Zhou dynasties) Bronze Age China history explained
The Origins of Ancient Chinese Civilization
The origins of ancient Chinese civilization can be traced back thousands of years to the Neolithic period. This period, which began around 10,000 BCE, marked the transition from hunting and gathering to settled agricultural communities in China. It was during this time that the foundations of Chinese civilization were established, including the development of agriculture, pottery, and early forms of social organization.
One of the key locations where ancient Chinese civilization began is in the Yellow River Valley in northern China. Often referred to as the “Cradle of Chinese Civilization,” this region provided fertile land for farming and facilitated the growth of early Chinese settlements. The availability of water from the Yellow River allowed for the cultivation of crops and the development of a stable food supply, which in turn led to the growth of larger communities.
The Neolithic Yangshao culture, which emerged around 5000 BCE, is one of the earliest known examples of settled agricultural communities in the Yellow River Valley. These communities practiced farming, raised livestock, and developed sophisticated pottery techniques. The Yangshao culture also displayed early signs of social differentiation, with evidence of communal burial sites and a division of labor.
As ancient Chinese civilization continued to develop, technological advancements such as the invention of writing and the discovery of bronze metallurgy emerged. The writing system, known as oracle bone script, was used for divination and communication with the spiritual realm. Bronze metallurgy allowed for the creation of tools, weapons, and ritual objects, further contributing to the growth and complexity of Chinese society.
The Xia Dynasty: Legendary Beginnings
The Xia Dynasty is considered the first dynasty of ancient China and is often regarded as the starting point of Chinese civilization. According to historical records and legends, the Xia Dynasty was founded by Yu the Great, who was said to have been appointed as the ruler due to his ability to control floods. The Xia Dynasty spanned from approximately 2070 to 1600 BCE and laid the groundwork for future dynasties to come.
While concrete evidence of the Xia Dynasty is limited, archaeological excavations in the Yellow River Valley have uncovered remnants of early settlements and artifacts that suggest the existence of an early complex society. These findings support the idea that the Xia Dynasty was a real historical entity, although much of its history has been overshadowed by legend and mythology.
During the Xia Dynasty, agriculture thrived, leading to population growth and the establishment of cities surrounded by defensive walls. The Xia rulers were also known for their efforts to control floodwaters, a crucial task in a region prone to devastating floods. The legendary figure of Yu the Great is credited with successfully taming the Yellow River’s floods, which helped protect settlements and ensure stable agricultural production.
Shang Dynasty: A Bronze Age Civilization
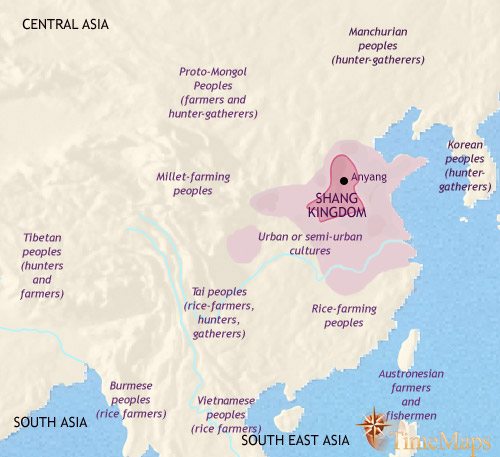
The Shang Dynasty succeeded the Xia Dynasty and is known as the first historically documented dynasty of ancient China. It lasted from approximately 1600 to 1046 BCE and is considered one of the early Bronze Age civilizations. The Shang Dynasty marked a period of significant cultural and technological advancements in ancient China.
The Shang rulers established a centralized government and developed a sophisticated system of writing known as oracle bone script. Oracle bones, which were inscribed with divination questions and answers, have provided invaluable insights into the social, political, and religious aspects of Shang society. The oracle bone script represents one of the earliest forms of writing in China and is considered a direct ancestor of the modern Chinese writing system.
During the Shang Dynasty, bronze metallurgy flourished, and elaborate bronze ritual vessels, weapons, and other artifacts were created. These objects served both practical and ritual purposes and were often adorned with intricate decorative motifs. The development of bronze technology not only elevated the Shang Dynasty’s status but also facilitated trade and cultural exchange with neighboring regions.
