Did you know that Russia was once closely connected to the Byzantine Empire? While it may not be widely known, the influence of the Byzantine Empire played a significant role in shaping the history and culture of Russia.
Russia’s connections to the Byzantine Empire date back to the 9th century when the Varangians, a group of Scandinavian warriors, ruled over the region. The Byzantine Empire’s influence can be seen in various aspects of Russian culture, including their art, architecture, and religious practices. This connection between Byzantium and Russia further solidified through trade and political alliances over the centuries, leaving lasting impacts on the development of the Russian state.
Russia was influenced by the Byzantine Empire, but it was not officially part of it. While Russia adopted many aspects of Byzantine culture and Orthodox Christianity, it maintained its own distinct political and cultural identity. The Byzantine Empire did have some influence on Russia’s architecture, art, and political structure, but Russia developed its own unique civilization separate from the Byzantines.
Contents
- The Influence of the Byzantine Empire on Russia
- Trading and Economic Ties Between Russia and Byzantium
- Russia’s Connection to the Byzantine Empire
- Key Takeaways
- Frequently Asked Questions
- 1. How was Russia influenced by the Byzantine Empire?
- 2. Was Russia ever a part of the Byzantine Empire?
- 3. Did Russia have any territorial connections to the Byzantine Empire?
- 4. Were there any conflicts between Russia and the Byzantine Empire?
- 5. How did the fall of the Byzantine Empire impact Russia?
- Russia’s Plan to Restore Byzantium in The 18th Century
The Influence of the Byzantine Empire on Russia
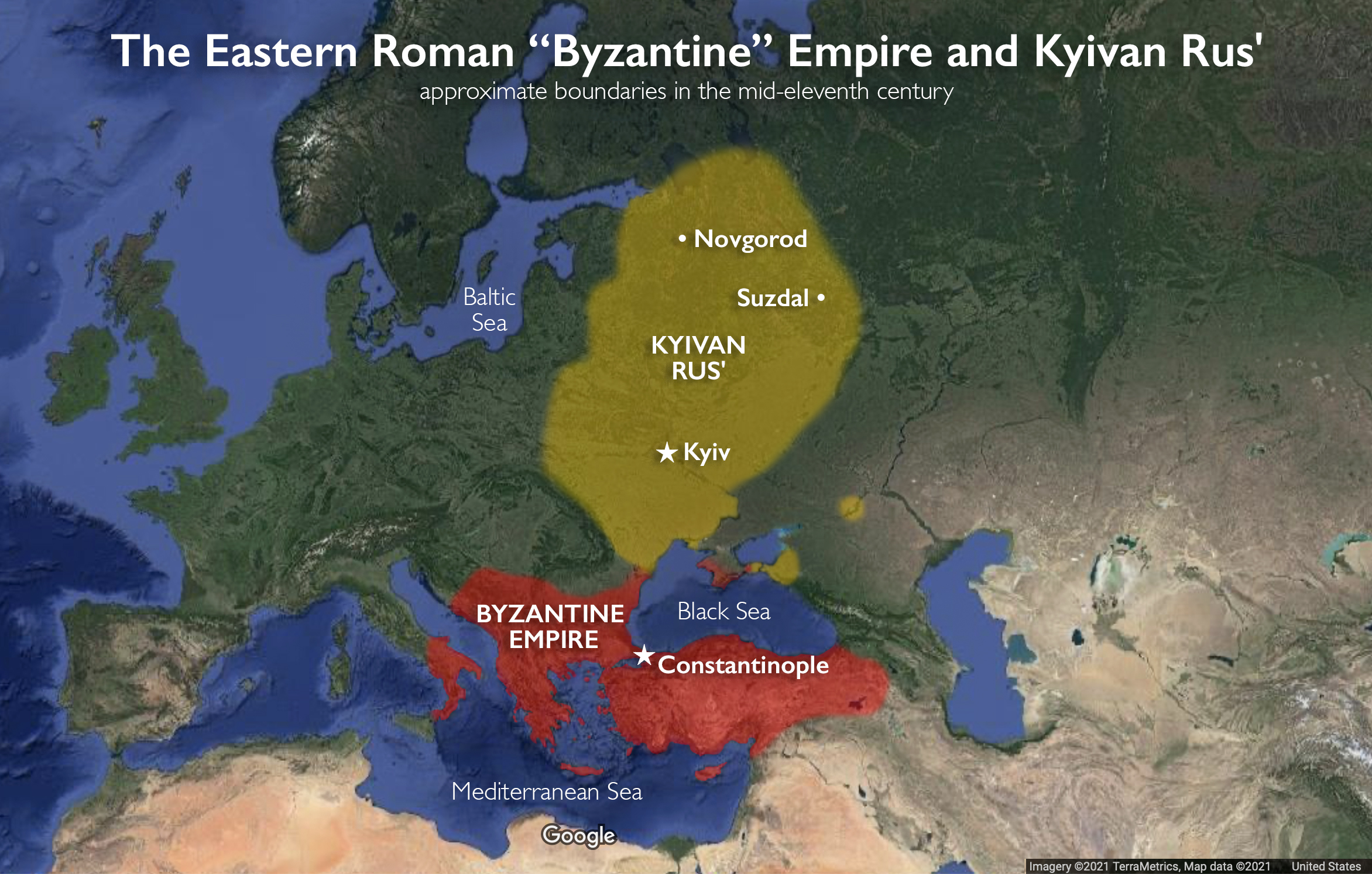
Russia’s relationship with the Byzantine Empire is a topic of historical interest and debate. While Russia was not officially part of the Byzantine Empire, it had significant cultural, political, and religious ties to Byzantium. These connections had a profound impact on the development of Russian civilization and shaped its unique identity.
1. Cultural Exchange and Influence
The Byzantine Empire had a profound influence on Russian culture. Byzantine art, architecture, and literature served as a source of inspiration for Russian artists and intellectuals. The architectural style of Russian churches, characterized by onion domes, was heavily influenced by Byzantine architecture. Icon painting, an important part of Russian religious art, was also influenced by Byzantine iconography.
Besides art and architecture, Byzantine culture influenced Russian literature. The Cyrillic alphabet, which is still used in Russia today, was developed by the Byzantine scholars Cyril and Methodius. This allowed for the translation of important religious texts and facilitated the spread of Christianity among the Slavic peoples.
