The Renaissance is often regarded as a pivotal period of cultural and intellectual rebirth, but why did it begin in Italy? One possible explanation lies in the country’s unique historical and geographical circumstances. Italy was home to the powerful city-states of Florence, Venice, and Rome, which became centers of trade and wealth in the late Middle Ages. These cities attracted wealthy patrons who supported artists, scholars, and thinkers, creating an environment conducive to innovation and creativity.
Furthermore, Italy’s close proximity to the remnants of the Roman Empire played a significant role in fostering the Renaissance. Many scholars and artists of the time were inspired by the classical ideals and achievements of ancient Rome. They studied Roman literature, architecture, and art, seeking to revive and emulate the greatness of the past. This classical influence, combined with the patronage and wealth of Italy’s city-states, formed the perfect breeding ground for the Renaissance to flourish.
The Renaissance began in Italy due to a combination of factors. Firstly, Italy was the birthplace of the Roman Empire, which had a profound influence on Italian culture and history. Additionally, Italy was at the crossroads of trade routes, which brought wealth and ideas from all over the world. Italian city-states such as Florence and Venice became centers of banking and commerce, fostering an environment that supported the arts and intellectual pursuits. Finally, Italian scholars rediscovered and translated classical Greek and Roman texts, fueling a renewed interest in learning and sparking the Renaissance.
Contents
- The Birthplace of the Renaissance
- A Unique Confluence of Factors
- Why Did The Renaissance Began In Italy?
- Geographical and Historical Factors
- Wealthy Patrons and Sponsorship
- Intellectual Environment and Humanism
- Key Takeaways
- Frequently Asked Questions
- 1. What were the key factors that contributed to the Renaissance taking place in Italy?
- 2. How did the Renaissance ideals align with Italian society?
- 3. How did Italy’s political and social structure contribute to the Renaissance?
- 4. How did Italian art and architecture contribute to the development of the Renaissance?
- 5. What impact did the Renaissance in Italy have on the rest of Europe?
- Why the Renaissance Began in Italy?
The Birthplace of the Renaissance
The Renaissance was a period of significant cultural and intellectual transformation that emerged in Europe between the 14th and 17th centuries. It marked a profound shift from the medieval period towards modernity, encompassing advancements in art, literature, science, philosophy, and politics. While the Renaissance had a significant impact across Europe, its origins can be traced back to Italy. Who would have thought that a relatively small city-state would become the birthplace of such a monumental movement? The question remains: Why did the Renaissance begin in Italy?
1. Geographic Location Perfect for Intellectual and Cultural Exchange
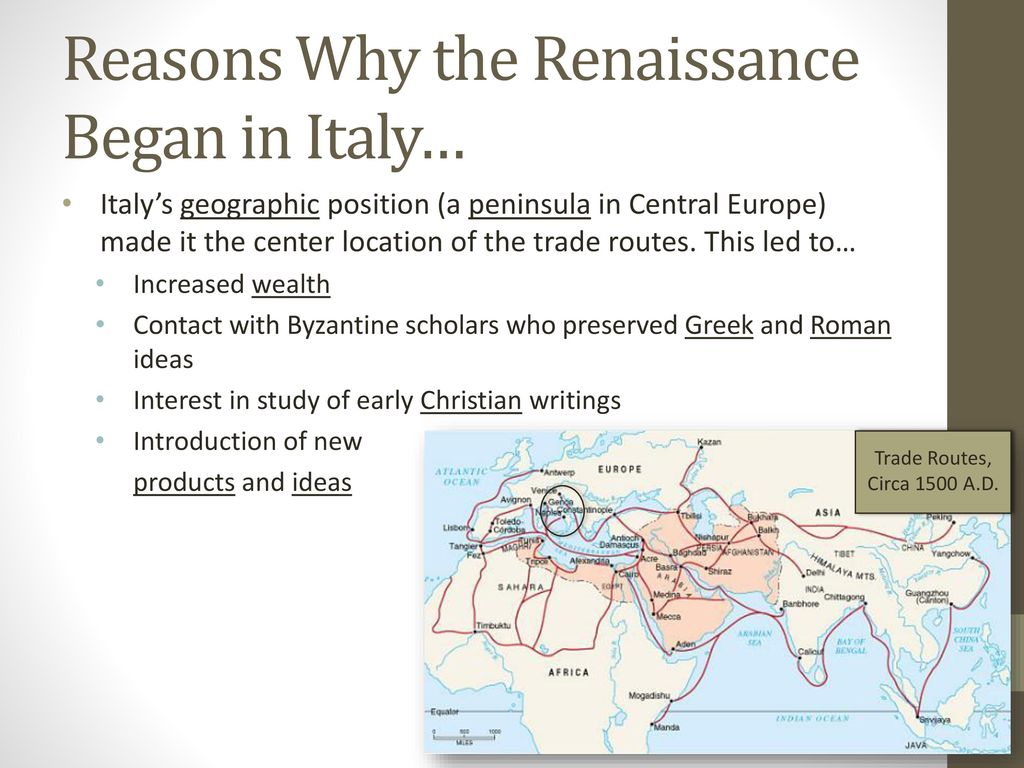
