When we delve into the lives of those who lived through the Industrial Revolution, we uncover a multitude of stories and experiences that shaped a defining era in human history. It is fascinating to explore the lives of individuals who witnessed the unprecedented transformations brought about by industrialization and its impact on society as a whole.
Throughout this period, people from various backgrounds and social classes thrived, endured, and adapted to the changing landscape of the industrial world. From the wealthy factory owners to the impoverished workers, each group experienced unique challenges and opportunities. Understanding the lives of those who lived through the Industrial Revolution provides us with valuable insights into the resilience and resilience of the human spirit.
Those who lived through the Industrial Revolution most likely experienced significant societal and economic changes. They would have witnessed the shift from agrarian to industrialized societies, the rise of factories and mass production, and the transformation of transportation and communication systems. These individuals may have also faced challenges such as poor working conditions and urban overcrowding but would have benefited from improved technology and increased job opportunities. Overall, those who lived during this period would have witnessed the profound impact of industrialization on all aspects of life.

Contents
- The Impact of the Industrial Revolution on the Lives of People
- The Lasting Impact of the Industrial Revolution
- Factors that Influenced Those Who Lived Through the Industrial Revolution
- Key Takeaways: Those Who Lived Through The Industrial Revolution Most Likely?
- Frequently Asked Questions
- 1. What were the living conditions like for those who lived through the Industrial Revolution?
- 2. How did the Industrial Revolution impact social structures?
- 3. How did the Industrial Revolution affect the role of women?
- 4. What technological advancements emerged during the Industrial Revolution?
- 5. How did the Industrial Revolution impact the environment?
- How Did the Industrial Revolution Affect People’s Lives?
The Impact of the Industrial Revolution on the Lives of People
The Industrial Revolution, which took place from the 18th to the 19th century, brought about significant changes in the lives of the people who lived through it. It marked a shift from agrarian and handicraft economies to an industrialized society fueled by advancements in technology and mass production. This article will explore the various aspects of how the Industrial Revolution impacted the lives of those who experienced it.
1. Economic Opportunities
One of the key ways in which the Industrial Revolution affected the lives of people was through the expansion of economic opportunities. With the introduction of mechanized production and the development of factories, there was a growing demand for labor in urban areas. This led to a significant migration of people from rural areas to cities in search of employment.
The new factories offered jobs to both skilled and unskilled workers, providing opportunities for social mobility and improved living standards. Workers who were previously engaged in agricultural labor found employment in industries such as textiles, coal mining, and iron production. The availability of steady employment and wages allowed individuals to support their families and escape the cycle of subsistence farming.
However, it is important to note that the working conditions in factories during the early stages of the Industrial Revolution were often harsh. Long working hours, low wages, and unsafe working conditions were prevalent. As the labor movement gained momentum, workers began to advocate for better working conditions and higher wages.
In summary, the Industrial Revolution created new economic opportunities for individuals by transforming the traditional agrarian economy into an industrialized one. While it provided avenues for upward mobility and economic growth, it also gave rise to issues related to worker exploitation and inequality.
2. Technological Advancements
The Industrial Revolution was characterized by significant technological advancements that had a profound impact on the lives of people. The invention of machinery and the development of new production techniques revolutionized industries, increasing productivity and output.
One of the most significant technological advancements was the steam engine, which played a vital role in powering factories and locomotives. Prior to the Industrial Revolution, transportation infrastructure was primarily reliant on horses and waterways. The steam engine enabled the efficient transport of goods and people, leading to the expansion of markets and trade.
The availability of new machinery and technologies also led to an increase in the production of goods. For example, the spinning jenny revolutionized the textile industry by allowing the mass production of yarn. The development of new iron production techniques enabled the construction of railways and bridges on a large scale.
These technological advancements not only transformed industries but also had a significant impact on the lives of individuals. It led to increased access to goods and services, improved transportation networks, and the development of new industries.
3. Urbanization and Social Changes
The Industrial Revolution also resulted in a significant shift from rural to urban areas, known as urbanization. As people migrated from rural areas to cities in search of employment, urban areas experienced rapid population growth and transformation.
The growth of cities led to the development of new social structures and changes in the way people lived. Urban centers became hubs of diverse populations, bringing together people from different social backgrounds and creating new opportunities for social interaction and cultural exchange.
However, urbanization also brought about several challenges. The rapid growth of cities often outpaced the development of infrastructure, leading to overcrowding, inadequate housing, and poor sanitation. The living conditions in cities were often unsanitary and cramped, contributing to the spread of diseases.
