During the Industrial Revolution, a wide range of machines were invented and made, revolutionizing the way goods were produced. These machines played a pivotal role in the transformation of the global economy and the shift towards modern industrialization. From steam engines to power looms, the Industrial Revolution was a period of remarkable innovation and technological advancement that forever changed the course of human history.
One of the most significant machines created during the Industrial Revolution was the steam engine. Invented by James Watt in the late 18th century, the steam engine provided a new and efficient source of power, enabling the development of factories and locomotives. This invention marked a turning point in industrial progress, as it allowed for the rapid expansion of industries such as mining, transportation, and manufacturing. With the steam engine, the world witnessed a shift from manual labor to the use of machines, laying the groundwork for modern industrialization.
During the Industrial Revolution, numerous machines were invented and revolutionized various industries. Some notable machines include the spinning jenny, water frame, and power loom, which transformed the textile industry. The steam engine, invented by James Watt, powered machines in factories and played a crucial role in transportation. Other significant inventions include the cotton gin, steamboat, and the telegraph. These machines paved the way for mass production, mechanization, and the modern industrial era.
Contents
- The Impact of Machines in the Industrial Revolution
- The Impact of Machines on the Industrial Revolution
- The Machines Invented During the Industrial Revolution
- Key Takeaways
- Frequently Asked Questions
- 1. What role did the spinning jenny play in the Industrial Revolution?
- 2. What impact did the steam engine have on the Industrial Revolution?
- 3. How did the power loom revolutionize the textile industry?
- 4. How did the cotton gin impact the production of cotton?
- 5. What impact did the steam-powered printing press have on the spread of information?
- I Built the The Machine that Made the Industrial Revolution
The Impact of Machines in the Industrial Revolution
The Industrial Revolution was a period of significant technological advancements that transformed various industries. This era, which began in the 18th century, saw the development and implementation of numerous machines that revolutionized manufacturing processes. These machines played a pivotal role in increasing productivity, improving efficiency, and shaping the modern world as we know it today. From textile manufacturing to agriculture, mining, and transportation, machines were at the heart of the Industrial Revolution. Let’s explore the machines that were made during this transformative period.
Textile Machinery
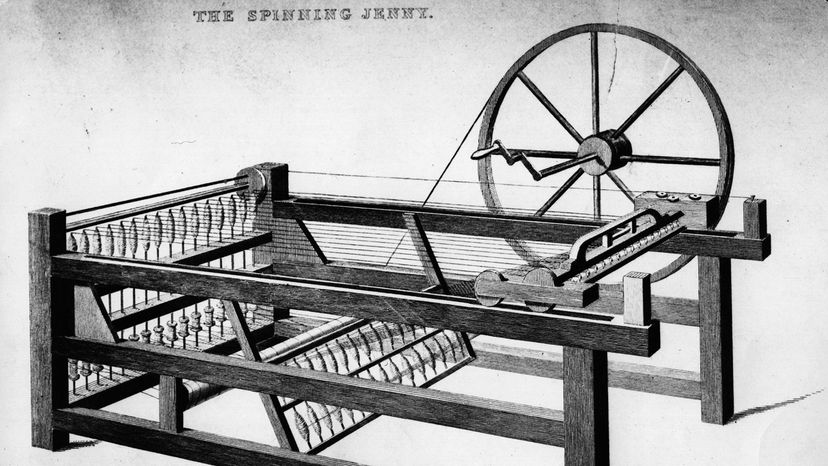
The textiles industry played a crucial role in the Industrial Revolution, and the advancements in textile machinery had a significant impact on manufacturing. The spinning jenny, invented by James Hargreaves in 1764, was one of the key inventions that revolutionized the production of yarn. The spinning jenny allowed a single worker to operate multiple spindles, significantly increasing the quantity of yarn produced. This machine marked the beginning of the mechanization of the textile industry.
Another important textile machine was the water frame, developed by Richard Arkwright in the late 1760s. The water frame used water power to drive spinning machines, providing even more efficient yarn production. Its success led to the establishment of large-scale textile factories and laid the foundation for the factory system.
One of the most iconic machines of the Industrial Revolution was the power loom, invented by Edmund Cartwright in 1785. The power loom mechanized the weaving process, allowing for the increased production of cloth. This innovation led to significant advancements in the textile industry, making cloth more affordable and accessible to a broader population.
Impact on Textile Industry and Society
The introduction of textile machinery transformed the textile industry. The ability to produce yarn and fabric at a much faster rate resulted in a significant increase in textile production. This increase in production led to the growth of textile factories, where large quantities of cloth could be manufactured more efficiently than ever before.
The textile industry became one of the driving forces of the Industrial Revolution, employing a significant portion of the population and contributing to economic growth. However, the mechanization of the industry also led to concerns about working conditions and the displacement of skilled workers. It sparked the Luddite movement, where workers protested against the introduction of machinery and the negative impact it had on their livelihoods.
Despite the challenges, the advancements in textile machinery paved the way for the modern textile industry. These machines laid the foundation for the mass production of clothing and textiles, and their impact can still be felt today.