Italy’s geographic location played a crucial role in fostering intellectual and cultural exchange during the Renaissance. Situated at the crossroads of Europe, Asia, and Africa, Italy was a hub for trade and commerce. As merchants and traders from different regions converged in Italian city-states, they brought with them not only goods but also ideas from various cultures. This cultural diversity and interaction provided fertile ground for the exchange of knowledge and the emergence of new ideas.
In addition, Italy’s position on the Mediterranean Sea facilitated the flow of people, goods, and ideas. The Mediterranean was a bustling maritime network, connecting Italy to other important centers of culture and learning such as Constantinople (present-day Istanbul) in the Byzantine Empire and the Islamic world. This maritime trade and contact allowed for the diffusion of knowledge and the introduction of new concepts, further fueling the intellectual atmosphere of the Renaissance.
Moreover, Italian city-states themselves were centers of intellectual and artistic patronage. Wealthy and powerful families like the Medici in Florence and the Sforza in Milan provided financial support to artists, scholars, and scientists. The patronage system allowed these individuals to dedicate themselves fully to their craft, free from financial constraints. This support system attracted renowned artists, thinkers, and scientists from across Europe, contributing to the vibrant intellectual climate of Italy during the Renaissance.
It is evident that Italy’s strategic location and the influx of diverse cultural influences created a conducive environment for the exchange of ideas and the development of the Renaissance.
2. Rediscovery of Classical Greek and Roman Culture
Another crucial factor in the birth of the Renaissance in Italy was the rediscovery and renewed interest in the ancient Greek and Roman civilizations. During the Middle Ages, much of the knowledge from classical antiquity was lost or forgotten. However, in Italy, there was a unique preservation and revival of this ancient cultural heritage.
The Italian city-states, particularly Florence, became centers for scholarship and the study of classical texts. Literary works by ancient Greek and Roman writers such as Plato, Aristotle, Cicero, and Virgil were eagerly sought after and meticulously copied. These texts, which had been preserved in monasteries and libraries, were now being disseminated among scholars and intellectuals.
The humanist movement, with its focus on the individual and the study of humanities (such as literature, history, and philosophy), played a crucial role in sparking the Renaissance. Humanist scholars placed an emphasis on the value of classical education and sought to reconnect with the wisdom of the ancient world. This revival of classical learning provided a foundation for the Renaissance’s intellectual and artistic achievements. It inspired new modes of thinking, artistic styles, and scientific inquiries.
Italy, with its rich collection of classical texts, became the epicenter of this cultural renaissance, attracting scholars and artists who were hungry for knowledge and eager to explore the wisdom of the past. The rediscovery of classical Greek and Roman culture served as a catalyst for the intellectual and artistic endeavors of the Renaissance.