The Zhou Dynasty and the Mandate of Heaven
The Zhou Dynasty, which followed the Shang Dynasty, is considered one of the most significant periods in ancient Chinese civilization. It lasted from approximately 1046 to 256 BCE and was characterized by political, social, and philosophical developments.
One of the key concepts that emerged during the Zhou Dynasty is the “Mandate of Heaven.” According to this belief, the ruling dynasty was granted its authority by the heavens as long as it governed with benevolence and provided good governance. If a dynasty failed to fulfill its responsibilities, it was believed that the mandate would be withdrawn, leading to a change in dynasty. This concept of the Mandate of Heaven had a profound impact on Chinese political and philosophical thought for centuries to come.
During the Zhou Dynasty, iron metallurgy began to replace bronze as the dominant metalworking technique. The use of iron tools and weapons revolutionized agriculture and warfare, leading to increased productivity and military strength. The Zhou Dynasty also saw the emergence of prominent philosophical schools, such as Confucianism and Taoism, which left a lasting imprint on Chinese culture and society.
The Silk Road: A Cultural Crossroads
The Silk Road, which connected China with Central Asia, the Middle East, and Europe, played a vital role in the exchange of goods, ideas, and cultures during ancient times. While the exact origins of the Silk Road are debatable, it became an established network of trade routes during the Han Dynasty (202 BCE – 220 CE).
Chinese civilization benefited greatly from the trade along the Silk Road, as it facilitated the exchange of Chinese silk, tea, and other luxury goods with foreign lands. In return, China received commodities such as precious metals, spices, ivory, and horses. The Silk Road also served as a conduit for the spread of knowledge, religious beliefs, and artistic influences between diverse civilizations.
The Silk Road not only contributed to economic prosperity but also fostered cultural and intellectual encounters. Buddhist ideas, which originated in India, were introduced to China through the Silk Road and eventually became a major religion in the country. Likewise, Chinese inventions and technologies, such as papermaking and silk production, spread to other regions along the Silk Road, transforming societies and shaping the course of history.
Contributions of Ancient Chinese Civilization
-
Agriculture: Ancient Chinese civilization developed advanced agricultural techniques, such as irrigation systems and the cultivation of rice, which allowed for increased food production and population growth.
-
Writing: The invention of writing in ancient China paved the way for the preservation of history, the dissemination of knowledge, and the development of a rich literary tradition.
-
Confucianism: The teachings of Confucius, a prominent philosopher during the Zhou Dynasty, have profoundly influenced Chinese society, ethics, and governance for over two millennia.
-
Technology: Ancient China made significant technological advancements, including the invention of gunpowder, papermaking, and the compass, which had a transformative impact on global history.
-
Art and Architecture: Ancient Chinese civilization produced magnificent works of art and architecture, such as the Great Wall, the Terracotta Army, and intricate jade carvings.
Ancient Chinese civilization began in the fertile Yellow River Valley, where the early settlements of the Neolithic period laid the groundwork for the development of agriculture, writing, and complex social structures. Over time, successive dynasties like the Xia, Shang, and Zhou, contributed to the growth and evolution of Chinese civilization. The Silk Road acted as a cultural crossroads, facilitating trade and the exchange of ideas between China and other regions. Ancient Chinese civilization left a lasting impact on the world, with its technological advancements, philosophical teachings, and rich cultural heritage.
Ancient Chinese Civilization Origins
The origins of ancient Chinese civilization can be traced back to the Yellow River Valley in present-day China. This region, known as the cradle of Chinese civilization, was where the earliest known settlements emerged around 5000 BCE. The early Chinese civilization, often referred to as the “Neolithic period,” showcased advancements in agriculture, pottery, and architecture.
The ancient Chinese civilization flourished during the Shang (1600–1046 BCE) and Zhou (1046–256 BCE) dynasties. The Shang dynasty marked the emergence of writing systems, bronze metallurgy, and complex societal structures. The Zhou dynasty introduced the concept of a centralized government and implemented the “Mandate of Heaven” ideology.
| The Yellow River Valley | Emergence of settlements |
| Neolithic period | Advancements in agriculture, pottery, and architecture |
| Shang dynasty | Development of writing systems, bronze metallurgy, and societal structures |
| Zhou dynasty | Introduction of a centralized government and the “Mandate of Heaven” ideology |
Key Takeaways – Where Did Ancient Chinese Civilization Begin?
