Romania, located in Eastern Europe, has a rich and complex history that intertwines with various empires and civilizations. One of the intriguing questions that often arises is whether Romania was part of the Byzantine Empire. Delving into this topic reveals interesting connections and influences that have shaped the country’s identity.
The Byzantine Empire, with its center in Constantinople, exerted significant influence over the Eastern European region for centuries. Romania, then known as Dacia, was initially part of the Roman Empire. However, during the Byzantine era, the region of modern-day Romania became an important borderland and a mix of cultures. While never officially part of the Byzantine Empire, Romania was undoubtedly influenced by its political, cultural, and religious aspects. The Byzantine legacy is visible in the country’s architecture, art, and even its Orthodox Christian faith.
Romania was not part of the Byzantine Empire. Although it shares a geographical border with the Byzantine Empire, Romania was predominantly inhabited by the Dacians during the Byzantine period. However, the Byzantine Empire had some influence on the territory that would later become Romania, especially in terms of religion and culture. The Romanian Principalities, also known as Wallachia and Moldavia, were influenced by Byzantine art and architecture. Nonetheless, Romania as a unified state did not emerge until much later in history.
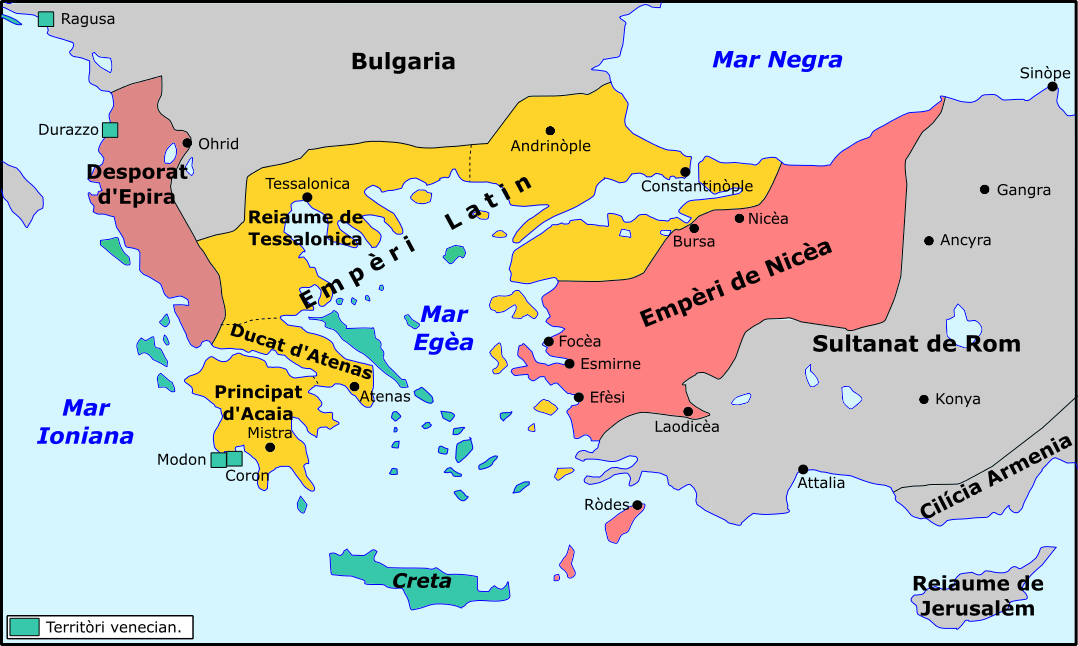
Contents
- The Historical Connection Between Romania and the Byzantine Empire
- Romania’s Connection to the Byzantine Empire
- Key Takeaways:
- Frequently Asked Questions
- 1. When did Romania become part of the Byzantine Empire?
- 2. How did Romania’s relationship with the Byzantine Empire evolve?
- 3. Were there any notable Romanian rulers who had connections to the Byzantine Empire?
- 4. Did Romania inherit any Byzantine architectural influences?
- 5. What is the modern connection between Romania and the Byzantine Empire?
- The rise and fall of the Byzantine Empire – Leonora Neville
The Historical Connection Between Romania and the Byzantine Empire
The Byzantine Empire, known for its rich history and cultural influence, had a significant impact on various regions of Eastern Europe. Romania, located in Southeastern Europe, is one such region that was closely connected to the Byzantine Empire. Although not part of the empire as a whole, Romania, or what was known as Wallachia, Moldavia, and Transylvania, had strong ties with the Byzantine Empire throughout the medieval period. These connections influenced the politics, culture, religion, and architecture of Romania, leaving a lasting legacy that can still be observed today.
