The rich history of ancient East African civilizations is a fascinating subject that unveils an array of astonishing achievements and cultural milestones. From the vibrant cities of Great Zimbabwe to the legendary empires of Axum and Kush, East Africa has been a crucible of civilization for centuries. Exploring the deep-rooted heritage of this region not only offers a glimpse into the past but also sheds light on the resilience and ingenuity of the ancient African societies.
Dating back thousands of years, the ancient East African civilizations left behind a legacy that continues to shape the cultural, political, and economic landscapes of the region today. These civilizations were centers of trade, innovation, and intellectual pursuits, fostering advancements in architecture, agriculture, and governance. Their networks spanned vast distances, connecting East Africa to the Indian Ocean trade routes and the Mediterranean world. As we delve into the rich history of these civilizations, we uncover tales of kings and queens, magnificent monuments, and cultural practices that have endured through the ages.
Discover the fascinating history of ancient East African civilizations, a rich tapestry of cultures, kingdoms, and empires that spanned thousands of years. From the mighty kingdoms of Kush and Aksum to the flourishing city-states along the Swahili Coast, East Africa was a hub of trade, scholarship, and innovation. Uncover the secrets of ancient ruins, sacred sites, and archaeological treasures that offer insights into the diverse civilizations that once thrived in this region. Delve into the ancient East African world and gain a deeper understanding of its contributions to human history.
Contents
- The Majesty of Ancient East African Civilizations
- Exploring Cultural Achievements and Technological Advancements
- The Enduring Influence of Ancient East African Civilizations
- Exploring the Rich History of Ancient East African Civilizations
- Key Takeaways
- Frequently Asked Questions
- 1. What were the main ancient East African civilizations?
- 2. What were some notable achievements of ancient East African civilizations?
- 3. How did ancient East African civilizations interact with other regions?
- 4. What led to the decline of ancient East African civilizations?
- 5. What is the significance of ancient East African civilizations today?
- The Untold Stories of the Great African Empires | A Journey Through Time
The Majesty of Ancient East African Civilizations
Ancient East African civilizations have a rich and storied history that spans thousands of years. From the ancient kingdom of Kush to the bustling port cities of the Swahili coast, this region of Africa has been a hub of civilization, trade, and cultural exchange. Exploring the rich history of these ancient civilizations is like peering into a treasure trove, uncovering fascinating stories, innovative achievements, and enduring legacies. This article delves into the profound advancements, cultural practices, and the vibrant tapestry of ancient East African civilizations.
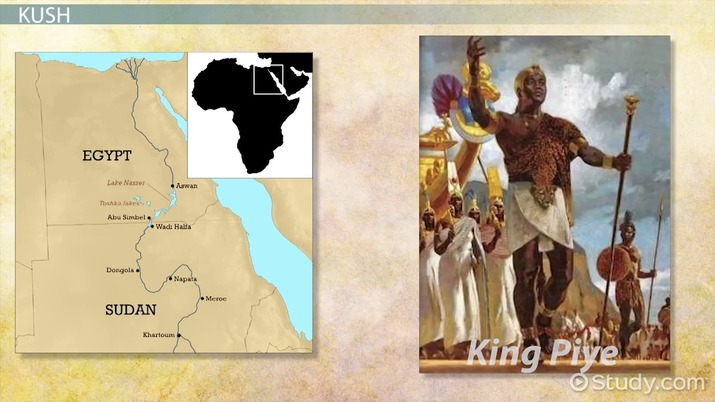
1. The Kingdom of Kush: A Center of Power and Culture
The Kingdom of Kush, located in what is now modern-day Sudan, was a powerful and influential ancient civilization that flourished from around 800 BCE to 350 CE. Known for its mighty warriors, advanced bronze metallurgy, and elaborate royal burials, Kush was a formidable rival to the ancient Egyptian empire. The capital city of Meroe served as the political, cultural, and economic center of the kingdom.
Kushite culture was heavily influenced by Egyptian civilization, and the Kushites adopted many aspects of Egyptian art, architecture, and religious practices. The most iconic remnants of Kushite civilization are the pyramids of Meroe, which served as burial sites for the Kushite monarchs. These pyramids, although smaller in size compared to their Egyptian counterparts, exhibit unique architectural features such as steep angles and elaborate ornamentation.
Additionally, the Kingdom of Kush played a crucial role in trans-Saharan trade, providing a vital link between the lucrative markets of the Mediterranean and the abundant resources of sub-Saharan Africa. The Kushites traded in luxury goods, such as gold, ivory, and precious stones, establishing prosperous economic networks that extended throughout the ancient world.
1.1 The Rulers of Kush: Black Pharaohs and Warrior Queens
The rulers of Kush were known as pharaohs, similar to their Egyptian counterparts. However, what sets the Kushite pharaohs apart is their distinctive African heritage. Referred to as the Black Pharaohs, these rulers left behind a legacy of political stability, military prowess, and a distinct cultural identity.
