Ancient China, one of the world’s oldest continuous civilizations, existed in a vast and diverse geographical area. It spanned across the East Asian region, primarily in the eastern part of the Asian continent. From the Yellow River basin in the north to the Yangtze River in the south, China’s ancient civilization flourished and left behind a rich cultural legacy that continues to influence the world today.
The ancient civilization of China thrived in a landscape that encompassed various terrains, including fertile plains, mountains, deserts, and river valleys. Its heartland was in the central and eastern regions, where the Yellow and Yangtze Rivers played fundamental roles in shaping the culture and development of the civilization. With a history that dates back thousands of years, ancient China witnessed the rise and fall of numerous dynasties, empires, and influential figures, leaving behind architectural marvels, works of art, philosophical teachings, and technological advancements that continue to captivate the world.
The ancient civilization of China existed primarily in the eastern part of modern-day China, along the Yellow and Yangtze Rivers. This region, known as the Central Plains, was home to several influential dynasties, such as the Zhou, Qin, and Han. The civilization flourished in this fertile area, benefiting from the agricultural opportunities provided by the rivers. It is important to note that the influence of ancient Chinese civilization extended beyond the Central Plains to encompass other parts of Asia as well.
Contents
- The Origins of Ancient Chinese Civilization
- The Legacy of Ancient Chinese Civilization
- Where Did The Ancient Civilization Of China Exist?
- Key Takeaways: Where Did The Ancient Civilization Of China Exist?
- Frequently Asked Questions
- 1. Which regions of China were part of the ancient civilization?
- 2. How did the geography of China influence its ancient civilization?
- 3. Were there different ancient civilizations within China?
- 4. How did the ancient civilization of China contribute to world history?
- 5. Did the ancient civilization of China have cultural influences beyond its borders?
- How Old Is Chinese Civilization? – Ancient Civilizations DOCUMENTARY
The Origins of Ancient Chinese Civilization
The ancient civilization of China is one of the oldest and most influential civilizations in history. It is fascinating to explore the origins of this ancient culture and understand where it first emerged. The origins of ancient Chinese civilization can be traced back to the Neolithic period, around 10,000 BCE.
During this time, several areas in modern-day China witnessed the development of settled agricultural communities. These communities laid the foundation for the growth and expansion of early Chinese civilization. Let us delve deeper into the regions where the ancient civilization of China flourished.
The Yellow River Valley
One of the key regions where the ancient Chinese civilization existed is the Yellow River valley. The Yellow River, also known as the Huang He, is the second-longest river in China and played a vital role in the agricultural development of the region. The fertile soil deposited by the river allowed for intensive farming, leading to the growth of early Chinese settlements.
The Yellow River valley witnessed the emergence of several Neolithic cultures, such as the Yangshao and Longshan cultures. These cultures developed advanced agricultural techniques, pottery, and weaving skills, establishing the foundation for the later dynastic civilizations of China. The development of these early settlements along the Yellow River laid the groundwork for the formation of the ancient Chinese civilization.
The Xia Dynasty
The Yellow River valley also served as the cradle of the Xia Dynasty, which is considered the first dynasty of ancient China. According to historical records and legends, the Xia Dynasty was established by the legendary Emperor Yu, who was believed to have controlled and managed the frequent flooding of the Yellow River.
The Xia Dynasty marked the transition from tribal communities to a centralized political system led by a ruler. It is important to note that the Xia Dynasty’s existence is still a subject of debate among historians, as there is limited archaeological evidence to support its existence. However, the legends and stories surrounding the Xia Dynasty have played a significant role in shaping the Chinese cultural identity.
The Shang Dynasty
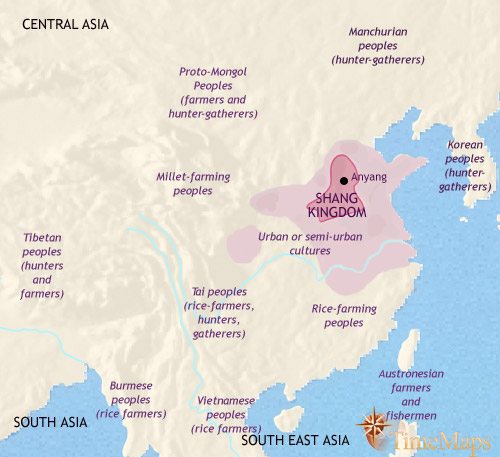
Following the Xia Dynasty, the ancient Chinese civilization entered the era of the Shang Dynasty. The Shang Dynasty emerged around 1600 BCE and is considered the first confirmed dynasty in Chinese history. It was centered in the Yellow River valley and is known for its sophisticated bronze metallurgy, oracle bone script, and social hierarchy.
The Shang Dynasty was a highly developed civilization characterized by advanced agriculture, urban planning, and religious practices. The rulers of the Shang Dynasty were powerful and governed through a centralized bureaucracy. The remains of the ancient city of Yin, near modern-day Anyang, serve as evidence of the grandeur and influence of the Shang Dynasty.
The Yangtze River Valley
Another significant region where the ancient civilization of China existed is the Yangtze River valley. The Yangtze River is the longest river in China and has been a vital transportation route and a source of fertile land for agriculture.
The Yangtze River valley witnessed the emergence of several important cultures, such as the Liangzhu culture and the Chu state. These cultures exhibited advanced agricultural practices, including wetland rice cultivation and hydraulic engineering systems.
The Liangzhu Culture
The Liangzhu culture, which flourished in the Yangtze River delta around 3300-2300 BCE, is renowned for its sophisticated jade artifacts, urban planning, and complex social organization. The Liangzhu culture represents an early form of state-level society, characterized by extensive public works, including the construction of large-scale water management systems.
