The map of the ancient Mayan civilization holds a treasure trove of information waiting to be discovered. From the grand temples to the intricate network of cities, exploring the map can unveil the secrets of one of history’s most fascinating civilizations.
The ancient Mayan civilization flourished for over 2,000 years, leaving behind a rich cultural heritage and a civilization unmatched in its achievements. By studying the map of ancient Mayan civilization, we can gain insights into their advanced astronomical knowledge, their complex system of writing, and their impressive architectural feats.
Embark on a detailed study of the map of the ancient Mayan civilization, uncovering its rich history and fascinating architecture. Explore the intricate network of cities, temples, and pyramids, each with its own unique significance in Mayan culture. Analyze the layout and placement of these structures, deciphering the ancient Mayan’s astronomical knowledge and understanding their advanced civilization. Immerse yourself in the world of the Mayans as you unravel the mysteries hidden within their map, providing invaluable insights into their culture and way of life.
Contents
- Ancient Mayan Civilization: Unveiling the Mysteries of its Map
- Exploring the Map of Ancient Mayan Civilization: A Detailed Study
- Key Takeaways
- Frequently Asked Questions
- 1. How did the Mayan civilization expand and where did they establish major cities?
- 2. How did the Mayans create their maps and what information did they contain?
- 3. What can we learn from studying the Mayan map?
- 4. Are there any surviving Mayan maps?
- 5. How does the Mayan map contribute to our understanding of the civilization’s decline?
- The Maya Civilization Explained in 11 Minutes
Ancient Mayan Civilization: Unveiling the Mysteries of its Map
The ancient Mayan civilization, known for its advanced knowledge and architectural wonders, left behind a profound legacy. One aspect of this legacy is the map of the ancient Mayan civilization, which offers clues about their geographical and cultural landscape. Exploring this map provides an intriguing glimpse into the fascinating world of the Mayans and their intricate understanding of the environment. Through the study of the Mayan map, we can unravel the mysteries of their civilization and gain insight into their customs, beliefs, and daily lives.
Mapping the Mayan World: Intricate Geography
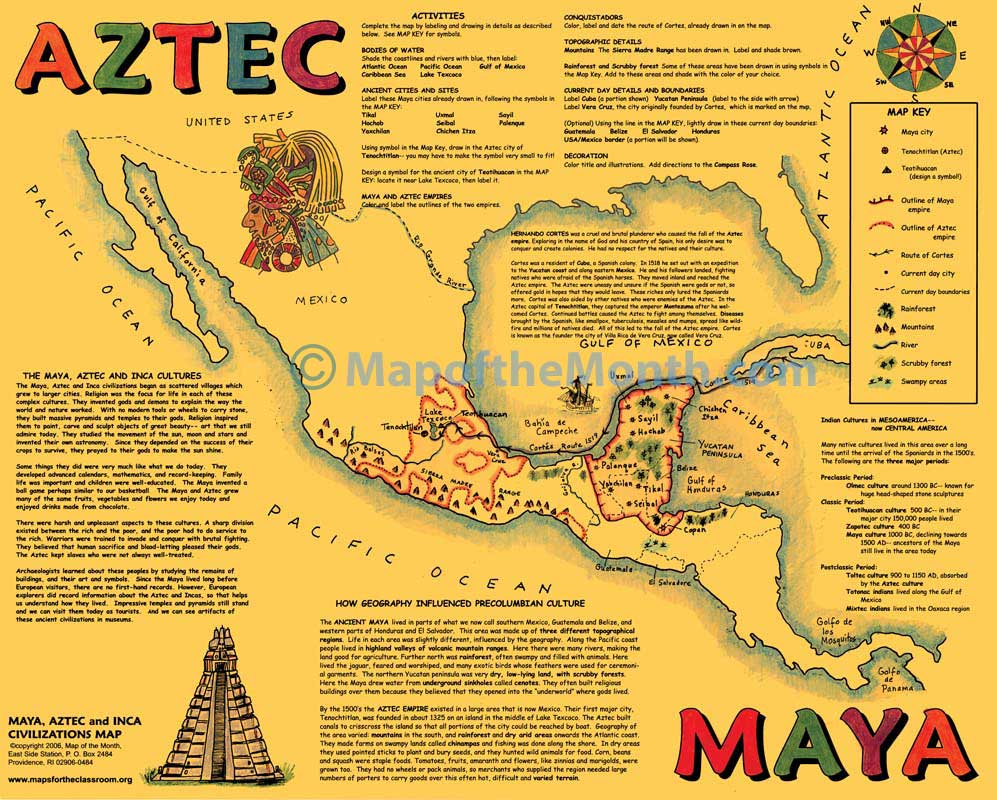
The Mayan civilization spanned across Mesoamerica, a region comprising present-day Mexico, Guatemala, Belize, Honduras, and El Salvador. The Mayans inhabited various environments, including dense rainforests, arid highlands, and coastal plains. The Mayan map reflected their deep understanding of these diverse landscapes and their ability to adapt and thrive in different environments.