3. Economic Prosperity and Patronage
Italy experienced a period of remarkable economic prosperity during the Renaissance, which contributed to the flourishing of the arts and sciences. Italian city-states, such as Florence, Venice, and Milan, were prominent centers of trade, banking, and manufacturing.
The wealth accumulated through trade and commerce allowed for substantial investment in the arts. Wealthy merchants and aristocrats became patrons of artists, supporting their work financially and providing a platform for their artistic expression. The Medici family, for example, were influential patrons in Florence, fostering the talent of renowned artists such as Michelangelo and Leonardo da Vinci.
Furthermore, the demand for luxury goods and artistic creations fueled the growth of artistic workshops and studios. Skilled craftsmen and artisans thrived in this environment, honing their skills and pushing the boundaries of artistic expression.
The economic prosperity of Italy during the Renaissance provided the necessary resources and support for artists, scientists, and scholars to push the boundaries of creativity and innovation.
4. Political Fragmentation
The political fragmentation of Italy during the Renaissance also played a significant role in the emergence of the cultural and intellectual movement. Italy was not a unified nation during this period but rather a collection of city-states, each with its own government and ruling elite.
This political fragmentation created a competitive environment among the Italian city-states. Each city-state vied for prestige, power, and cultural dominance. This competition fueled the desire to attract and retain talented individuals, leading to an environment conducive to artistic and intellectual growth.
The constant rivalry and competition among city-states fostered an environment of innovation, creativity, and rivalry in artistic, intellectual, and scientific pursuits. The flourishing of the Renaissance in Italy can be attributed, in part, to this political fragmentation.
A Unique Confluence of Factors
The Renaissance began in Italy due to a unique confluence of factors. Italy’s geographic location facilitated cultural and intellectual exchange, while the rediscovery of classical Greek and Roman culture ignited a revival of learning. The economic prosperity of Italian city-states, coupled with the patronage system, provided the necessary resources and support for artistic and scientific endeavors. Additionally, the political fragmentation of Italy fostered competition and a desire for cultural dominance among the city-states.
Why Did The Renaissance Began In Italy?
The Renaissance was a period of cultural, artistic, and intellectual rebirth that occurred from the 14th to the 17th century in Europe. It is widely acknowledged that the Renaissance began in Italy, specifically in cities such as Florence, Rome, and Venice. There are several reasons why Italy became the birthplace of this influential movement.
Geographical and Historical Factors
Italy was at the heart of the Roman Empire and the center of trade and commerce during the Middle Ages. This rich history provided fertile ground for the rediscovery of classical texts, art, and ideas. The proximity to ancient ruins and manuscripts allowed Italian scholars to have direct access to the works of ancient thinkers such as Plato and Aristotle. Furthermore, Italy’s favorable geographical position, serving as a gateway between Europe and the East, facilitated cultural exchanges and the influx of new ideas.
Wealthy Patrons and Sponsorship
The Italian city-states, particularly Florence, were centers of immense wealth and power. The wealthy merchant families, like the Medici, were great patrons of the arts and sciences. They sponsored artists, architects, and scholars, providing them with the resources and encouragement to pursue their creative endeavors. This financial support allowed artists such as Leonardo da Vinci and Michelangelo to flourish and produce masterpieces that defined the Renaissance.
Intellectual Environment and Humanism
Italy was home to a thriving intellectual environment, where scholars began to challenge traditional beliefs and embrace humanism. Humanism emphasized the importance of the individual and the potential for human achievement. Italian scholars like Petrarch and Erasmus played a significant role in promoting humanistic ideals and fueling the intellectual curiosity that characterized the Renaissance.
Key Takeaways
- The Renaissance began in Italy due to its strategic location as a hub of trade and commerce.
