Interchangeable parts revolutionized the manufacturing industry during the Industrial Revolution, leading to increased efficiency and productivity. Before interchangeable parts were introduced, products were often made by skilled artisans who crafted each piece individually. This process was time-consuming and costly, limiting the scale of production. However, with the advent of interchangeable parts, factories were able to mass-produce goods with standardized components, allowing for faster assembly and easier repair.
The impact of interchangeable parts was significant, as it not only transformed the manufacturing process but also had broader implications for society. With the ability to produce goods more efficiently and at a lower cost, the prices of consumer goods decreased, making them more accessible to a wider population. This led to an increase in demand, which in turn fueled further industrialization and economic growth. Interchangeable parts played a crucial role in shaping the modern industrial world, setting the stage for the advancements and mass production capabilities we see today.
The introduction of interchangeable parts had a profound impact on the Industrial Revolution. It revolutionized manufacturing by enabling mass production and streamlining the assembly process. Interchangeable parts allowed for faster and more efficient production, leading to increased productivity and lower costs. This innovation also resulted in improved product quality and reliability. With interchangeable parts, manufacturers could easily replace faulty components, reducing the need for skilled labor and making repairs easier. Overall, interchangeable parts played a crucial role in the industrialization of various industries, fueling economic growth and shaping the modern world.

Contents
- The Revolutionary Impact of Interchangeable Parts in the Industrial Revolution
- Advancing Industries and Accelerating Progress
- Impact of Interchangeable Parts on the Industrial Revolution
- Key Takeaways
- Frequently Asked Questions
- 1. What are interchangeable parts?
- 2. How did interchangeable parts impact the manufacturing process?
- 3. What industries were most impacted by interchangeable parts?
- 4. What were the advantages of using interchangeable parts?
- 5. How did interchangeable parts contribute to the growth of the Industrial Revolution?
- The Invention of Interchangeable Parts 1798
The Revolutionary Impact of Interchangeable Parts in the Industrial Revolution
The industrial revolution in the 18th and 19th centuries brought significant advancements in manufacturing processes, leading to increased productivity and economic growth. One of the key drivers of this revolution was the introduction of interchangeable parts. The concept of interchangeable parts revolutionized manufacturing by allowing for mass production, standardization, and ease of repair. This article delves into the impact of interchangeable parts on the industrial revolution, exploring its effects on efficiency, production scale, and economic development.
The Birth of Interchangeable Parts
The concept of interchangeable parts, also known as standardized parts, emerged in the late 18th century. Previously, skilled craftsmen manufactured goods by hand, making each piece unique and customized. However, this method was time-consuming, inefficient, and required highly skilled workers. The demand for mass-produced goods and the need for efficient manufacturing processes drove the development of interchangeable parts.
Eli Whitney, an American inventor, is widely attributed with popularizing the concept of interchangeable parts. In the late 1700s, Whitney pioneered the production of muskets with standardized parts. He demonstrated that by using precise measurements and standardized designs, individual parts could be manufactured separately and then assembled together, greatly reducing production time and costs. Whitney’s work laid the foundation for the widespread adoption of interchangeable parts in various industries.
The development of the cotton gin, also by Eli Whitney, further showcased the benefits of interchangeable parts. The cotton gin revolutionized the cotton industry by automating the process of separating cotton fibers from seeds. It consisted of multiple interchangeable parts that could be easily replaced or repaired, improving the efficiency and maintenance of the machine.
With the success of Whitney’s interchangeable parts in firearm and cotton gin manufacturing, the concept quickly spread to other industries such as textiles, transportation, and machinery.
Standardization and Efficiency
One of the key impacts of interchangeable parts was the standardization of manufacturing processes. Previously, every product was custom-made, requiring skilled workers to craft each piece by hand. With the introduction of interchangeable parts, manufacturers could produce standardized components that fit together seamlessly. This allowed for greater efficiency in production as it eliminated the need for skilled craftsmen to handcraft each component. Instead, less-skilled workers could be trained to operate specialized machinery, resulting in faster production and reduced labor costs.
Standardization also led to increased efficiency in the assembly line. By having interchangeable parts, workers could quickly and easily replace defective components, minimizing downtime and increasing productivity. This streamlined production process enabled manufacturers to meet growing demand and produce goods at a faster rate.
Furthermore, the use of interchangeable parts facilitated repair and maintenance. Instead of requiring specialized knowledge to repair a complex product, individuals could simply replace the malfunctioning part with a standardized one. This meant that repairs could be carried out by a wider range of individuals, reducing the dependency on highly skilled technicians and making maintenance more accessible and cost-effective.