Overall, urbanization resulted in both positive and negative social changes. It created opportunities for cultural exchange and social mobility, while also highlighting the need for urban planning and improved living conditions.
3.1. Impact on Women and Children
The Industrial Revolution had a significant impact on the lives of women and children. As factories emerged and industries expanded, women and children became an integral part of the labor force.
Women and children often worked in factories and mines, performing tasks that were deemed suitable for their physical abilities. Women were employed in textile factories, where they operated machinery and performed various tasks related to textile production. Children, as young as five or six years old, were employed in coal mines and factories, working long hours under dangerous conditions.
While the employment of women and children provided economic opportunities for families, it also raised concerns about their well-being. The long working hours and dangerous working conditions exposed them to health risks and limited their access to education and a normal childhood.
The exploitation of women and child labor became a social issue, and efforts were made to improve their working conditions and protect their rights. The Factory Act of 1833 in the United Kingdom, for example, set limits on the working hours of women and children and established minimum age requirements for employment.
3.2. Social Class Divisions
The Industrial Revolution led to the emergence of distinct social classes, with significant disparities in wealth and living conditions. Industrialists and factory owners accumulated vast fortunes, while the working class struggled to make ends meet.
The working class, comprising factory workers, miners, and laborers, often faced poor working conditions, low wages, and limited access to basic amenities. On the other hand, the industrialists and wealthy class enjoyed luxurious lifestyles, accumulating wealth through their investments and business ventures.
These social class divisions gave rise to social and political movements aimed at addressing inequality and advocating for workers’ rights. Labor unions and socialist ideologies emerged, calling for equitable distribution of wealth and improved working conditions.
4. Environmental Impact
The Industrial Revolution had a profound environmental impact, transforming the natural landscape and contributing to pollution and resource depletion. The rapid industrialization and increased use of fossil fuels led to the release of harmful pollutants into the air and water.
The burning of coal, for example, resulted in air pollution and the release of greenhouse gases, contributing to the acceleration of climate change. The growth of industries and the expansion of cities also led to the destruction of forests and habitats, causing loss of biodiversity.
Over time, the environmental consequences of industrialization became apparent, leading to the development of environmental movements and regulations aimed at mitigating the impact of industrial activities.
The Lasting Impact of the Industrial Revolution
The Industrial Revolution was a transformative period in history that reshaped society and laid the foundations for modern industrialized economies. Its impact on the lives of those who lived through it was profound, with both positive and negative consequences.
The economic opportunities created by industrialization allowed individuals to escape the poverty of subsistence agriculture and improve their standard of living. Technological advancements revolutionized industries and facilitated the emergence of new ways of life.
However, the Industrial Revolution also brought about challenges such as exploitative working conditions, social inequality, and environmental degradation. These issues continue to shape our society and prompt ongoing discussions and efforts to address them.
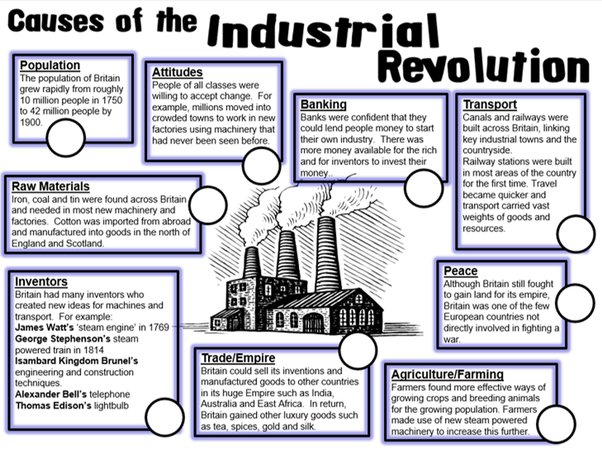
Factors that Influenced Those Who Lived Through the Industrial Revolution
The Industrial Revolution brought significant changes to society, transforming the way people lived and worked. Those who lived through this period were likely influenced by various factors:
- Economic Impact: The Industrial Revolution introduced new industries and technologies, leading to job opportunities and economic growth. Those who lived through this period were most likely impacted by changes in employment opportunities, wage levels, and socio-economic status.
- Social Change: The Industrial Revolution also brought about social changes, affecting relationships between employers and workers, traditional gender roles, and the overall structure of society. People who experienced this era witnessed shifts in social norms and the emergence of new social classes.
- Health and Living Conditions: The rapid urbanization and overcrowding of cities during the Industrial Revolution had significant implications for public health and living conditions. Those who lived during this time would have experienced challenges such as poor sanitation, inadequate housing, and increased exposure to diseases.