The presence of advanced agricultural and urban planning techniques in the Yangtze River valley highlights the significance of this region in the development of ancient Chinese civilization.
The Silk Road
Beyond the river valleys, the ancient Chinese civilization also expanded and thrived along the Silk Road. The Silk Road was a network of trade routes that connected China to various regions of Asia, Europe, and Africa. It served as a vital conduit for cultural, economic, and technological exchange.
The Silk Road allowed the Chinese civilization to establish connections with diverse cultures, facilitating the spread of Chinese ideas, goods, and innovations to other parts of the world. This cultural exchange significantly influenced Chinese art, technology, religion, and philosophy, as well as contributing to the prosperity and development of ancient China.
The Han Dynasty
The Han Dynasty, which succeeded the Qin Dynasty, played a key role in promoting trade and cultural exchange along the Silk Road. The Han Dynasty’s policies encouraged the development of a unified empire and facilitated the transportation of goods, particularly silk, along the Silk Road.
The Han Dynasty’s focus on trade and diplomacy led to a significant expansion of the ancient Chinese civilization’s influence along the Silk Road, enabling China to forge connections with neighboring regions and establish itself as a regional power.
The Legacy of Ancient Chinese Civilization
The ancient Chinese civilization’s existence in the Yellow River and Yangtze River valleys, as well as its expansion along the Silk Road, laid the foundation for China’s rich cultural heritage and enduring contributions to human civilization. From the early agricultural communities to the sophisticated dynastic empires, ancient China’s innovations in agriculture, art, technology, philosophy, and governance continue to influence the world to this day.
Where Did The Ancient Civilization Of China Exist?
The ancient civilization of China existed primarily in the eastern part of Asia. It is believed to have originated in the Yellow River valley, also known as the Huang He valley, which is located in present-day China. This region was the cradle of Chinese civilization and witnessed the rise of several early Chinese dynasties.
China’s ancient civilization also expanded beyond the Yellow River valley and extended to other parts of China, such as the Yangtze River valley. The Yangtze River, known as Chang Jiang in Chinese, is the longest river in Asia and played a significant role in the development of ancient Chinese culture and civilization.
The ancient civilization of China was characterized by great achievements in various areas, including art, literature, philosophy, technology, and governance. It left a lasting impact on the world and continues to influence modern Chinese society and culture.
Key Takeaways: Where Did The Ancient Civilization Of China Exist?
- Ancient Chinese civilization existed primarily in the Yellow River and Yangtze River regions.
- The Yellow River, also known as the “Mother River of China,” was the birthplace of Chinese civilization.
- The Yellow River region is in northern China and is characterized by its fertile soil.
- The Yangtze River region is in central and southern China and is known for its diverse geography.
- Ancient Chinese civilization spread beyond these two main regions to other parts of China over time.
Frequently Asked Questions
The ancient civilization of China existed in various regions throughout the country. It has a rich history that dates back thousands of years, with different dynasties and kingdoms ruling over different parts of the land.
1. Which regions of China were part of the ancient civilization?
The ancient civilization of China was mainly concentrated in the Yellow River and Yangtze River valleys. These regions, known as the cradle of Chinese civilization, were the heartland of Chinese culture and played a significant role in the development of the country.
In addition to the river valleys, other regions such as the North China Plain, the Sichuan Basin, and the regions along the Silk Road also played important roles in the ancient civilization of China.
2. How did the geography of China influence its ancient civilization?
The geography of China had a profound impact on its ancient civilization. The presence of two major rivers, the Yellow River and the Yangtze River, provided fertile land for agriculture, leading to the development of advanced agricultural techniques.
The mountainous terrain and natural barriers, such as the Himalayas and the Gobi Desert, shaped the political and cultural landscape of China. These geographical features acted as natural boundaries and influenced the interactions between different regions and civilizations.
3. Were there different ancient civilizations within China?
Yes, there were multiple ancient civilizations within China. Throughout its history, China has seen the rise and fall of various dynasties and kingdoms, each with its own unique culture, traditions, and contributions to Chinese civilization.
Some of the notable ancient civilizations within China include the Shang Dynasty, the Zhou Dynasty, the Qin Dynasty, the Han Dynasty, and the Tang Dynasty. These civilizations left behind a legacy of art, architecture, philosophy, and advancements in various fields.
4. How did the ancient civilization of China contribute to world history?
The ancient civilization of China made significant contributions to world history. It was responsible for many inventions and discoveries, including papermaking, printing, gunpowder, compass, and silk production.
Chinese philosophers, such as Confucius and Laozi, developed influential schools of thought that had a lasting impact on not only Chinese society but also on the global philosophical discourse.
5. Did the ancient civilization of China have cultural influences beyond its borders?
Yes, the ancient civilization of China had far-reaching cultural influences beyond its borders. The Silk Road, a network of trade routes connecting China with the Middle East, Central Asia, and Europe, played a crucial role in the exchange of goods, ideas, and cultural practices.
Chinese art, literature, cuisine, and philosophies spread to neighboring regions and had a profound influence on the cultures and civilizations of East Asia and Southeast Asia.
How Old Is Chinese Civilization? – Ancient Civilizations DOCUMENTARY
In summary, the ancient civilization of China existed primarily in East Asia, spanning a vast geographical area.
China’s civilization can be traced back thousands of years and its rich history includes significant contributions to art, science, philosophy, and governance. The ancient Chinese civilization thrived along the Yellow, Yangtze, and Pearl Rivers, as well as in the regions surrounding the North and East China Seas.