Mass Production and Scale
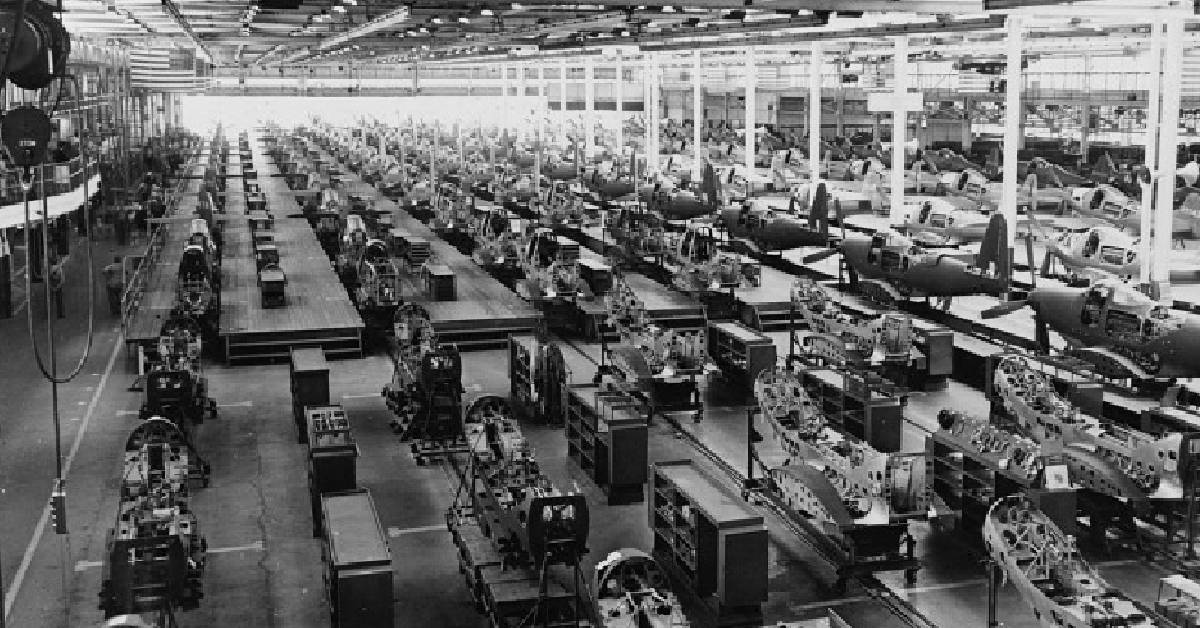
Interchangeable parts paved the way for mass production, which was a central feature of the industrial revolution. Before the introduction of interchangeable parts, goods were typically manufactured in small quantities due to the time-consuming nature of handcrafted production. However, with standardized components, manufacturers could produce large quantities of identical products.
The ability to produce goods at a significantly larger scale had numerous economic advantages. First, it allowed manufacturers to benefit from economies of scale, reducing the cost per unit as production volume increased. This made products more affordable and accessible to a wider range of consumers.
Second, mass production created new employment opportunities. As factories grew in size and expanded their production capacity, more workers were needed to operate the machinery and assemble the products. This led to urbanization and the rise of industrial cities, attracting people from rural areas looking for job prospects.
Lastly, mass production fueled international trade. With the ability to manufacture goods at a larger scale, industries could fulfill domestic demand and also export products to foreign markets. This enabled countries to specialize in certain industries and develop comparative advantages, contributing to global economic growth.
Technological Advancements and Innovation
The widespread adoption of interchangeable parts spurred technological advancements and innovation during the industrial revolution. Manufacturers developed new types of machines and tools to produce standardized components more efficiently.
One notable development was the invention of the screw-cutting lathe by Henry Maudslay. This machine enabled the mass production of screws with standardized threads, revolutionizing industries such as construction, machinery, and transportation. It simplified assembly processes, improved the reliability of products, and facilitated the interchangeability of parts.
The use of interchangeable parts also encouraged innovation and experimentation. With standardized components readily available, inventors and engineers could focus their efforts on improving product design and functionality rather than spending time on individual part manufacturing. This led to the creation of more advanced and complex machines, driving further technological progress.
Furthermore, the concept of interchangeable parts laid the groundwork for the development of assembly line production, which emerged later in the industrial revolution. Assembly lines allowed for the seamless integration of interchangeable parts, enabling products to be assembled rapidly and efficiently. This innovation revolutionized manufacturing on a larger scale, including industries such as automotive production.
Improved Product Quality and Accessibility
Another significant impact of interchangeable parts was the improvement in product quality and accessibility. By using standardized components, manufacturers could produce goods with higher precision and consistency. This reduced variability in the manufacturing process, resulting in higher-quality products that met the expectations of consumers.
The accessibility of products also increased with the use of interchangeable parts. As manufacturers were able to produce goods at a larger scale, prices decreased, making products more affordable to a broader population. Interchangeable parts also made repairs and maintenance easier, extending the lifespan of products and making them more accessible to a wider range of individuals.