- Italy’s rich history and access to ancient Roman and Greek texts fueled intellectual curiosity and creativity.
- The patronage of wealthy Italian families like the Medici provided financial support for artists and thinkers.
- The city-states of Italy, such as Florence and Venice, fostered a competitive environment that encouraged artistic innovation.
- The rediscovery of classical art and architecture, coupled with advancements in science and technology, shaped the Renaissance in Italy.
Frequently Asked Questions
The Renaissance was a period of great cultural, artistic, and intellectual development that originated in Italy during the 14th to 17th centuries. It was a time of significant advancements in various fields such as art, literature, architecture, and science. The question of why the Renaissance began in Italy has puzzled historians for centuries. Here are some frequently asked questions about this topic.
1. What were the key factors that contributed to the Renaissance taking place in Italy?
Several key factors contributed to the Renaissance taking place in Italy:
1.1 Geographical location: Italy’s central location in Europe allowed for extensive trade and cultural exchanges with other regions. As a result, Italian cities became centers of economic and intellectual activity.
1.2 Wealth and prosperity: Italy was home to powerful city-states such as Florence, Venice, and Rome, which accumulated substantial wealth through trade and banking. This wealth provided financial support for patronage of the arts and sciences.
1.3 Classical heritage: Italy was the birthplace of the ancient Roman Empire and the center of the Roman Catholic Church. The rediscovery and admiration for classical Greek and Roman culture played a crucial role in inspiring Renaissance thinkers and artists.
2. How did the Renaissance ideals align with Italian society?
The Renaissance ideals, which emphasized humanism, individualism, and the pursuit of knowledge and beauty, resonated strongly with Italian society:
2.1 Humanism: Italian society placed a renewed focus on human potential and achievements, embracing the idea that individuals could excel in various fields through education and application of reason.
2.2 Patronage of the arts: Italian city-states had wealthy influential families who viewed patronage of the arts as a way to enhance their prestige and demonstrate their power and wealth.
Italy’s political and social structure created an environment conducive to the Renaissance:
3.1 City-states: Italy consisted of independent city-states, allowing for competition among them. This competition fostered innovation and creativity as rulers and wealthy families vied for prestige through the support of arts and culture.
3.2 Middle class emergence: The rise of the merchant class in Italian cities created a new social class that had wealth, influence, and a desire for cultural enrichment. This middle class became patrons of the arts and supported artists and thinkers.
4. How did Italian art and architecture contribute to the development of the Renaissance?
Italian art and architecture played a crucial role in the development of the Renaissance:
4.1 Rediscovery of ancient techniques: Artists in Italy rediscovered and studied ancient Greek and Roman art, architecture, and sculpture. They drew inspiration from these classical works and incorporated the principles of balance, proportion, and perspective into their own creations.
4.2 Wealthy patrons: Italian artists were able to pursue their craft thanks to the support of wealthy patrons who commissioned art and provided financial stability. These patrons allowed artists the freedom to experiment and push the boundaries of artistic expression.
5. What impact did the Renaissance in Italy have on the rest of Europe?
The Renaissance in Italy had a profound impact on the rest of Europe:
5.1 Spread of ideas and knowledge: Italian scholars and artists traveled and shared their knowledge and ideas with other European countries. This dissemination of intellectual and artistic achievements helped spark the Renaissance in other parts of Europe.
5.2 Influence on art and culture: The artistic and architectural innovations that originated in Italy during the Renaissance influenced and shaped the artistic trends and cultural development in other European countries.
Why the Renaissance Began in Italy?
In conclusion, The Renaissance began in Italy due to several key factors.
Firstly, Italy was the birthplace of the ancient Roman Empire, which had a deep influence on Italian culture and history. The rediscovery and interest in classical Greek and Roman texts and art during the Renaissance period sparked a renewed interest in exploring and reviving the ancient knowledge. Italian scholars and artists were at the forefront of this revival, becoming catalysts for intellectual and artistic growth.