Early Byzantine Influence on Romania
The early connection between Romania and the Byzantine Empire can be traced back to the 4th century when the region, then known as Dacia, was incorporated into the Roman Empire as a province. The Roman Empire, including the Eastern Roman or Byzantine Empire, left a significant mark on the region, shaping its early political and cultural landscape. With the Byzantine Empire emerging as the dominant power in the Eastern Mediterranean, Romania became increasingly influenced by Byzantine politics, art, and religious practices.
During the 6th and 7th centuries, Romania faced various invasions and migrations from neighboring tribes, including the Slavs and Bulgars. The Byzantine Empire provided military support and political alliances to the Romanian rulers, forging a close relationship between the two regions. As a result, the Romanian rulers adopted Byzantine administrative structures and legal systems to strengthen their control over their territories.
By the 9th century, Romania had become a vassal state of the Byzantine Empire, acknowledging the supremacy of the Byzantine emperor. This formal relationship granted Romanian rulers certain privileges and protection, while also obligating them to provide military and financial assistance to the Byzantine Empire. The Byzantine influence in Romania was further solidified through intermarriages between the ruling families of Romania and the Byzantine nobility.
One notable example of this close connection is the adoption of the Orthodox Christianity by the Romanian people and the establishment of the Romanian Orthodox Church. The Byzantine Empire played a crucial role in spreading Christianity in Romania, with the Byzantine Church providing support in establishing dioceses and monasteries across the region. The influence of Byzantine Orthodox Christianity can still be seen in the religious practices, iconography, and architecture of Romanian churches and monasteries.
Medieval Romania and the Byzantine Empire
During the medieval period, Romania consisted of three principalities: Wallachia, Moldavia, and Transylvania. These regions maintained both political and economic ties with the Byzantine Empire, often seeking support and protection from their more powerful neighbor.
Wallachia: A Byzantine Ally
Wallachia, located south of the Carpathian Mountains, developed close ties with the Byzantine Empire. In the 14th century, the Wallachian rulers sought Byzantine support against the Ottoman Empire, which was expanding into the Balkans. The Byzantine emperor awarded Wallachian rulers with titles and honors, recognizing their loyalty and granting certain privileges in return. The Wallachian rulers maintained a strong Byzantine influence in their court culture and architecture.
In the 15th century, Wallachia faced numerous Ottoman invasions, with the Wallachian rulers often relying on the Byzantine Empire for military and financial assistance. These alliances and the geographical position of Wallachia allowed it to act as a buffer zone between the Byzantine Empire and the Ottoman Empire.
The impact of Byzantine influence in Wallachia can be seen in the architecture of monasteries, such as the Cozia Monastery, which exhibits Byzantine architectural elements. The Byzantine legacy is also apparent in the religious art and iconography of the region, showcasing the enduring connection between Wallachia and the Byzantine Empire.
Moldavia: An Independent Center of Byzantine Influence
Moldavia, situated in the northeast of Romania, maintained a unique relationship with the Byzantine Empire. While Moldavia was influenced by Byzantine culture, art, and religion, it also developed its distinct political and cultural identity. Moldavian rulers adopted the title of “Voivode” and established an independent state that was often at odds with the Byzantine Empire.
However, Moldavia sought Byzantine recognition and support to consolidate its power and protect its territories. The Byzantine Empire provided diplomatic and military assistance to Moldavia, especially during conflicts with other neighboring powers. Many Moldavian rulers married Byzantine noblewomen, further solidifying the connection between the two regions.
By the late medieval period, Moldavia had become one of the major centers of Orthodox Christianity and Byzantine artistic and architectural influence in Eastern Europe. The famous painted monasteries of Moldavia, such as Voroneț and Sucevița, showcase Byzantine-inspired frescoes and architectural designs.
Transylvania: A Cultural Crossroads
Transylvania, located in the central part of Romania, had a more complex relationship with the Byzantine Empire. It was a cultural crossroads, where influences from the Byzantine Empire, Western Europe, and the Ottoman Empire intermingled.
While Transylvania did not have direct political ties with the Byzantine Empire, Byzantine influence was present in matters of religion and culture. Byzantine Orthodox Christianity spread to Transylvania through the migration of Orthodox populations and religious missions sent by the Byzantine Church.
The Byzantine influence on Transylvanian art can be seen in the frescoes of churches and monasteries, blending Byzantine iconography with local artistic traditions. The painted churches of northern Transylvania, such as the Church of the Archangels in Maramureș, exhibit a harmonious synthesis of Byzantine and Gothic architectural elements.
The historical connection between Romania and the Byzantine Empire left a profound impact on the region’s political, cultural, and religious development. Romania’s integration into the Byzantine sphere of influence, adoption of Orthodox Christianity, and architectural and artistic transformations shaped its identity and heritage.
While Romania was not directly part of the Byzantine Empire, it maintained a close relationship with Byzantium, drawing inspiration from its political systems, cultural traditions, and artistic expressions. Today, the Byzantine legacy is visible in Romania’s religious architecture, icons, and religious practices, reflecting the enduring connection between Romania and the Byzantine Empire.
