Ancient Greece, a civilization renowned for its cultural and intellectual achievements, holds a special place in the annals of human history. But where exactly was this remarkable civilization located?
Situated in southeastern Europe on the southern tip of the Balkan Peninsula, Greece is surrounded by the Ionian Sea to the west and the Aegean Sea to the east. The ancient civilization of Greece was established in the mainland region of the country, with city-states such as Athens, Sparta, and Corinth becoming the centers of political, cultural, and intellectual activity during their respective periods of dominance.
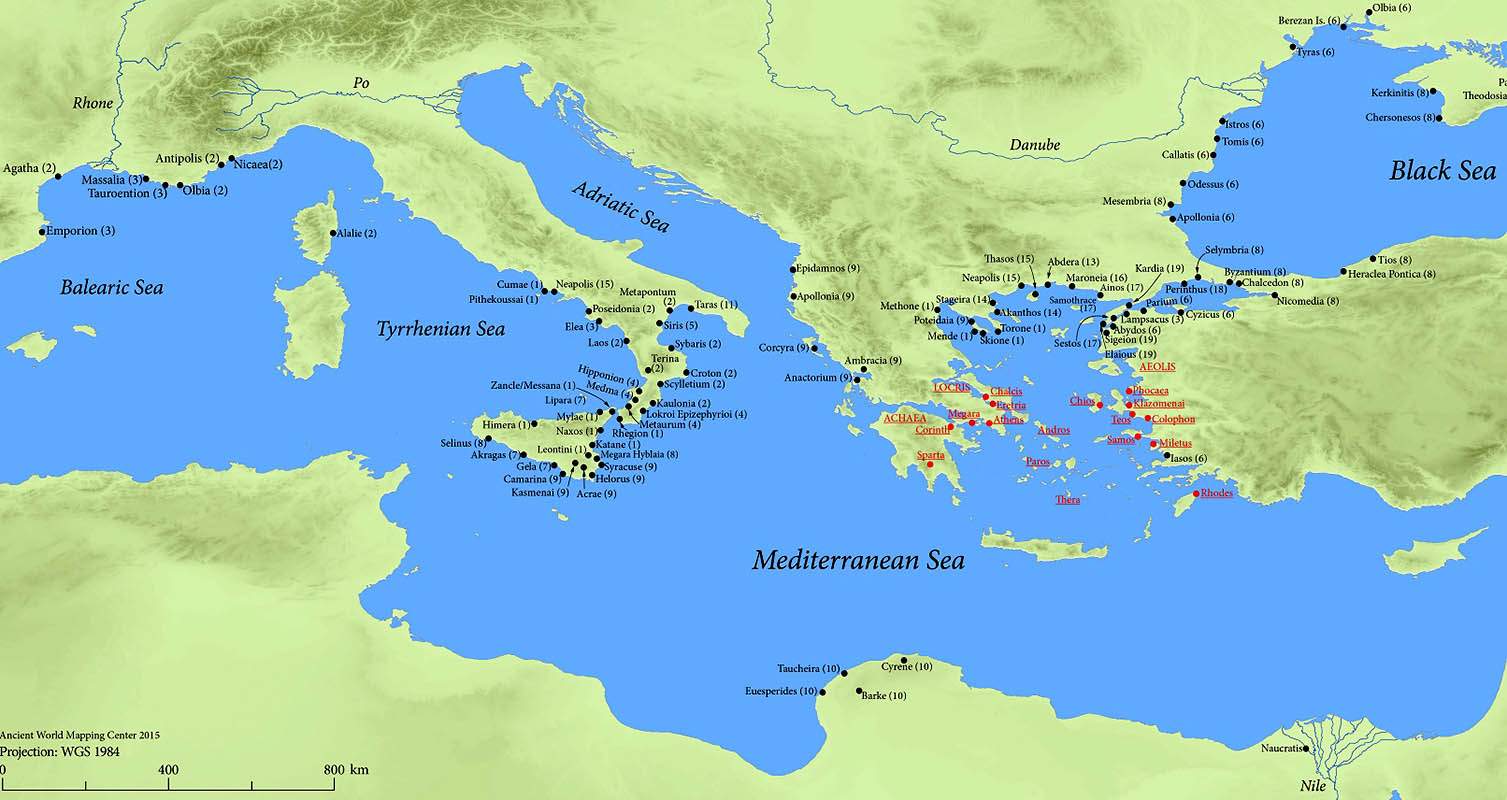
The ancient civilization of Greece was located in southeastern Europe, on the southern tip of the Balkan Peninsula. Greece is bordered to the east by the Aegean Sea, to the south by the Mediterranean Sea, and to the west by the Ionian Sea. The country’s geographic location made it a crossroads between Europe, Asia, and Africa, which greatly influenced its history, culture, and trade. Greece is known for its rich archaeological sites, such as Athens, Delphi, and Mycenae, which offer a glimpse into the ancient glory of this extraordinary civilization.
