The ancient Egyptian civilization, one of the most fascinating and influential in history, flourished in a region known as the Nile Valley. Spanning over 3,000 years, this civilization left behind magnificent monuments, remarkable art, and a wealth of knowledge that continues to captivate us today.
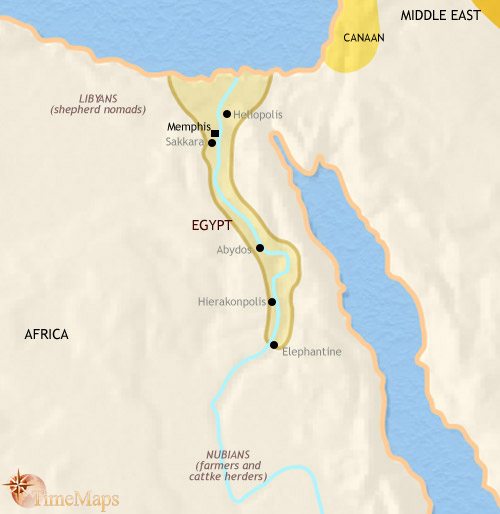
The Nile Valley, located in northeastern Africa, was the heartland of ancient Egypt. It encompassed the fertile floodplain of the Nile River, which provided the ancient Egyptians with abundant resources for agriculture, trade, and transportation. The civilization developed along the banks of the Nile, from the delta in the north to the southernmost reaches of Upper Egypt.
The ancient Egyptian civilization was located in northeastern Africa, along the banks of the Nile River. It spanned over several thousand years, with its origins in the Nile Valley around 3100 BCE. The main regions of Ancient Egypt included Upper Egypt in the south and Lower Egypt in the north, both defined by the Nile River. The civilization thrived due to the fertile soil provided by the annual flooding of the Nile, which supported agriculture and enabled the growth of a complex society.
Contents
- Egypt: The Birthplace of an Ancient Civilization
- The Location of Ancient Egyptian Civilization
- Key Takeaways
- Frequently Asked Questions
- 1. Which continent was the ancient Egyptian civilization located?
- 2. Why was the Nile River important for the ancient Egyptian civilization?
- 3. Did the ancient Egyptian civilization have any natural barriers or boundaries?
- 4. Did the ancient Egyptian civilization expand beyond its original location?
- 5. Are there any remnants of the ancient Egyptian civilization that still exist today?
- Ancient Egypt 101 | National Geographic
Egypt: The Birthplace of an Ancient Civilization
The ancient Egyptian civilization, one of the most fascinating and influential in history, thrived for thousands of years in the northeastern corner of Africa. Renowned for its enigmatic pharaohs, impressive pyramids, and advancements in various fields, ancient Egypt left an indelible mark on human civilization. This article aims to explore the fascinating location of the ancient Egyptian civilization, highlighting its unique geography, prosperous cities, and significant historical sites.
Geographical Location: A Blessing from the Nile
The ancient Egyptian civilization was primarily located in the Nile River valley, extending along the banks of the Nile River in present-day Egypt. The Nile, the longest river in the world, played a crucial role in shaping every aspect of ancient Egyptian life. Its annual flooding provided fertile soil, creating an ideal environment for agriculture.
The civilization flourished in the arid desert surroundings, with the Nile serving as a lifeline. The river allowed the Egyptians to cultivate crops such as wheat, barley, and flax, enabling them to sustain a large population and establish prosperous cities.
Moreover, the Nile River also facilitated transportation and trade, allowing the ancient Egyptians to connect with neighboring regions and establish extensive trade networks both within Africa and beyond.
Key Cities: Vibrant Hubs of Power and Culture
Within the ancient Egyptian civilization, several cities emerged as vibrant hubs of power and culture. These cities played a significant role in shaping the civilization’s political and cultural landscape.
1. Memphis: Located near the Nile delta, Memphis served as the capital of ancient Egypt for over eight centuries. It was a bustling metropolis, home to magnificent temples, elaborate palaces, and administrative centers. Memphis was the center of political power, where pharaohs ruled and oversaw the administration of the kingdom.
2. Thebes: Situated on the east bank of the Nile, Thebes (modern-day Luxor) was a sacred city and the religious capital of ancient Egypt. It housed the grand temples of Karnak and Luxor, dedicated to various gods and goddesses. Thebes was also the burial site of many pharaohs, including the famous Valley of the Kings.
3. Alexandria: Founded by Alexander the Great in 331 BCE, Alexandria was a thriving center of Hellenistic culture and learning. It became Egypt’s capital during the Ptolemaic period and was known for its renowned library, the Library of Alexandria, which housed a vast collection of ancient knowledge.
Historical Sites: Preserving the Rich Heritage
The ancient Egyptian civilization left behind numerous historical sites that provide valuable insights into their rich culture, beliefs, and achievements. These sites serve as a testament to the advanced architectural skills and artistic mastery of the ancient Egyptians.
1. The Great Pyramids of Giza: Located on the outskirts of Cairo, the Great Pyramids of Giza are iconic symbols of ancient Egypt. Built as monumental tombs for pharaohs, the pyramids continue to awe and intrigue visitors from around the world. The largest of the pyramids, the Great Pyramid of Khufu, is considered one of the Seven Wonders of the Ancient World.
2. The Temples of Abu Simbel: Situated in southern Egypt, the Temples of Abu Simbel were carved into solid rock and relocated during the construction of the Aswan High Dam to preserve them from flooding. These temples, dedicated to pharaoh Ramesses II and his queen Nefertari, showcase the grandeur and splendor of ancient Egyptian temple architecture.
3. Karnak Temple Complex: Located near Luxor, the Karnak Temple Complex is a vast complex of temples, chapels, pylons, and obelisks. It was dedicated to the worship of the ancient Egyptian gods and served as a center for religious ceremonies and festivals.