The Mayan map featured intricate geography that included detailed depictions of mountains, rivers, lakes, and coastlines. They used symbols and hieroglyphs to represent these geographical features, often incorporating them into their architecture and art. This attention to detail is a testament to the Mayans’ profound connection with their surroundings. By examining their map, we can unravel the importance of geography in their lives and understand how it influenced their culture and daily activities.
Furthermore, the Mayan map also showcased their extensive trade networks and the interconnectivity of their cities and regions. The strategic placement of cities along trade routes and natural resources can be deciphered from the map, shedding light on the economic and political dynamics of the Mayan civilization.
It is remarkable to witness how the ancient Mayans, without modern technology, were able to accurately map their vast territories, displaying an advanced understanding of cartography and a remarkable attention to detail.
Sacred Sites and Rituals: Insights from the Map
The Mayan map goes beyond geographical depictions and provides invaluable insights into the spiritual and religious aspects of their civilization. Sacred sites and ceremonial centers were meticulously marked on the map, offering a glimpse into the religious practices and rituals of the Mayans.
One notable example is the city of Tikal, located in present-day Guatemala. Tikal was one of the largest and most significant Mayan cities, and its prominence is evident on the map. The presence of large temple complexes, plazas, and ball courts marked on the map suggests the importance of rituals and ceremonies in this city. At these sacred sites, the Mayans performed religious ceremonies, including offerings, sacrifices, and other rituals to honor their deities.
By studying the Mayan map, archaeologists and historians have been able to locate and excavate these sacred sites, providing a deeper understanding of Mayan religious practices. This wealth of information has expanded our knowledge of the spiritual beliefs and customs of the Mayan civilization, further enriching our understanding of their history and culture.
Ancient Mayan Trade Routes: Tracing the Pathways
The Mayan map offers valuable insights into their extensive trade networks and the routes that connected different regions. Trade was a crucial aspect of Mayan society, facilitating the exchange of goods, ideas, and cultural influences.
The map reveals the major trade routes that crisscrossed the Mayan civilization, connecting distant cities and regions. These trade routes were lifelines for the Mayan economy, allowing the flow of commodities such as jade, obsidian, textiles, pottery, and agricultural products.
For example, the famous Cacao trade played a significant role in the Mayan civilization. The Mayan map features the cacao-growing regions, such as the areas surrounding the Guatemalan highlands and Belize, where cacao was grown and traded. By following these trade routes on the map, we can trace the journey of cacao and understand its economic and cultural importance to the Mayans.
Studying the trade routes depicted on the Mayan map allows us to grasp the extent of the Mayan civilization and the influence they exerted over the wider Mesoamerican region. It also illuminates the interconnectedness of various cities and regions, showcasing the complexity of the Mayan society.
Navigating the Mayan Waterways: Coastal Trade and Maritime Culture
The Mayans were skilled seafarers and utilized their extensive coastline to engage in maritime trade. The Mayan map showcases their prowess in navigating waterways and highlights the significance of coastal settlements in their trade networks.
The map reveals the coastal trade routes, depicting the ports and cities along the coast where maritime trade flourished. Coastal settlements such as Tulum and Xcaret in present-day Mexico were important trading hubs, facilitating the exchange of goods between the Mayans and other coastal societies.
Furthermore, the map showcases their understanding of the seasonality of coastal currents and winds, enabling them to navigate these waterways effectively. This maritime expertise allowed the Mayans to establish strong maritime trade networks and expand their reach beyond the inland regions.
Archaeological Discoveries and Mayan Map
The study of the Mayan map has significantly contributed to archaeological discoveries and the understanding of the Mayan civilization. By comparing the map with the physical landscape and conducting excavations in the marked areas, archaeologists have unearthed numerous ancient cities, monuments, and artifacts.
For example, the discovery of the city of Caracol in modern-day Belize was made possible through the analysis of the Mayan map. The presence of a well-defined road network on the map led archaeologists to search for Caracol in the dense rainforests of Belize, ultimately resulting in its rediscovery. This highlights the crucial role the Mayan map plays in guiding archaeological research and uncovering lost ancient sites.
By combining the information gleaned from the Mayan map with archaeological excavations, researchers have been able to piece together the puzzle of the Mayan civilization, offering fascinating insights into their social structure, architecture, agricultural practices, and more.
Beyond the Map: Continual Discoveries
The exploration of the Mayan map is an ongoing journey that continues to yield new discoveries and deeper understanding. Each new finding deepens our appreciation for the ingenuity and sophistication of the ancient Mayan civilization.
As technology advances and new archaeological techniques emerge, the study of the Mayan map will undoubtedly uncover more hidden secrets of this enigmatic civilization. It serves as a testament to the enduring legacy of the Mayans and their contribution to the fields of cartography, archaeology, and our understanding of ancient civilizations.