Contents
- Geographical Location of Ancient Greece
- Archaeological Sites of Ancient Greece
- In Conclusion
- Location of the Ancient Civilization of Greece
- Key Takeaways:
- Frequently Asked Questions
- 1. What is the geographical location of ancient Greece?
- 2. Which modern-day countries are encompassed by ancient Greece?
- 3. What were some famous cities in ancient Greece?
- 4. How did the geography of ancient Greece influence its civilization?
- 5. Are there any remnants of the ancient civilization of Greece still visible today?
- Ancient Greece 101 | National Geographic
Geographical Location of Ancient Greece
Ancient Greece, one of the most influential civilizations in history, was located in southeastern Europe on the southern tip of the Balkan Peninsula. It encompassed a variety of city-states, including Athens, Sparta, Corinth, and Thebes. The geography of Greece played a significant role in shaping the development and culture of this ancient civilization. The unique location of Greece had a profound impact on its history, economy, politics, and cultural practices.
The Balkan Peninsula
The Balkan Peninsula, situated in southeastern Europe, was the home of ancient Greece. It is bordered by the Adriatic Sea to the west, the Ionian Sea to the south, and the Aegean Sea to the east. Strategically positioned between the European and Asian continents, the Balkans served as a crossroads for trade and cultural exchange. Ancient Greece benefited from this location as it facilitated trade with other civilizations and allowed for the dissemination of ideas and innovation.
The mountainous terrain of the Balkan Peninsula played a crucial role in the isolation of individual city-states within ancient Greece. The rugged landscape created natural boundaries between the different regions, leading to the development of independent city-states. These city-states, such as Athens and Sparta, had distinct political and social systems and often engaged in wars or alliances with one another.
Additionally, the Balkan Peninsula provided protection from invasions, allowing Greek civilization to flourish. The mountain ranges acted as barriers, making it difficult for foreign armies to penetrate the region. These natural defenses contributed to the security and stability of ancient Greece, enabling the city-states to focus on internal development and cultural achievements.
The Mediterranean Sea
The ancient civilization of Greece was in close proximity to the Mediterranean Sea, which greatly influenced its development and expansion. The Mediterranean Sea provided access to important trade routes and connected Greece to other ancient civilizations, such as Egypt, Phoenicia, and Rome. This proximity to the sea facilitated trade and cultural exchanges, allowing the Greeks to acquire valuable resources and knowledge.
Furthermore, the Mediterranean Sea was a central hub of maritime activity, with Greek city-states becoming proficient in navigation and seafaring. The Greeks established colonies along the coastlines of the Mediterranean, expanding their influence and spreading their culture to distant lands. The sea also played a crucial role in the defense of ancient Greece, as the Greek fleet was known for its naval prowess.
In addition to its economic and military significance, the Mediterranean Sea also shaped the cultural identity of ancient Greece. The sea’s proximity inspired the Greeks’ fascination with maritime exploration and adventure, which is evident in their mythology and literature. The tales of Odysseus’ epic journey in Homer’s “Odyssey” and the adventures of Jason and the Argonauts are examples of the influence of the Mediterranean Sea on Greek literature and mythology.
Islands of the Aegean Sea
The Aegean Sea, located to the east of mainland Greece, is dotted with numerous islands that played a significant role in the ancient Greek civilization. These islands, including Crete, Rhodes, and Delos, were not only strategically important for trade and defense but also served as centers of culture and learning.
Crete, the largest of the Greek islands, was home to the Minoan civilization, one of the earliest advanced civilizations in Europe. The Minoans developed a sophisticated culture and traded extensively with other Mediterranean civilizations. The island of Rhodes was known for its maritime power and contributed to the spread of Greek culture throughout the Mediterranean. Delos, a sacred island in Greek mythology, was a vibrant religious and commercial center.
The islands of the Aegean Sea provided the Greeks with a secure base for their naval operations and facilitated their expansion and trade. The sea routes between the islands and the mainland were vital for commerce, allowing the Greeks to access resources and establish colonies in other parts of the Mediterranean.