The Legacy: Enriching the World
The ancient Egyptian civilization’s location along the Nile River allowed it to thrive and develop into a powerful and influential society. Its advancements in art, architecture, literature, medicine, and mathematics continue to inspire and astonish researchers and scholars to this day.
The influence of ancient Egypt can be seen in the numerous civilizations that followed, including the Greeks, Romans, and later European cultures. The ancient Egyptians’ deep understanding of astronomy and their development of sophisticated technologies, such as irrigation systems, also contributed to the progress of civilization as a whole.
The location of the ancient Egyptian civilization played a significant role in its growth and success, shaping its unique culture and leaving behind a rich heritage that continues to captivate the world.
The Location of Ancient Egyptian Civilization
The ancient Egyptian civilization was located in Northeastern Africa, specifically along the banks of the Nile River. This region is known as the Nile Valley and covers present-day Egypt and parts of Sudan.
The Nile River was a vital resource for the ancient Egyptians, providing water, fertile soil, and transportation. The civilization developed along the river’s floodplain, where the soil was rich and suitable for agriculture. The Nile also facilitated trade and communication, allowing the Egyptians to establish a prosperous civilization.
The main cities and centers of ancient Egyptian civilization were located near the Nile River. These include Memphis, the capital city of the Old Kingdom, and Thebes, the capital during the Middle and New Kingdoms. Other important cities included Heliopolis, Alexandria, and Luxor.
The ancient Egyptians believed that the Nile River was a divine gift, and their civilization thrived for over three thousand years in this region. The rich history and cultural heritage of ancient Egypt continue to captivate people around the world.
Key Takeaways
- The Ancient Egyptian civilization was located in northeastern Africa.
- It was situated along the fertile banks of the Nile River.
- Egypt, the country where the civilization flourished, is located in present-day North Africa.
- Ancient Egyptians built their cities and settlements around the Nile River.
- The Nile River provided water for irrigation, transportation, and agriculture, which was vital for their civilization’s success.
Frequently Asked Questions
The ancient Egyptian civilization was one of the most remarkable and enduring civilizations in history. Known for its advanced culture, architecture, and achievements, the ancient Egyptians thrived for thousands of years. Here are some frequently asked questions about the location of the ancient Egyptian civilization.
1. Which continent was the ancient Egyptian civilization located?
The ancient Egyptian civilization was primarily located in northeastern Africa, along the banks of the Nile River. The Nile River played a significant role in the growth and development of the civilization as it provided the Egyptians with fertile land for agriculture, transportation, and trade.
The civilization extended from modern-day Egypt through present-day Sudan, Ethiopia, and Eritrea. However, the heart of the ancient Egyptian civilization resided in the Nile Valley and the Nile Delta, where the majority of the population lived and thrived.
2. Why was the Nile River important for the ancient Egyptian civilization?
The Nile River was crucial for the ancient Egyptian civilization due to its numerous benefits. Firstly, the river provided fertile soil that allowed the Egyptians to engage in agriculture and grow crops. The annual flooding of the Nile deposited rich sediment that rejuvenated the land and made it suitable for farming.
Secondly, the Nile River served as a source of transportation and trade. The Egyptians used boats and ships to navigate the river, enabling them to transport goods, such as grains, pottery, and precious materials, to different parts of the civilization and beyond.
3. Did the ancient Egyptian civilization have any natural barriers or boundaries?
The ancient Egyptian civilization had natural barriers and boundaries that protected it from potential invasions and external threats. To the west, the desert acted as a natural barrier, making it difficult for invaders to penetrate into the heart of the civilization.
The Nile River itself also served as a protective boundary. Its vastness made it challenging for adversaries to cross, especially during certain seasons when the river swelled or flooded. Additionally, the Nile Delta, with its many distributaries, created marshy and swampy areas that deterred invaders.
4. Did the ancient Egyptian civilization expand beyond its original location?
Yes, the ancient Egyptian civilization expanded beyond its original location along the Nile River. As the civilization grew and flourished, the Egyptians extended their influence and control over neighboring regions. They established colonies and trade networks throughout the eastern Mediterranean, including modern-day Lebanon, Syria, and Palestine.
Some pharaohs also led military campaigns into Nubia (modern-day Sudan) to secure valuable resources and maintain control over trade routes. The influence of the ancient Egyptian civilization reached its peak during the New Kingdom period, when the empire expanded its territories and exerted its power on a larger scale.
5. Are there any remnants of the ancient Egyptian civilization that still exist today?
Yes, there are several remnants of the ancient Egyptian civilization that still exist today. The most notable are the great pyramids of Giza, including the iconic Pyramids of Khufu, Khafre, and Menkaure. These monumental structures, built as tombs for the pharaohs, demonstrate the architectural and engineering prowess of the ancient Egyptians.
Furthermore, ancient temples such as the Karnak Temple Complex in Luxor and the Abu Simbel temples in Aswan bear witness to the grandeur and religious significance of the civilization. The hieroglyphic writings, preserved in temples and tombs, are invaluable sources of information about the ancient Egyptian culture, religion, and history.
Ancient Egypt 101 | National Geographic
In summary, the ancient Egyptian civilization was located in the northeastern part of Africa along the banks of the Nile River. This civilization thrived for thousands of years, from around 3100 BC to 30 BC. It was known as one of the most advanced and sophisticated civilizations of its time.
The Nile River played a crucial role in the development of the ancient Egyptian civilization. It provided fertile land for agriculture, facilitated trade and transportation, and served as a source of life and spiritual significance. The civilization was centered around major cities such as Memphis, Thebes, and Alexandria, where monumental structures, temples, and tombs were built to honor their gods and pharaohs.