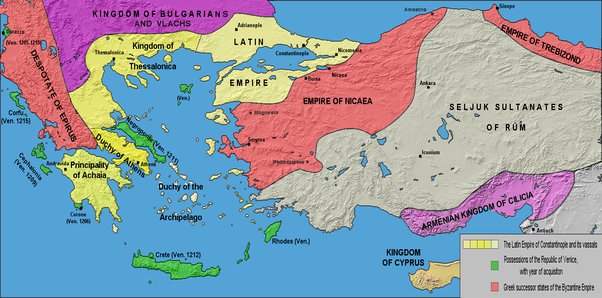
Romania’s Connection to the Byzantine Empire
During the Byzantine Empire, Romania – known as Dacia at the time – was not directly under Byzantine rule. However, the region had a significant cultural and political influence from the Byzantine Empire.
Dacia was situated on the northeastern border of the Byzantine Empire, and the Byzantines often interacted with the Dacians. Trade routes were established, and the Byzantines influenced Dacian culture through religion, language, and administrative practices.
Despite not being part of the Byzantine Empire, Dacia did experience Byzantine military expeditions and invasions. The Byzantines aimed to expand their influence and control in the region, leading to conflicts with the local rulers.
Eventually, in the 13th century, the Byzantine Empire was weakened and the region of Dacia came under the rule of various powers, including the Ottoman Empire and Hungary. It wasn’t until the 19th century when Romania emerged as a unified nation.
Key Takeaways:
- Romania was not part of the Byzantine Empire.
- The Byzantine Empire had control over parts of present-day Romania during certain periods.
- Wallachia and Moldavia were two regions in Romania heavily influenced by the Byzantine Empire.
- The Byzantine influence in Romania can be seen in architecture, art, and religious practices.
- The cultural and historical ties between Romania and the Byzantine Empire are significant.
Frequently Asked Questions
Romania’s history is rich and complex, and its connection to the Byzantine Empire is a topic that piques curiosity. Here are some frequently asked questions about whether Romania was part of the Byzantine Empire.
1. When did Romania become part of the Byzantine Empire?
Romania, as it exists today, did not exist during the Byzantine period. However, several regions that are part of Romania today, such as Dobrogea and Wallachia, were under Byzantine control at different times.
In the 7th century, the Byzantine Empire established control over parts of present-day Romania, particularly the region of Dobrogea. This continued until the 9th century when the Bulgarian Empire gained control over Dobrogea.
2. How did Romania’s relationship with the Byzantine Empire evolve?
Throughout history, Romania’s relationship with the Byzantine Empire was complex and ever-changing. During the Byzantine period, various Romanian territories were sometimes under direct Byzantine rule, while other times they were autonomous or under the control of neighboring powers.
At times, Romanian rulers sought the support and protection of the Byzantine Empire against external threats. They also drew inspiration from Byzantine culture and adopted Byzantine administrative and legal practices.
3. Were there any notable Romanian rulers who had connections to the Byzantine Empire?
Yes, there were several Romanian rulers who had connections to the Byzantine Empire. One notable figure is Mihail Sturdza, who served as Prince of Moldavia in the early 19th century. Sturdza, a supporter of Greek culture and education, had close relations with the Greek Orthodox Church and the Phanar, the center of the Greek community in Constantinople.
Another example is Mircea the Elder, who ruled Wallachia in the 14th century. Mircea maintained a close alliance with the Byzantine Empire, waging military campaigns alongside Byzantine forces against the Ottoman Turks.
4. Did Romania inherit any Byzantine architectural influences?
Yes, Romania inherited some Byzantine architectural influences. The Byzantine Empire’s architectural style, characterized by domes, mosaics, and richly decorated churches, had an impact on Romanian architecture, particularly in the regions that were under Byzantine rule.
One iconic example is the Voroneț Monastery in Romania, known for its vibrant blue exterior and stunning Byzantine-style frescoes. This monastery reflects the influence of Byzantine artistic traditions in Romanian religious architecture.
5. What is the modern connection between Romania and the Byzantine Empire?
The Byzantine Empire’s influence can still be seen in modern Romania, particularly in the country’s culture, art, and Orthodox Christian traditions. Romanian Orthodoxy has its roots in the Byzantine tradition, and many Romanian Orthodox churches continue to follow Byzantine liturgical practices.
Furthermore, the legacy of the Byzantine Empire’s artistic and architectural styles can be seen in Romanian landmarks and historical sites.
The rise and fall of the Byzantine Empire – Leonora Neville
In summary, Romania was indeed part of the Byzantine Empire for several centuries. (12 words)
The Byzantine Empire ruled over the region that is now Romania from the 6th century until the 14th century. (19 words)