Furthermore, the Byzantine Empire played a crucial role in the dissemination of knowledge and education in Russia. Byzantine missionaries and scholars established schools and monasteries in Russia, bringing with them a rich tradition of learning and intellectual thought. These institutions became centers of religious and secular education, fostering the growth of literacy and intellectual pursuits in Russia.
2. Political Relations
While Russia was not formally part of the Byzantine Empire, it maintained diplomatic and political relations with Byzantium. The Varangians, Scandinavian warriors who settled in Russia, established trading connections with the Byzantine Empire. These trade routes brought wealth and cultural exchange, as well as political alliances.
Russian princes often sought alliances with Byzantine emperors, both for political support and to legitimize their rule. A prime example is the baptism of Vladimir the Great, the Grand Prince of Kiev, in 988. Vladimir converted to Christianity and chose Byzantine Christianity as the official religion of the Kievan Rus, a move that solidified the political ties between Russia and Byzantium.
Furthermore, the Byzantine Empire served as a political model for Russia. The idea of the “Third Rome,” which emerged in the 15th century, proclaimed Moscow as the successor to Rome and Constantinople, the capitals of the Roman Empire and Byzantium, respectively. This ideology reinforced the political and cultural ties between Russia and the Byzantine Empire.
3. Religious Influence
Religion played a crucial role in the connection between Russia and the Byzantine Empire. The Byzantine Emperor was considered the leader of the Eastern Orthodox Church, and Russian Christianity was deeply influenced by Byzantine Orthodox Christianity.
The Orthodox faith, with its rituals, liturgy, and religious art, was adopted and adapted by the Russian Church, contributing to the development of a distinct Russian Orthodox tradition. Byzantine missionaries brought religious texts, liturgical practices, and theological teachings, which solidified the bond between the Russian and Byzantine Orthodox Churches.
The relationship between Russia and the Byzantine Empire was further strengthened by the establishment of the Patriarchate of Moscow in 1589. This granted the Russian Orthodox Church greater autonomy and independence from the Greek Orthodox Church based in Constantinople.
4. Legacy and Historical Significance
The influence of the Byzantine Empire on Russia cannot be overstated. It shaped Russian culture, politics, and religion, leaving a lasting legacy that continues to resonate today. The Byzantine legacy can be seen in Russian Orthodox architecture, iconography, and liturgical practices.