One of the notable Kushite queens was Amanirenas, who led her armies against the mighty Roman Empire in defense of her kingdom. Her military campaigns were remarkably successful, and she negotiated a peace treaty that allowed Kush to maintain its independence and sovereignty.
The Black Pharaohs of Kush left a lasting impact on the history and culture of Africa. Their artistic and architectural achievements stand as a testament to the kingdom’s grandeur, and their legacy continues to shape the identity of modern Sudan and its people.
2. The Swahili Coast: A Melting Pot of Trade and Culture
As we move closer to the present day, the Swahili Coast emerges as a vibrant and influential region along the eastern shores of Africa. Stretching from Somalia in the north to Mozambique in the south, the Swahili Coast encompasses the coastal regions of Kenya and Tanzania. The region owes its name to the Swahili language, a Bantu language that developed as a lingua franca for trade.
The Swahili Coast was a hub of trade between the African hinterland, the Arab world, and the Indian Ocean region. Arab and Persian merchants established thriving trading settlements along the coast, fostering a unique blend of African, Arab, and Indian cultures. These city-states, such as Kilwa, Mombasa, and Zanzibar, became cosmopolitan centers of trade, commerce, and cultural exchange.
One of the significant contributions of the Swahili Coast was the development of a maritime culture that rivaled the European powers of the time. Swahili sailors ventured into the vast Indian Ocean, using their advanced navigational skills to establish trade networks with distant lands, including China and India.
2.1 The Architecture and Artistry of the Swahili Coast
The Swahili Coast is renowned for its distinctive architecture, characterized by intricately carved doors, coral stone buildings, and narrow streets that wind through ancient towns. The fusion of African, Arab, and Indian influences is evident in the architectural features and decorative motifs found in Swahili buildings.
The cities of the Swahili Coast also flourished as centers of Islamic learning, with scholars and theologians contributing to the spread of Islam in East Africa. Mosques, such as the famous Gede Mosque, embody the architectural prowess and spiritual significance of the region.
Moreover, Swahili arts and crafts, such as intricate woodcarvings, pottery, and textiles, are celebrated for their exquisite beauty and cultural significance. These crafts showcase the fusion of local African traditions with influences from the Arab and Indian worlds.
Exploring Cultural Achievements and Technological Advancements
The rich history of ancient East African civilizations encompasses more than just political power and trade. These civilizations made significant contributions to the realms of culture, art, and technology, leaving behind a legacy that continues to inspire and captivate.
3. Ancient East African Art: A Triumph of Expression
The art of ancient East African civilizations is an expression of their identity, beliefs, and cultural practices. From intricate rock paintings and petroglyphs to stunning sculptures and pottery, these artworks offer a glimpse into the creative spirit of the people.
The rock art of East Africa provides insights into the daily lives and cultural activities of ancient communities. These paintings, found in sites such as the Kondoa Rock Art Sites in Tanzania, depict scenes of hunting, dancing, and communal rituals.
Another remarkable artistic achievement of the region is the terracotta sculptures of Nok, located in present-day Nigeria. These lifelike sculptures, dating back to 500 BCE, demonstrate the sophisticated artistic skills and representational techniques of ancient African civilizations.
3.1 Music and Dance: A Celebration of Rhythm and Tradition
Music and dance played a vital role in ancient East African societies, serving as a means of communication, cultural expression, and social cohesion. Traditional musical instruments, such as the mbira and the drum, continue to be an integral part of East African music today.
The cultural dances of East Africa vary from region to region, with each community preserving its unique traditions and movements. From the spirited gumboot dance of South Africa to the graceful makossa dance of Cameroon, these vibrant dance forms are a celebration of African heritage.
Ancient East African civilizations understood the power of music and dance in fostering a sense of community and preserving cultural heritage. Today, these artistic practices continue to thrive, connecting past and present through rhythm and movement.
4. Technological Advancements: Engineering Marvels of Ancient East Africa
The ancient East Africans were not only masters of trade and culture but also accomplished engineers and craftsmen. Their technological innovations are a testament to their ingenuity and problem-solving abilities.
One prominent example of East African engineering prowess is the Great Zimbabwe, an imposing stone structure that served as the political and economic center of a flourishing civilization. The massive stone walls and intricate architecture of Great Zimbabwe demonstrate the advanced construction techniques employed by ancient African engineers.
The East African coast also witnessed remarkable achievements in maritime technology. The construction of advanced dhows, traditional sailing vessels, enabled the Swahili people to navigate the treacherous Indian Ocean and engage in long-distance trade.
Additionally, the ancient East Africans were skilled metalworkers, producing intricate iron tools and weapons. Their expertise in iron smelting and forging played a crucial role in the development of their societies, providing them with essential tools for agriculture, hunting, and defense.
The Enduring Influence of Ancient East African Civilizations
The rich history of ancient East African civilizations leaves an indelible mark on the region, shaping the identity and culture of modern-day countries. The legacy of the Kingdom of Kush can be seen in the archaeological sites and cultural practices of Sudan, while the Swahili Coast continues to thrive as a vibrant hub of trade and cultural exchange.