Exploring the map of the ancient Mayan civilization offers us a window into their rich history and culture. It allows us to decipher the interconnectedness of their cities, understand their religious and trade practices, and unravel the mysteries of their everyday lives. The Mayan map continues to captivate researchers and enthusiasts alike, fueling our curiosity and driving us to explore further into the wonders of this remarkable ancient civilization.
Exploring the Map of Ancient Mayan Civilization: A Detailed Study
The ancient Maya civilization, known for its advanced art, architecture, and mathematical systems, flourished in Mesoamerica from approximately 2000 BCE until the Spanish conquest in the 16th century CE. Exploring the map of the Mayan civilization provides valuable insights into their expansive territory, cultural practices, and trade networks.
The Mayan civilization stretched across present-day countries of Mexico, Guatemala, Belize, Honduras, and El Salvador. Its heartland was the southern lowlands of Mesoamerica, where impressive cities such as Tikal, Palenque, and Chichen Itza were located. These cities were centers of political, religious, and economic power.
Maps of ancient Mayan civilization reveal the interconnectedness of their cities through an extensive network of roads and causeways. They also provide a glimpse into the agricultural systems that sustained the population, with intricate irrigation canals and terraced fields.
Furthermore, Mayan maps depict the locations of sacred sites, including temples, pyramids, and observatories, highlighting the significance of astronomy and religion in their society. It is through these detailed maps that we can explore the immense complexity and cultural richness of the Mayan civilization.
Key Takeaways
- The ancient Mayan civilization flourished in Mesoamerica, primarily in present-day Mexico and Central America.
- The Mayans were exceptional architects and built impressive cities with intricate structures, such as palaces, pyramids, and ball courts.
- A significant characteristic of the Mayan civilization was their advanced writing system consisting of hieroglyphs.
- Mayans were skilled astronomers and developed a highly accurate calendar.
- Despite their achievements, the Mayan civilization faced factors that led to its decline, including warfare, droughts, and the collapse of city-states.
Frequently Asked Questions
Welcome to our FAQ section on exploring the map of the ancient Mayan civilization. Here, we aim to answer some of the most common questions about the Mayan civilization and their geographical distribution. By understanding the significance of the Mayan map and its role in understanding this ancient civilization, we can gain valuable insights into their culture, achievements, and way of life.
1. How did the Mayan civilization expand and where did they establish major cities?
The Mayan civilization expanded throughout Mesoamerica, covering parts of present-day Mexico, Guatemala, Belize, Honduras, and El Salvador. They built their major cities in areas with fertile land, water sources, and strategic locations for trade and defense. Some notable Mayan cities include Tikal, Chichen Itza, Palenque, and Copan.
Their expansion was influenced by factors such as agricultural opportunities, access to minerals and trade routes, and the development of advanced agricultural techniques.
2. How did the Mayans create their maps and what information did they contain?
The Mayans created their maps using a combination of pictographs, symbols, and grid systems. These maps, known as codices, contained valuable information about the geography, celestial bodies, trade routes, and political boundaries of the Mayan civilization. They were intricate and detailed, showing the accuracy and sophistication of their geographical knowledge.
The maps also had religious and cultural significance, with representations of sacred sites and mythological figures. They were used for navigation, planning agricultural activities, and understanding the cosmos.
3. What can we learn from studying the Mayan map?
Studying the Mayan map provides us with valuable insights into their advanced understanding of astronomy, mathematics, and geography. It helps us understand the expansion and distribution of their civilization, their trade networks, and their religious and cultural practices. The map also offers clues about their agricultural practices, water management systems, and environmental adaptations.
Furthermore, studying the Mayan map allows us to appreciate their artistic and intellectual achievements, as well as their complex societal structures.
4. Are there any surviving Mayan maps?
Yes, there are surviving Mayan maps known as codices. However, only four of the original codices are known to have survived. These are the Dresden Codex, Madrid Codex, Paris Codex, and Grolier Codex. These codices provide valuable information about Mayan history, religion, and societal structures.
Other surviving maps include murals and stelae found in Mayan archaeological sites.
5. How does the Mayan map contribute to our understanding of the civilization’s decline?
The Mayan map, along with other historical records and archaeological evidence, helps researchers understand the factors that contributed to the decline of the Mayan civilization. By analyzing changes in trade routes, population distribution, and political boundaries depicted on the map, researchers can explore potential causes such as environmental degradation, warfare, and socio-political instability.
Furthermore, studying the decline of the Mayan civilization provides valuable lessons about the potential consequences of unsustainable resource management and societal challenges.
The Maya Civilization Explained in 11 Minutes
In conclusion, exploring the map of the ancient Mayan civilization provides us with a wealth of knowledge about their impressive achievements and complex society.
The map reveals the vastness of their territory, the locations of their major cities, and the intricate network of trade routes that connected them. It also highlights the incredible architecture and engineering skills showcased in their cities, temples, and observatories. Additionally, the map showcases the sacred sites and natural landmarks that held great significance for the Mayans.