- The ancient Chinese civilization began in the Yellow River Valley.
- The Yellow River Valley provided fertile land for farming and natural resources.
- The civilization started around 4,000 years ago during the Neolithic period.
- Ancient Chinese civilization is known for its significant contributions to art, philosophy, and technology.
- The Chinese language and writing system originate from this ancient civilization.
Frequently Asked Questions
Ancient Chinese civilization is one of the oldest and most influential civilizations in history. It emerged in the fertile lands of East Asia and left a lasting impact on the world. In this section, we’ll explore where this remarkable civilization first took root and flourished.
1. What is the origin of ancient Chinese civilization?
Ancient Chinese civilization originated in the Yellow River Valley, also known as the Huang He Valley. This region, located in present-day China, provided fertile soil for agriculture and easy access to water resources. The early Chinese settlers developed complex agricultural techniques, built irrigation systems, and cultivated crops like millet and rice, which formed the foundation of their civilization.
The Yellow River Valley was home to several ancient Chinese dynasties, including the Xia, Shang, and Zhou dynasties. These early civilizations laid the groundwork for the development of Chinese culture, language, philosophy, and governance.
2. When did ancient Chinese civilization first emerge?
Ancient Chinese civilization emerged around 2100 BCE during the Xia Dynasty. This period marked the beginning of organized societies and the development of the fundamental institutions that shaped Chinese civilization. The Xia Dynasty was followed by the Shang Dynasty, which further expanded and consolidated the early Chinese civilization.
The Zhou Dynasty, which succeeded the Shang Dynasty, brought significant advancements in government administration, education, and literature. This period is often referred to as the “Axial Age” of Chinese history, as it witnessed the flourishing of philosophical ideologies, such as Confucianism and Daoism.
3. How did ancient Chinese civilization spread and evolve?
Ancient Chinese civilization spread through a combination of cultural diffusion, migration, and conquests. As Chinese society developed, neighboring regions and tribes were influenced by Chinese advancements in agriculture, technology, and governance.
The Silk Road, a network of trade routes connecting China with the rest of Asia and Europe, played a crucial role in spreading Chinese culture, goods, and ideas across vast distances. This exchange of goods and knowledge contributed to the evolution and enrichment of ancient Chinese civilization.
4. What were the major achievements of ancient Chinese civilization?
Ancient Chinese civilization achieved remarkable advancements in various fields. Some of the major achievements include:
- Development of complex writing system (Chinese characters)
- Invention of papermaking
- Scientific discoveries, such as the invention of gunpowder and compass
- Artistic achievements, including exquisite ceramics and silk production
- Architectural marvels, such as the Great Wall of China
5. What is the legacy of ancient Chinese civilization?
The ancient Chinese civilization has left a lasting legacy that continues to shape the world today. Some notable aspects of this legacy include:
- Influential philosophical and religious traditions, including Confucianism, Daoism, and Buddhism
- The use of Chinese characters as a writing system
- Traditional Chinese medicine and holistic healing practices
- Chinese cuisine and culinary traditions
- Important contributions to science, mathematics, and technology
How did Chinese Civilization begin? (Shang and Zhou dynasties) Bronze Age China history explained
The ancient Chinese civilization started in the fertile valleys of the Yellow River, also known as the Huang He. This river provided the necessary resources for agriculture and became the lifeline of the Chinese people. The early Chinese settlements began around 7000 BCE, with the most prominent being the Yangshao and Longshan cultures. These societies developed advanced agricultural techniques and pottery skills, laying the foundation for the later Chinese civilization.
Over time, the ancient Chinese civilization expanded its influence and formed several dynasties, such as the Xia, Shang, and Zhou dynasties. These dynasties marked significant periods of cultural and political development. The ancient Chinese civilization influenced neighboring regions and left a lasting impact on art, literature, philosophy, and governance. The origins of the rich and diverse Chinese culture can be traced back to the ancient settlements along the Yellow River.