Political Divisions within Ancient Greece
Ancient Greece was not a unified nation but a collection of independent city-states, each with its own government and identity. These city-states were often small in size and focused on local affairs, but they played a vital role in shaping Greek civilization.
Some of the most prominent city-states in ancient Greece included Athens, Sparta, Corinth, Thebes, and Argos. Athens, known for its democracy and intellectual achievements, was located in the region of Attica. Sparta, famous for its military prowess and disciplined society, was situated in the region of Laconia. Corinth, a major trading city, lay in the region of Corinthia. Thebes, known for its military strength and cultural contributions, was located in Boeotia. Argos, an ancient city with a rich mythological and historical heritage, was situated in the Peloponnese.
These city-states had their own governments, laws, and political systems. Athens, for example, developed the world’s first known democracy, where citizens had the right to participate in decision-making. Sparta, on the other hand, had a unique system of government known as a dual monarchy, with two kings reigning simultaneously.
The independent nature of these city-states often led to conflicts, alliances, and rivalries. Throughout history, Athens and Sparta were two of the most powerful and influential city-states, and their competition ultimately led to the Peloponnesian War, which had a significant impact on ancient Greek civilization.
The Influence of Mount Olympus
Mount Olympus, the highest mountain in Greece and home to the gods and goddesses of Greek mythology, held immense cultural and religious significance for the ancient Greeks. Situated in Thessaly, Mount Olympus became a symbol of Greek unity and identity.
The mythical realm of Mount Olympus, ruled by the Olympian gods led by Zeus, played a prominent role in Greek religious and cultural practices. The Greeks believed that the gods influenced their everyday lives and intervened in human affairs. Mount Olympus became the focal point of religious gatherings and festivals, where the Greeks paid homage to the gods through sacrifices and rituals.
Mount Olympus also represented the connection between the divine and mortal realms. The myths and stories associated with the gods and goddesses of Olympus provided the Greeks with a framework for understanding the world and their place in it. These myths were passed down through generations and continue to be influential in Western literature, art, and philosophy.
Archaeological Sites of Ancient Greece
The rich archaeological heritage of ancient Greece provides a glimpse into the civilization’s history, art, and culture. Numerous archaeological sites across Greece offer valuable insights into the ancient world.
Acropolis of Athens
The Acropolis of Athens, located on a rocky hilltop overlooking the city, is one of the most famous archaeological sites in Greece. It is home to the iconic Parthenon, a temple dedicated to the goddess Athena, as well as other ancient structures such as the Propylaea, the Erechtheion, and the Temple of Athena Nike.
The Acropolis is a testament to the architectural and artistic achievements of ancient Greece. The intricate carvings, detailed sculptures, and grandeur of the structures showcase the skill and mastery of Greek artisans. Visiting the Acropolis allows one to immerse themselves in the rich history and cultural heritage of Athens.
Alongside the Acropolis, the Agora of Athens offers a glimpse into the public and social life of ancient Greece. It was the heart of the city-state’s political, commercial, and cultural activities.
Delphi
Delphi, located on the slopes of Mount Parnassus, was considered the center of the world in ancient Greek mythology. It was the site of the Oracle of Apollo, where priests and priestesses delivered prophecies and guided the decisions of individuals and city-states. Delphi was also home to numerous temples, treasuries, and monuments.
Today, Delphi is a well-preserved archaeological site and a UNESCO World Heritage Site. Visitors can explore the ruins of the Temple of Apollo, the Theater, and the Tholos. The beauty of the site, combined with its historical and mythical significance, makes Delphi a must-visit destination for anyone interested in ancient Greece.
Mycenae
Mycenae, located in the northeastern Peloponnese, was a major center of Mycenaean civilization, predating classical Greece. It was a fortified city-state characterized by monumental architecture, such as the iconic Lion Gate, the Treasury of Atreus, and the Palace Complex.
The archaeological remains at Mycenae provide insights into the Mycenaean civilization, including its political structure, military organization, and cultural practices. Exploring the site allows visitors to step back in time and experience the grandeur and might of this ancient city-state.
Other notable archaeological sites in Greece include Olympia, the birthplace of the Olympic Games; Knossos, the ancient capital of Crete; and Epidaurus, renowned for its well-preserved theater.
In Conclusion
Ancient Greece, nestled in the southeastern part of Europe on the Balkan Peninsula, was a civilization shaped by its unique geography. The Balkan Peninsula provided a strategic location for trade and cultural exchange, while the Mediterranean Sea and the islands of the Aegean Sea played a crucial role in the economic, military, and cultural development of ancient Greece.