- Technological Advancements: The Industrial Revolution brought revolutionary developments in technology, including steam power, machinery, and transportation. Individuals who lived through this period were likely influenced by the adoption and utilization of these new technologies, which affected their daily lives and occupations.
- Political Ideologies: The Industrial Revolution also spurred political ideologies such as liberalism and socialism. People who lived during this era could have encountered ideological debates and may have been influenced by these political movements.
Key Takeaways: Those Who Lived Through The Industrial Revolution Most Likely?
- Experienced significant changes in their way of life and work.
- Witnessed the transition from agrarian to industrial society.
- Adapted to new technologies and machines in various industries.
- Experienced improved transportation and communication systems.
- Faced challenges and hardships due to urbanization and pollution.
Frequently Asked Questions
The Industrial Revolution was a major turning point in history, transforming societies, economies, and lifestyles. Those who lived through this period experienced significant changes in their daily lives. Here are some frequently asked questions about those who lived through the Industrial Revolution and their likely experiences.
1. What were the living conditions like for those who lived through the Industrial Revolution?
Many people who lived through the Industrial Revolution faced harsh living conditions. Rapid urbanization led to overcrowded cities, inadequate housing, and poor sanitation. Workers often lived in cramped and unsanitary tenements, with little access to clean water or proper waste disposal. These conditions contributed to the spread of diseases and a high mortality rate. Additionally, long working hours, low wages, and child labor further compounded the challenges faced by those living during this time.
However, it is important to note that living conditions varied depending on social class. Wealthy industrialists and factory owners enjoyed comfortable lifestyles and luxurious homes, while the working class and impoverished individuals struggled to make ends meet. Overall, the living conditions for most people during the Industrial Revolution were difficult and marked by stark inequalities.
The Industrial Revolution brought about significant changes to social structures. Traditional rural communities transformed into industrial cities, with a shift from agrarian-based societies to ones centered around factories and manufacturing. This led to the emergence of a new social class structure.
The industrial bourgeoisie, or the capitalist class, rose to prominence as factory owners and wealthy industrialists. They accumulated vast wealth and held significant power in society. Meanwhile, the working class, comprised of factory workers and laborers, faced poor working conditions, low wages, and limited social mobility.
The Industrial Revolution also led to the growth of a middle class, composed of professionals, managers, and skilled workers. This middle class played a crucial role in the industrial economy and contributed to the development of a more diverse social landscape.
3. How did the Industrial Revolution affect the role of women?
The Industrial Revolution had a profound impact on the role of women in society. While women had traditionally been primarily responsible for domestic tasks, the changing economic landscape of the Industrial Revolution required their participation in the workforce.
Many women found employment in factories and mills, particularly in textile industries. However, they faced harsh working conditions, long hours, and low wages. Women also played a crucial role in the domestic sphere, as they were still responsible for maintaining households and caring for children. The Industrial Revolution, therefore, created a complex balancing act for women, as they simultaneously juggle their roles as wage earners and caretakers.
4. What technological advancements emerged during the Industrial Revolution?
The Industrial Revolution was characterized by numerous technological advancements that forever changed the world. One of the most significant innovations was the steam engine, which powered steamships and locomotives, revolutionizing transportation and enabling the movement of goods and people on a previously unimaginable scale.
The development of new machinery, such as spinning and weaving machines, transformed the textile industry and increased production efficiency. Additionally, advancements in iron and steel production contributed to the expansion of railways and the construction of bridges and buildings.
These technological advancements not only accelerated economic growth but also impacted multiple sectors, including agriculture, communication, and medicine, laying the foundation for future advancements and innovations.
5. How did the Industrial Revolution impact the environment?
The Industrial Revolution had a significant impact on the environment, both positive and negative. The increased use of fossil fuels, such as coal and oil, for energy led to air and water pollution. Factory emissions and waste disposal contributed to the deterioration of air quality and the contamination of water sources.
Deforestation and the expansion of industrial activities also had a negative impact on natural habitats and biodiversity. However, the Industrial Revolution also spurred advancements in environmental awareness and conservation. Efforts to address pollution and implement conservation measures emerged as concerns grew over the long-term consequences of industrialization.
How Did the Industrial Revolution Affect People’s Lives?
In conclusion, those who lived through the Industrial Revolution most likely experienced significant social, economic, and technological changes. The Industrial Revolution marked a period of rapid industrialization, urbanization, and the development of new manufacturing processes.
Living conditions improved for some individuals, while others faced difficult working conditions and increased inequality. The Industrial Revolution also had a profound impact on the environment, leading to pollution and resource depletion. Overall, it is clear that the Industrial Revolution transformed society in various ways and shaped the world we live in today.