Agricultural Machinery
The development of agricultural machinery was another significant aspect of the Industrial Revolution. These machines transformed farming practices, increasing efficiency and productivity in the agricultural sector.
One of the notable inventions was the seed drill, created by Jethro Tull in 1701. The seed drill mechanized the process of sowing seeds, allowing for more precise planting and improved crop yields. Previously, seeds were sown by hand, resulting in uneven distribution and lower productivity.
The threshing machine was another important invention. Patented by Andrew Meikle in 1784, the threshing machine automated the process of separating grain from its stalks, making it faster and more efficient than traditional manual methods. This machine revolutionized agriculture by significantly reducing labor requirements and increasing the speed of grain production.
The mechanical reaper, invented by Cyrus McCormick in the 1830s, was another groundbreaking machine that transformed agriculture. The reaper automated the process of cutting and gathering crops, replacing the labor-intensive process of manual harvesting. This innovation revolutionized farming, increasing productivity and allowing for larger-scale crop production.
Impact on Agriculture and Food Production
The introduction of agricultural machinery had a profound impact on food production. These machines enabled farmers to increase the efficiency of their operations and produce larger quantities of crops. The seed drill, threshing machine, and mechanical reaper all contributed to significant advancements in farming practices and helped meet the growing demand for food.
The mechanization of agriculture resulted in increased crop yields, improved food security, and a reduction in labor requirements. It also led to changes in the rural population, as fewer people were needed for manual labor on farms. Many individuals migrated to urban areas in search of employment in the growing industrial sector.
Mining Machinery
The mining industry also experienced significant advancements during the Industrial Revolution. Machines were developed to extract minerals and resources more efficiently, revolutionizing the mining process and enabling the exploitation of new resources.
One of the key inventions was the steam engine, crucial for pumping water out of mines and powering machinery underground. The steam engine, developed by Thomas Newcomen in 1712 and improved by James Watt in the late 18th century, provided a reliable and efficient source of power for mines.
The steam engine also facilitated the transportation of goods and materials in the mining industry. It powered locomotives and steamships, enabling the efficient movement of minerals across long distances. This innovation revolutionized logistics and contributed to the growth of the global mining industry.
Impact on Mining Industry and Industrial Growth
The advancements in mining machinery had a transformative impact on the industry and contributed to the overall industrial growth during the period. The ability to extract minerals at a faster rate and in larger quantities fueled the expansion of various industries, including construction, manufacturing, and transportation.
The steam engine played a crucial role in powering machinery in mines and factories, driving industrialization forward. It provided a reliable and efficient source of power, replacing traditional manual labor and significantly increasing productivity. The mining industry itself grew rapidly, with new mines being opened to access previously untapped resources.
The impact of mining machinery on industrial growth cannot be overstated. It fueled the development and expansion of other industries, created employment opportunities, and contributed to economic prosperity.
Transportation Machinery
The Industrial Revolution also saw significant advancements in transportation machinery. The development of steam-powered engines revolutionized transportation, making it faster, more efficient, and influencing the way goods and people were moved.
One of the most iconic machines of the Industrial Revolution was the steam locomotive. Invented by George Stephenson in the early 19th century, steam locomotives enabled the efficient transportation of goods and people over long distances. Railways were constructed, connecting various cities and regions, facilitating trade and contributing to economic growth.
Steamships were another important transportation innovation. These ships, powered by steam engines, made ocean voyages faster and more reliable. They facilitated international trade, connecting different parts of the world and enabling the transportation of goods and people on a global scale.
Impact on Transportation and Global Connectivity
The advancements in transportation machinery had a profound impact on society, trade, and global connectivity. Steam-powered locomotives and steamships revolutionized the movement of goods and people, making it faster, more reliable, and cost-effective.
The construction of railways and the use of steam locomotives transformed the transportation of goods within countries. It connected various regions, facilitated trade, and contributed to economic growth. The development of steamships made long-distance travel and international trade more accessible and efficient, further connecting nations and continents.
The advancements in transportation machinery also played a crucial role in the urbanization and growth of cities. It enabled people to travel more easily and faster between cities and regions, contributing to the development of urban centers and the concentration of economic activities in specific areas.
The Impact of Machines on the Industrial Revolution
The machines developed during the Industrial Revolution had a profound and lasting impact on society, ushering in a new era of productivity and technological advancements. These machines revolutionized manufacturing processes, transforming various industries and shaping the modern world.
The advancements in textile machinery mechanized the production of yarn and cloth, increasing productivity and making textiles more accessible to the general population. The development of agricultural machinery revolutionized farming practices, increasing crop yields, and improving food production. Mining machinery enabled the extraction of minerals at a faster rate, supporting industrial growth and economic prosperity. Transportation machinery, particularly steam-powered engines, facilitated the efficient movement of goods and people, connecting regions and contributing to global trade.
The impact of these machines was not only economic but also social. The Industrial Revolution brought about a shift from manual labor to machine labor, leading to significant changes in working conditions and the division of labor. While it brought about unprecedented opportunities for innovation and economic growth, it also raised concerns about the well-being of workers and social inequality.