The political divisions within ancient Greece, with independent city-states such as Athens and Sparta, reflected the diverse and fragmented nature of the civilization. The influence of Mount Olympus and Greek mythology permeated every aspect of Greek society and culture. The rich archaeological heritage of ancient Greece, including sites like the Acropolis of Athens and Delphi, provides a window into the achievements and legacy of this remarkable civilization.
Location of the Ancient Civilization of Greece
The ancient civilization of Greece was located in the southeastern part of Europe, primarily on the Balkan Peninsula. Greece is surrounded by the Aegean Sea to the east, the Ionian Sea to the west, and the Mediterranean Sea to the south. It is bordered by Albania, North Macedonia, Bulgaria, and Turkey. The country consists of mainland Greece, which is a mountainous region, as well as numerous islands, including Crete, the Cyclades, and the Dodecanese.
Greece is known for its rich history and contributions to Western civilization, particularly in the areas of philosophy, literature, art, and democracy. The ancient Greeks established city-states, such as Athens and Sparta, which became centers of culture and power. The city-state of Athens, in particular, played a significant role in the development of democracy and produced renowned philosophers like Socrates, Plato, and Aristotle.
Today, Greece is a popular tourist destination, attracting visitors from around the world to explore its ancient ruins, picturesque islands, and vibrant culture. The legacy of the ancient Greek civilization continues to influence modern society in various fields, including language, literature, architecture, and politics.
Key Takeaways:
- The ancient civilization of Greece was located in southeastern Europe.
- Greece is bordered by the Ionian Sea to the west and the Aegean Sea to the east.
- The country is surrounded by Albania, North Macedonia, Bulgaria, and Turkey.
- Athens, the capital city of Greece, is located in the southeastern part of the country.
- The ancient Greeks established numerous city-states, including Athens, Sparta, and Corinth.
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are some common questions about the location of the ancient civilization of Greece.
1. What is the geographical location of ancient Greece?
Ancient Greece was located in southeastern Europe, on the southern tip of the Balkan Peninsula. It was surrounded by the Aegean Sea to the east, the Ionian Sea to the west, and the Mediterranean Sea to the south.
The mainland of ancient Greece was made up of mountainous terrain, with the Pindus Mountains running down the center. This rugged topography, along with numerous islands dotting the coast, shaped the history, culture, and political dynamics of the ancient Greeks.
2. Which modern-day countries are encompassed by ancient Greece?
Modern-day Greece is the most direct descendant of the ancient Greek civilization. However, the ancient Greek influence also extended to parts of other countries in the region.
Some of the modern-day countries that were encompassed by ancient Greece include Greece itself, as well as parts of Turkey, Bulgaria, Albania, and North Macedonia.
3. What were some famous cities in ancient Greece?
Ancient Greece was home to many famous cities that played significant roles in the civilization’s development.
Some of the notable ancient Greek cities include Athens, the capital and cultural center of ancient Greece; Sparta, known for its militaristic society; Corinth, an important trade hub; and Thebes, a major power in mainland Greece.
4. How did the geography of ancient Greece influence its civilization?
The geography of ancient Greece had a profound impact on its civilization. The mountainous terrain and numerous islands led to the development of individual city-states, as communication and travel were often difficult.
This geography also fostered a seafaring and trading culture, as ancient Greeks relied on the sea for commerce and transportation. It also influenced the development of agriculture, as the mountainous landscape necessitated terracing and limited the amount of arable land.
5. Are there any remnants of the ancient civilization of Greece still visible today?
Yes, there are still remnants of the ancient civilization of Greece that can be seen today.
Some of the most famous archaeological sites in Greece include the Acropolis in Athens, home to the iconic Parthenon; Delphi, the site of the ancient Oracle and Temple of Apollo; and Olympia, the birthplace of the Olympic Games.
Ancient Greece 101 | National Geographic
To sum up, the ancient civilization of Greece was located in the southeastern part of Europe, known as the Balkan Peninsula. Greece itself is a country and the birthplace of western civilization, with a rich history and a significant influence on arts, sciences, politics, and philosophy.
The ancient Greeks developed various city-states, including Athens, Sparta, and Corinth. These city-states were known for their unique political systems, cultural achievements, and architectural wonders such as the Parthenon. The ancient civilization of Greece has left a lasting legacy on the world, shaping our understanding of democracy, literature, and the arts.