Advancing Industries and Accelerating Progress
The impact of interchangeable parts on the industrial revolution cannot be understated. The introduction of standardized components revolutionized manufacturing processes by enabling mass production, standardization, and ease of repair. This led to increased efficiency, larger-scale production, and economic development. Interchangeable parts not only transformed industries but also paved the way for technological advancements and innovation. By improving product quality and accessibility, interchangeable parts propelled the industrial revolution forward and continue to shape manufacturing processes to this day.
Impact of Interchangeable Parts on the Industrial Revolution
The development and widespread use of interchangeable parts had a profound impact on the Industrial Revolution. This innovation revolutionized manufacturing processes and led to significant advancements in productivity, efficiency, and standardization.
Prior to the introduction of interchangeable parts, products were handmade, often requiring skilled craftsmen to individually craft each component. This process was time-consuming, expensive, and prone to errors. With the adoption of interchangeable parts, manufacturers could produce goods more quickly and at a lower cost. This increase in efficiency allowed for mass production, creating a new era of industrialization.
The use of interchangeable parts also facilitated repair and maintenance processes. Rather than requiring specialized craftsmen to repair broken items, which was costly and time-consuming, interchangeable parts made it easier to replace faulty components, extending the lifespan and usability of products.
Moreover, the standardization of interchangeable parts established uniformity and consistency, enabling mass production on a scale previously unseen. This not only drove down costs but also allowed for the assembly line production system, a key component of modern industrial manufacturing.
Key Takeaways
- Interchangeable parts revolutionized manufacturing in the Industrial Revolution.
- Interchangeable parts increased efficiency and reduced production costs.
- Standardization of parts allowed for mass production and assembly line production.
- Interchangeable parts led to the rise of consumer goods and the growth of the middle class.
- Interchangeable parts laid the foundation for modern manufacturing processes.
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are some commonly asked questions about how interchangeable parts impacted the Industrial Revolution:
1. What are interchangeable parts?
Interchangeable parts are standardized components that are manufactured to be identical and can be easily substituted for one another. This means that each part can fit and function in any assembly of the same type.
In the context of the Industrial Revolution, interchangeable parts revolutionized the manufacturing process by allowing for mass production and efficient assembly of products.
2. How did interchangeable parts impact the manufacturing process?
Interchangeable parts had a significant impact on the manufacturing process during the Industrial Revolution. Before the advent of interchangeable parts, products were typically handcrafted, and each piece had to be custom-made. This process was time-consuming, costly, and often resulted in inconsistencies in the final product.
With the introduction of interchangeable parts, manufacturers could produce components in bulk, leading to faster and more cost-effective production. This allowed for assembly line manufacturing, where each worker specialized in a specific task, further increasing efficiency and productivity.
3. What industries were most impacted by interchangeable parts?
Interchangeable parts had a profound impact on several industries during the Industrial Revolution. The most notable industries that benefited from the use of interchangeable parts include:
a) Textile industry: The production of textiles, such as cotton goods and clothing, significantly increased due to the adoption of interchangeable parts in textile machinery.
b) Firearms industry: The use of interchangeable parts in firearms manufacturing revolutionized the industry, allowing for faster and more standardized production.
c) Machinery industry: The manufacturing of machinery, including steam engines and agricultural equipment, was greatly improved with the implementation of interchangeable parts.
4. What were the advantages of using interchangeable parts?
The use of interchangeable parts offered several advantages during the Industrial Revolution:
a) Increased efficiency: Interchangeable parts enabled faster production and assembly processes, leading to improved efficiency and productivity.
b) Cost-effectiveness: Mass production of standardized interchangeable parts reduced manufacturing costs and made products more affordable for consumers.
c) Quality control: Interchangeable parts allowed for better quality control as faulty components could be easily replaced without the need to rework the entire product.
5. How did interchangeable parts contribute to the growth of the Industrial Revolution?
The introduction of interchangeable parts played a crucial role in the growth of the Industrial Revolution by:
a) Facilitating mass production: Interchangeable parts enabled the efficient production of goods on a large scale, leading to the growth of industries and increased economic output.
b) Driving technological advancements: The implementation of interchangeable parts required the development of new manufacturing techniques and machinery, leading to technological advancements in various industries.
c) Fueling industrialization: The use of interchangeable parts accelerated the process of industrialization by streamlining production processes and creating a more efficient and mechanized manufacturing sector.
The Invention of Interchangeable Parts 1798
In conclusion, the advent of interchangeable parts during the Industrial Revolution had a profound impact on manufacturing and production processes.
It revolutionized the way products were made by allowing for mass production, increased efficiency, and reduced costs. The use of interchangeable parts also led to the standardization of products, making them more consistent and reliable. This innovation paved the way for the development of assembly lines and the rise of factories, which greatly accelerated industrialization and economic growth. The concept of interchangeable parts continues to shape modern manufacturing processes, making it one of the key advancements of the Industrial Revolution.