Overall, the machines made in the Industrial Revolution played a pivotal role in transforming society, increasing productivity, and shaping the world we live in today.

The Machines Invented During the Industrial Revolution
The Industrial Revolution, which took place between the 18th and 19th centuries, brought about significant advancements in machinery and technology. These inventions revolutionized various industries and transformed the way work was done. Several machines were made during this period, each serving a unique purpose and contributing to the growth of industries. Some notable machines invented during the Industrial Revolution include:
- The Spinning Jenny: This machine allowed the simultaneous spinning of multiple threads, increasing textile production.
- The Water Frame: Invented by Richard Arkwright, it used water power to drive textile machinery, replacing the need for manual labor.
- The Steam Engine: Revolutionized transportation, power generation, and manufacturing by converting fuel into mechanical energy.
- The Cotton Gin: Patented by Eli Whitney, this machine automated the separation of cotton seeds from the fibers, boosting cotton production.
- The Power Loom: Increased textile production by mechanizing the weaving process.
- The Spinning Mule: Combined features of the Spinning Jenny and the Water Frame, enabling high-quality textile production.
These machines marked a significant shift from manual labor to machine-powered production, leading to increased efficiency and mass production. They played a crucial role in the Industrial Revolution’s economic and social impact and set the foundation for modern industrialization.
Key Takeaways
- The Industrial Revolution saw the development of numerous machines that transformed various industries.
- The steam engine was a key invention of the Industrial Revolution, powering locomotives and factory machinery.
- The spinning jenny revolutionized the textile industry by allowing for faster and more efficient production of yarn.
- The power loom automated the weaving process and increased productivity in the textile industry.
- The cotton gin revolutionized the processing of cotton by automating the separation of seeds from the fibers.
Frequently Asked Questions
The Industrial Revolution brought about monumental advancements in technology and machinery. Here are some commonly asked questions about the machines that were made during this transformative period:
1. What role did the spinning jenny play in the Industrial Revolution?
The spinning jenny revolutionized the textile industry during the Industrial Revolution. Invented by James Hargreaves in the 1760s, this machine enabled multiple spindles of thread to be spun at once, greatly increasing production efficiency. With the spinning jenny, one person could operate multiple spindles simultaneously, replacing the need for many manual spinners.
The spinning jenny played a crucial role in the mechanization of the textile industry, leading to the mass production of yarn and thread. This machine paved the way for further developments in textile machinery, transforming the industry and driving economic growth.
2. What impact did the steam engine have on the Industrial Revolution?
The invention of the steam engine by James Watt in the late 18th century was a key catalyst for the Industrial Revolution. This revolutionary machine harnessed the power of steam to produce mechanical energy, enabling the development of factories, railways, and various other industries.
The steam engine transformed transportation, making it possible to transport goods and people over long distances in a shorter time. It also powered machinery in factories, replacing traditional manual labor and significantly increasing productivity. The steam engine played a pivotal role in driving industrialization and shaping modern society.
3. How did the power loom revolutionize the textile industry?
The power loom, invented by Edmund Cartwright in the late 18th century, revolutionized the textile industry by automating the process of weaving. Prior to its invention, weaving was done manually, which limited production capacity and required skilled labor.
The power loom mechanized the weaving process, allowing for faster and more efficient production of textiles. It reduced the reliance on skilled handloom weavers and increased the output of woven fabrics. The power loom played a significant role in the growth of the textile industry and contributed to the overall industrialization of society.
4. How did the cotton gin impact the production of cotton?
The cotton gin, invented by Eli Whitney in the late 18th century, revolutionized the production of cotton. Prior to its invention, separating cotton fibers from the seeds was a labor-intensive and time-consuming process.
The cotton gin mechanized this process by using a series of rotating brushes to separate the cotton fibers from the seeds. This significantly increased the efficiency of separating cotton, making it possible to process larger quantities in a shorter time. The cotton gin revolutionized the cotton industry, making it a highly profitable and widely cultivated crop in the southern United States.
5. What impact did the steam-powered printing press have on the spread of information?
The steam-powered printing press, invented by Friedrich Koenig in the early 19th century, revolutionized the printing industry and had a profound impact on the spread of information during the Industrial Revolution.
Before the steam-powered press, printing was a labor-intensive process that limited the production of books and newspapers. The steam-powered press automated the printing process, increasing the speed and efficiency of printing. This allowed for the mass production of books, newspapers, and other printed materials.
The steam-powered printing press played a crucial role in the dissemination of knowledge and ideas, contributing to the spread of literacy and the democratization of information. It played a part in shaping the modern media landscape and transforming the way information is shared.
I Built the The Machine that Made the Industrial Revolution
In conclusion, the Industrial Revolution saw the invention and development of numerous machines that revolutionized the way we live and work. These machines played a vital role in shaping the modern world and continue to impact our lives today.
During the Industrial Revolution, machines such as the steam engine, spinning jenny, power loom, and steam locomotive were created. These machines transformed industries like textile manufacturing and transportation, enabling mass production and faster transportation of goods.