Moreover, the Byzantine Empire played a pivotal role in the formation of Russian statehood and identity. Russian rulers drew inspiration from Byzantine political institutions and ideology. The Byzantine connection also contributed to the Russification of the Eastern Slavs and the establishment of the Russian Empire.
While Russia was not officially part of the Byzantine Empire, the cultural, political, and religious links between the two civilizations were profound and enduring. These connections shaped Russian history and identity, making Russia deeply indebted to its Byzantine heritage.
Trading and Economic Ties Between Russia and Byzantium
In addition to the cultural and political connections, Russia and the Byzantine Empire also had significant trading and economic ties. The trade routes connecting the Baltic Sea with the Black Sea and the Mediterranean facilitated the exchange of goods, leading to economic prosperity for both regions.
Russian merchants, known as Novgorodian or Varangian traders, traveled to Constantinople to engage in commercial activities. They brought furs, wax, honey, and other commodities from Russia, which were highly sought after in the Byzantine Empire.
In return, Byzantine merchants imported luxury goods such as silk, spices, and precious metals into Russia. These trade relations not only contributed to the economic growth of both regions but also fostered cultural exchange and the spread of ideas.
1. The Role of Constantinople in Trade
Constantinople, the capital of the Byzantine Empire, played a pivotal role as a trading hub. Located at the crossroads of several important trade routes, it became a center for the exchange of goods and ideas between East and West.
The city’s strategic location made it a gateway for goods arriving from Asia, Europe, and Africa. Russian merchants traveled to Constantinople to take advantage of its extensive market network and secure profitable trade agreements.
Constantinople’s economic influence extended beyond trade. It also served as a center of craftsmanship and production, known for its fine textiles, metalwork, and jewelry. Russian merchants had access to these goods, which further enriched their trade relations with the Byzantine Empire.
2. The Importance of Fur and Slavic Goods
Russian traders brought furs, particularly sable and beaver pelts, which were highly prized in the Byzantine Empire. These furs were used for luxury garments and accessories, and their scarcity in Byzantium made them valuable commodities.
Along with furs, Russian traders exported other Slavic goods such as honey, wax, hides, and grains. The Byzantines relied on these products for their own consumption and for export to other regions. The trade in these goods not only brought economic prosperity but also facilitated cultural exchanges and the spread of Russian influence.
3. Luxury Imports from Byzantium
Byzantine merchants exported a variety of luxury goods to Russia, including silk, spices, and precious metals. Silk textiles, in particular, were highly sought after in Russia due to their rarity and exquisite quality.
These luxury imports from Byzantium, along with the Byzantine cultural influence, had a profound impact on Russian society. They were coveted by the elite and nobility, contributing to the development of a sophisticated and refined Russian court culture.
4. Economic Interdependence and Exchange of Ideas
The trading relationship between Russia and the Byzantine Empire fostered economic interdependence and the exchange of ideas. Russian merchants gained knowledge and expertise in trade and commerce from their Byzantine counterparts.
The influence of Byzantine economic practices and market systems can be seen in the development of trade routes and markets in Russia. The connections established during this period laid the foundation for future economic development in Russia.
Furthermore, the economic ties between the two regions facilitated the transmission of cultural and intellectual ideas. Along with goods, ideas, and knowledge flowed between Byzantium and Russia, enriching both civilizations and contributing to their respective growth and development.
The relationship between Russia and the Byzantine Empire was multifaceted, encompassing cultural, political, religious, and economic aspects. While Russia was not officially part of the Byzantine Empire, the influence and connections between the two civilizations were undeniable. The cultural exchange, political alliances, and economic ties shaped Russian history and identity, leaving a lasting legacy that continues to resonate today.
Russia’s Connection to the Byzantine Empire
During its early history, Russia was influenced by the Byzantine Empire in various aspects, including religion, culture, and politics. While Russia was not directly part of the Byzantine Empire, it maintained close ties with the empire and considered itself the successor to Byzantium.
One of the most significant connections between Russia and the Byzantine Empire was through religion. In the 10th century, the Russian ruler, Vladimir the Great, adopted Orthodox Christianity as the state religion after being exposed to the Byzantine Orthodox tradition. This decision had a lasting impact on the development of Russian culture and society.