Moreover, the artistic and technological achievements of ancient East African civilizations inspire contemporary artists, scholars, and researchers. They remind us of the intellectual and cultural richness that thrived in these societies and encourage us to celebrate and learn from their remarkable achievements.
Exploring the Rich History of Ancient East African Civilizations
East Africa is home to a rich and diverse history of ancient civilizations that have shaped the region for thousands of years. From the ancient kingdom of Kush to the powerful civilization of Aksum, this region has been a hub of cultural, economic, and political development.
The history of East African civilizations dates back to prehistoric times, with evidence of early human ancestors found in the region. The rise and fall of kingdoms and empires have left a lasting impact on the area, with archaeological sites and ancient ruins serving as reminders of this rich heritage.
Notable civilizations in East Africa include the Kingdom of Kush, which flourished from around 2500 BC to 350 AD and was known for its powerful ruling dynasty and advanced civilization. The Aksumite Empire, which emerged around the 1st century AD, played a crucial role in trade and was a major center of Christianity in the region.
Exploring the history of ancient East African civilizations allows us to understand their contributions to art, architecture, trade, and cultural exchange. It also sheds light on the complex social and political structures that existed in the region, as well as the interactions between different societies.
Key Takeaways
- Ancient East African civilizations have a rich and diverse history.
- They were known for their advanced architectural and engineering skills.
- Trade played a crucial role in the development of these civilizations.
- Art and culture flourished in ancient East Africa.
- These civilizations left a lasting impact on the region and influenced future societies.
Frequently Asked Questions
When it comes to exploring the rich history of ancient East African civilizations, many questions arise. Here are some frequently asked questions about the topic.
1. What were the main ancient East African civilizations?
Ancient East Africa was home to several notable civilizations that left a lasting impact on the region’s history. One of the most prominent civilizations was the Kingdom of Kush, which flourished in what is now modern-day Sudan. Another important civilization was Axum, which thrived in present-day Ethiopia and Eritrea. The Swahili civilization, rooted in the coastal areas of modern-day Kenya and Tanzania, also played a significant role in the region’s history.
These civilizations were characterized by their advanced societies, prosperous trade networks, and architectural achievements, including impressive pyramids, temples, and palaces. They also had rich cultural and artistic traditions, as evidenced by their intricate carvings, pottery, and jewelry.
2. What were some notable achievements of ancient East African civilizations?
Ancient East African civilizations made significant contributions in various fields. One notable achievement was the development of a writing system. The Kingdom of Kush, for example, had its own hieroglyphic script known as Meroitic, which was an early form of writing in the Nile Valley.
Trade was another area in which these civilizations excelled. The Kingdom of Axum controlled a vast trading network that connected East Africa with the Roman Empire and the Arabian Peninsula. This trade brought wealth and cultural exchange to the region.
3. How did ancient East African civilizations interact with other regions?
Ancient East African civilizations had extensive interactions with neighboring regions and beyond. The Kingdom of Axum, for instance, established trade and diplomatic relations with the Roman Empire, India, and other Eastern Mediterranean civilizations. Axum’s ports along the Red Sea were crucial hubs for international trade.
The Swahili civilization, with its strategically located coastal cities, thrived as a center of trade between the African interior, the Arabian Peninsula, and the Indian Ocean. This led to a fusion of African, Arab, and Persian influences in the region’s language, culture, and architecture.
4. What led to the decline of ancient East African civilizations?
The decline of ancient East African civilizations can be attributed to various factors. The Kingdom of Kush, for example, faced invasions from the Kingdom of Aksum and later from the Roman Empire. Additionally, the shifting trade routes and political changes in the region contributed to its decline.
The decline of the Swahili civilization was linked to the arrival of European colonizers in the 15th century, which disrupted the region’s trade networks and led to the establishment of European-controlled port cities.
5. What is the significance of ancient East African civilizations today?
The ancient East African civilizations have a lasting significance. They serve as a testament to the rich and diverse history of the region. The architectural marvels, cultural traditions, and advancements made by these civilizations continue to inspire and educate people today.
Furthermore, the legacy of ancient East African civilizations can be seen in the present-day cultural practices, traditions, and languages of the region. Studying and exploring their history provides valuable insights into the development of societies and civilizations in East Africa.
The Untold Stories of the Great African Empires | A Journey Through Time
Exploring the rich history of ancient East African civilizations reveals a remarkable story of innovation, culture, and resilience. These civilizations, such as the ancient kingdoms of Aksum and Kush, left behind a legacy of architectural wonders, trade networks, and cultural achievements that continue to awe and inspire us today.
From the towering obelisks of Aksum to the pyramids of Meroe, the ancient East African civilizations showcased advanced engineering skills and a deep appreciation for art and culture. The Kushites built vast cities and traded with distant lands, while Aksum became a prosperous center of commerce connecting Africa, Arabia, and the Mediterranean. Through their impressive achievements, these civilizations have left an indelible mark on the heritage of East Africa and the world.