Furthermore, Russia looked to the Byzantine Empire as the embodiment of political and cultural sophistication. Byzantine art, architecture, and literature heavily influenced Russian culture during the medieval period. Russian rulers sought to emulate the grandeur of Byzantium in their own territories.
Though not part of the empire itself, Russia’s historical connection to the Byzantine Empire had a profound influence on its development and identity. The legacy of the Byzantine Empire can still be seen in Russian Orthodox Christianity, architecture, and culture today.
Key Takeaways
- Russia was influenced by the Byzantine Empire in terms of culture, religion, and architecture.
- Russia’s adoption of Orthodox Christianity was heavily influenced by the Byzantine Empire.
- Russian rulers considered themselves the spiritual successors of the Byzantine emperors.
- The Byzantine Empire provided political and military support to Russia against invaders.
- Russian artists and craftsmen were influenced by Byzantine art and craftsmanship.
Frequently Asked Questions
Here, we answer some common questions about Russia’s connection to the Byzantine Empire.
1. How was Russia influenced by the Byzantine Empire?
Russia was strongly influenced by the Byzantine Empire in terms of religion, culture, and political organization. The spread of Orthodox Christianity to Russia can be credited to the Byzantine Empire. The Cyrillic alphabet, which is still used in modern Russian, was derived from the Greek alphabet used in the Byzantine Empire. Additionally, Russia adopted the Byzantine style of art and architecture in the form of onion-domed churches.
Politically, the Byzantine Empire played a significant role in shaping Russia’s early statehood. The idea of a “Third Rome” was popularized in Russia, with Moscow being seen as the successor to Rome and Constantinople. Russian rulers also modeled their administrative systems after the Byzantine Empire, adopting titles such as “tsar” and establishing a centralized autocratic rule.
2. Was Russia ever a part of the Byzantine Empire?
No, Russia was not officially a part of the Byzantine Empire. However, the influence of the Byzantine Empire can be seen in various aspects of Russian culture, religion, and governance. The Byzantine Empire and Russia maintained diplomatic and trade relations, and there were periods of close cooperation between the two, but Russia remained a separate entity.
3. Did Russia have any territorial connections to the Byzantine Empire?
While Russia did not have direct territorial connections to the Byzantine Empire, there were instances where Russian rulers exerted their influence in regions once controlled by the Byzantine Empire. For example, during the 15th century, the Russian state of Muscovy expanded its territories to include areas in modern-day Ukraine that were previously under Byzantine control.
Furthermore, the fall of the Byzantine Empire to the Ottoman Turks in 1453 resulted in an influx of Byzantine scholars and artists seeking refuge in Russia. These individuals brought with them a wealth of knowledge and cultural heritage, further enriching Russian society.
4. Were there any conflicts between Russia and the Byzantine Empire?
There were instances of conflicts and tensions between Russia and the Byzantine Empire. The two powers had different geopolitical interests, especially in the Black Sea region. Additionally, religious differences sometimes led to strained relations, with the Byzantine Empire practicing Orthodox Christianity and Russia later adopting its own distinct Orthodox tradition.
Despite these conflicts, there were also periods of cooperation and mutual support, such as during the Mongol invasions when both powers faced similar threats. Overall, Russia’s relationship with the Byzantine Empire was complex and influenced by numerous factors.
5. How did the fall of the Byzantine Empire impact Russia?
The fall of the Byzantine Empire had a significant impact on Russia. With the collapse of the Byzantine Empire and the rise of the Ottoman Turks, Russia saw itself as the last bastion of Orthodox Christianity and the successor to the Byzantine legacy. This ideology fueled Russian expansion and the desire to defend Orthodox Christianity.
The fall of Constantinople also led to an influx of Byzantine scholars and artists into Russia, which contributed to the Renaissance of Orthodox Christian culture and the development of new artistic styles in Russia.
Russia’s Plan to Restore Byzantium in The 18th Century
In conclusion, while Russia was not officially part of the Byzantine Empire, it had a complex relationship with it. The Byzantine Empire exerted significant cultural, religious, and political influence on Russia.
Russia adopted many aspects of Byzantine culture, including the Orthodox Christianity and Byzantine-style architecture. Additionally, the Byzantine Empire played a crucial role in the conversion of Russia to Christianity in the 10th century.